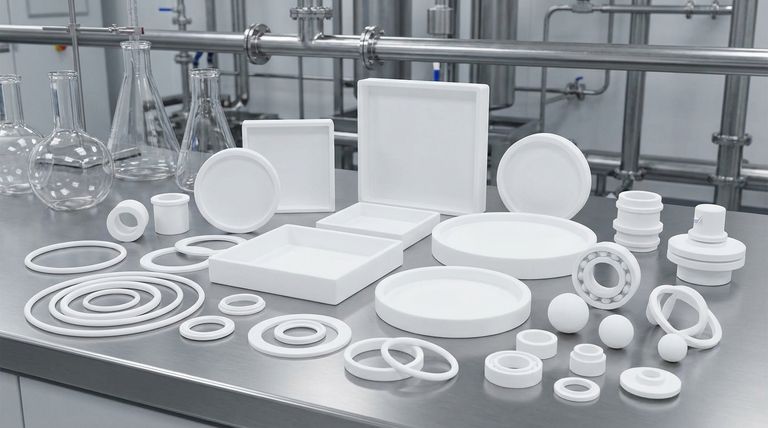
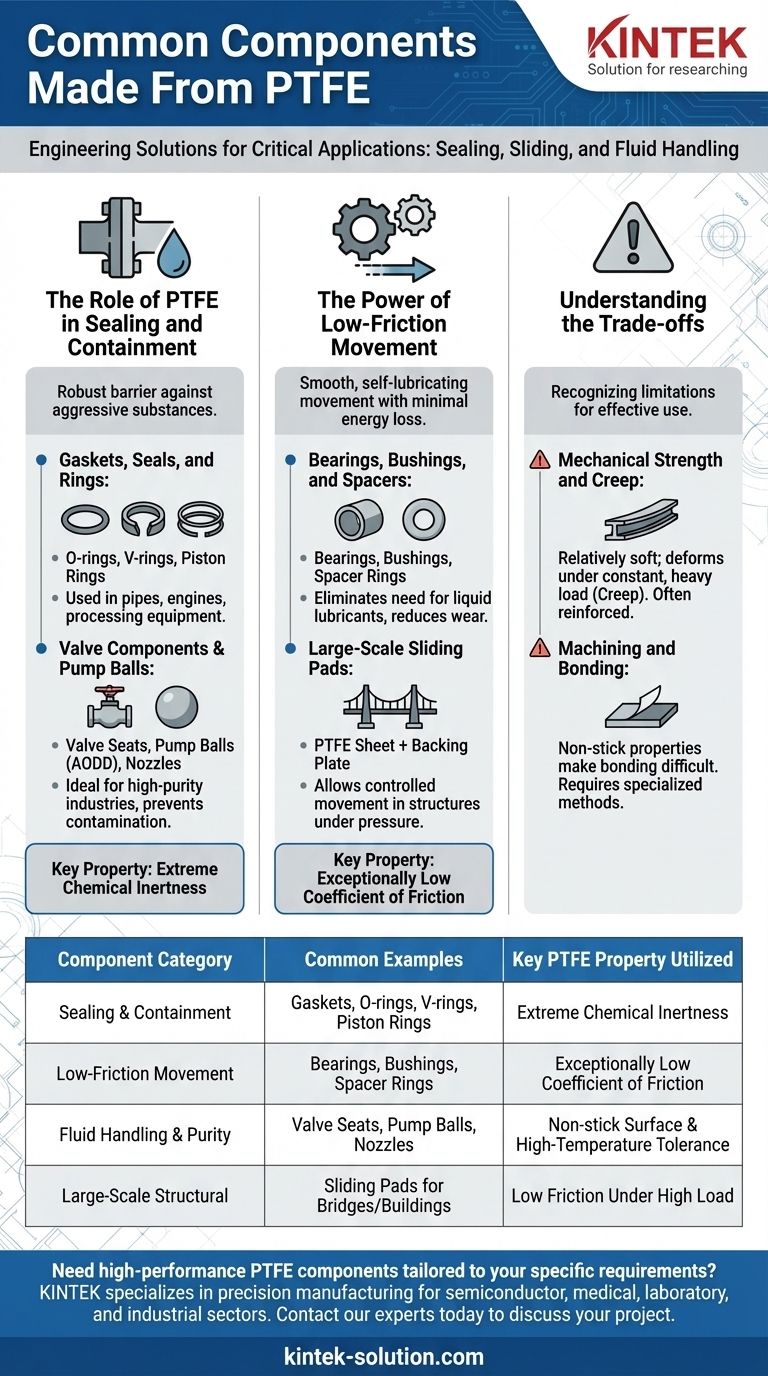
In short, Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is used to create a wide range of critical engineering components. These commonly include high-performance seals, gaskets, O-rings, and V-rings for preventing leaks, as well as bearings, bushings, and piston rings designed for low-friction movement. It is also shaped into valve components, pump balls, and electrical insulators for specialized industrial applications.
The core reason PTFE is chosen for these parts is its unique combination of properties. Its extreme chemical inertness, exceptionally low friction, and high-temperature tolerance make it an essential problem-solver for sealing, sliding, and fluid-handling challenges where other materials would fail.

The Role of PTFE in Sealing and Containment
The most common use for PTFE is creating a robust barrier between two environments. Its chemical resilience makes it indispensable for applications involving aggressive substances.
Gaskets, Seals, and Rings
PTFE’s ability to resist nearly all industrial chemicals and solvents makes it a premier material for gaskets and seals.
These components are used in pipes, engines, and processing equipment to prevent leaks under demanding conditions.
Variations like O-rings, V-rings, and piston rings are specifically designed to create a tight seal in dynamic or static applications, ensuring system integrity and efficiency.
Valve Components and Pump Balls
In high-purity industries like pharmaceuticals, food processing, and semiconductor manufacturing, preventing contamination is critical.
PTFE's non-stick, inert surface ensures that fluids pass through valves, balls, and nozzles without reacting with or adhering to the component material.
This makes it ideal for components like Air-Operated Double-Diaphragm (AODD) pump balls and other parts in high-purity fluid transfer systems.
The Power of Low-Friction Movement
PTFE has one of the lowest coefficients of friction of any solid material, a property often compared to wet ice on wet ice. This makes it a primary choice for parts that must move against each other smoothly and with minimal energy loss.
Bearings, Bushings, and Spacers
Bearings and bushings made from PTFE allow parts to slide, rotate, or oscillate with very little resistance and without the need for liquid lubricants.
This is crucial in applications where maintenance is difficult or where lubricants could contaminate the product, such as in food processing equipment or medical devices.
Spacer rings and washers also leverage this property to separate moving parts and reduce wear over time.
Large-Scale Sliding Pads
A powerful application of PTFE's low friction is in large structural engineering projects, like bridges and buildings.
PTFE sliding pads typically consist of a PTFE sheet bonded to a backing plate, which slides against a polished stainless steel plate.
This system allows massive structures to move slightly—due to thermal expansion, contraction, or seismic activity—in a controlled manner and under immense pressure.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While its properties are exceptional, PTFE is not a universal solution. Understanding its limitations is key to using it effectively.
Mechanical Strength and Creep
PTFE is a relatively soft material. Under a constant, heavy load, it can slowly deform over time in a process known as creep.
This means it is not suitable for high-load structural components on its own and is often reinforced or contained within a harder material.
Machining and Bonding
The same non-stick properties that make PTFE so useful also make it difficult to bond to other surfaces using conventional adhesives.
Specialized surface treatments or mechanical designs, such as recessing the PTFE into a pocket, are often required to hold it securely in place.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting PTFE is about matching its unique strengths to a specific engineering challenge.
- If your primary focus is preventing leaks in harsh environments: PTFE gaskets, seals, and O-rings are the definitive choice due to their unmatched chemical inertness.
- If your primary focus is reducing friction and wear: PTFE bearings, bushings, and sliding pads provide smooth, self-lubricating movement for mechanical systems.
- If your primary focus is maintaining absolute purity: PTFE valve seats, pump balls, and nozzles are essential for contamination-free fluid handling in sensitive industries.
Ultimately, PTFE components are specified when performance, reliability, and chemical resistance are non-negotiable.
Summary Table:
| Component Category | Common Examples | Key PTFE Property Utilized |
|---|---|---|
| Sealing & Containment | Gaskets, O-rings, V-rings, Piston Rings | Extreme Chemical Inertness |
| Low-Friction Movement | Bearings, Bushings, Spacer Rings | Exceptionally Low Coefficient of Friction |
| Fluid Handling & Purity | Valve Seats, Pump Balls, Nozzles | Non-stick Surface & High-Temperature Tolerance |
| Large-Scale Structural | Sliding Pads for Bridges/Buildings | Low Friction Under High Load |
Need high-performance PTFE components tailored to your specific requirements?
At KINTEK, we specialize in the precision manufacturing of PTFE seals, liners, labware, and custom components for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Whether you need a prototype or a high-volume order, our expertise ensures a solution that delivers reliability and chemical resistance where it matters most.
Contact our experts today to discuss your project and get a quote!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What are the components of Teflon encapsulated O-rings? A Guide to Their Dual-Material Design
- Are PTFE and PEEK backup rings usually pure, or do they contain fillers? Discover the Role of Fillers in High-Performance Seals
- What are critical installation practices for PTFE O-rings? Avoid Leaks and Ensure a Perfect Seal
- How does the chemical resistance of Filled PTFE compare to Virgin PTFE? A Guide to Material Selection
- What are the primary applications of PTFE-lined ball valves? Control Corrosive & High-Purity Fluids
- What are the different forms of PTFE packing? Choose the Right Seal for Your Equipment
- What pressure considerations apply to PTFE lined butterfly valves? Avoid Liner Failure and Ensure Safe Operation
- What additional qualities make PTFE energized seals suitable for aerospace use? Ensuring Reliability in Extreme Environments



















