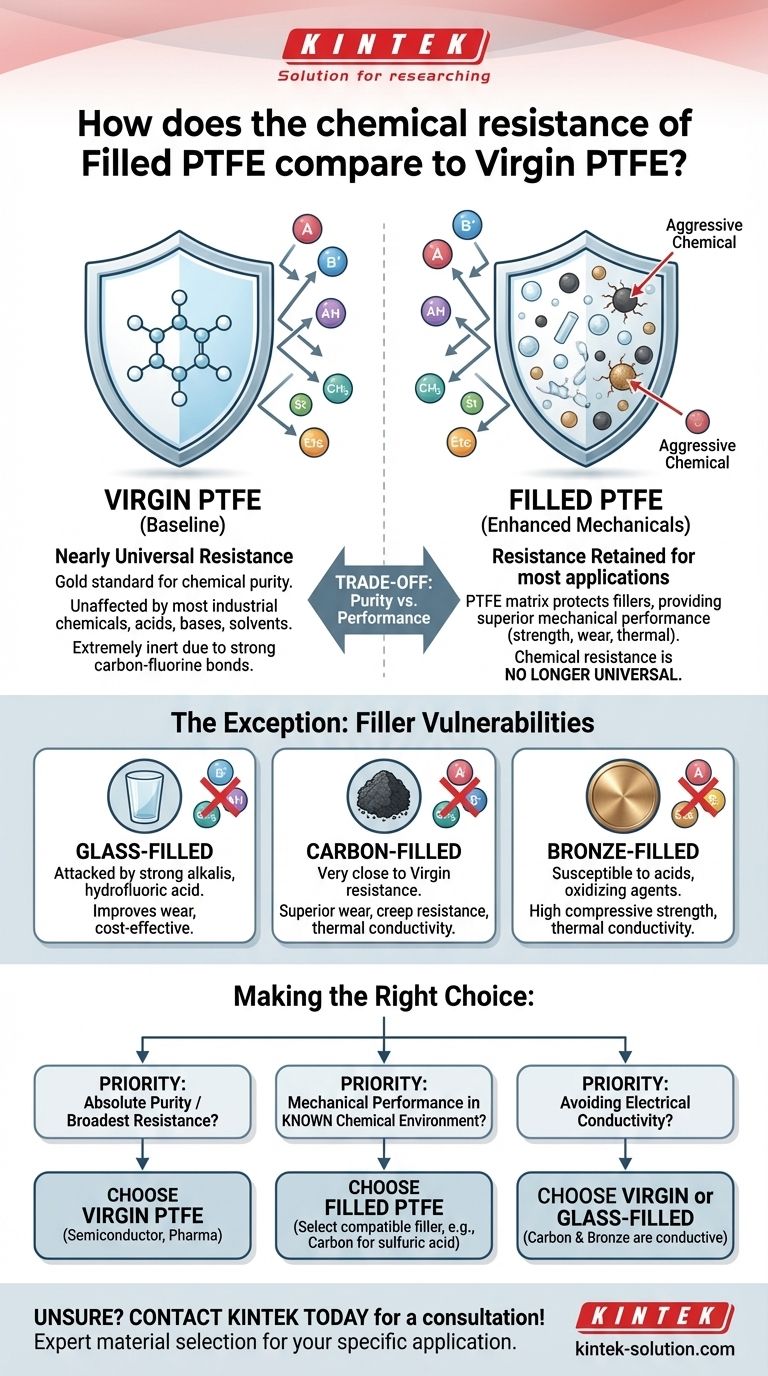
For most applications, the chemical resistance of Filled PTFE is considered equivalent to Virgin PTFE, but this is a critical simplification. While the PTFE resin itself remains inert, the filler material can be attacked by certain chemicals, making Virgin PTFE the superior choice for the absolute broadest range of chemical services.
The core issue is not whether Filled PTFE is less resistant, but rather that its resistance is no longer universal. The choice depends on balancing the pristine chemical inertness of Virgin PTFE against the superior mechanical properties of a Filled PTFE grade within a specific chemical environment.

The Baseline: Virgin PTFE's Unmatched Inertness
Nearly Universal Resistance
Virgin Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is one of the most chemically inert polymers known. It is stable and unaffected by the vast majority of industrial chemicals, acids, bases, and solvents.
This exceptional stability comes from the strong carbon-fluorine bonds that make up its molecular structure, which are extremely difficult for chemical agents to break.
The Few Known Exceptions
Only a very small and specific list of substances are known to attack PTFE. These include molten or dissolved alkali metals (like sodium), fluorine gas, and a few other highly potent fluorinating agents or oxidizers at elevated temperatures and pressures.
For virtually all other applications, Virgin PTFE is considered the gold standard for chemical compatibility.
Introducing Fillers: Enhancing Mechanical Properties
Why Add Fillers?
While chemically robust, Virgin PTFE is mechanically soft. It can be prone to creep (cold flow) under load and has relatively high wear rates.
Fillers are added to create a composite material that significantly improves key physical properties. These enhancements include greater compressive strength, better wear resistance, reduced deformation under load, and higher thermal conductivity.
The PTFE Matrix Protects the Filler
In a filled PTFE compound, the particles of the filler material (like glass, carbon, or bronze) are encapsulated within the dense PTFE matrix. This encapsulation provides a primary layer of chemical protection for the filler.
The Critical Comparison: How Fillers Impact Resistance
The General Rule: Resistance is Retained
For a wide range of chemical services, the PTFE matrix effectively shields the filler material. In these cases, a filled PTFE component retains the excellent chemical resistance of its virgin counterpart while providing superior mechanical performance.
This is why filled grades are often described as having "better performance in chemical service"—the component maintains its structural integrity and shape far better than a virgin part would under the same mechanical stress.
The Exception: When the Filler Becomes the Weak Link
The critical vulnerability appears when the process chemical can attack the filler material itself. If an aggressive chemical can permeate the PTFE matrix over time or finds an exposed filler particle on the surface, it can degrade the filler, compromising the integrity of the component.
Common Filler Types and Their Limitations
The specific chemical resistance of a filled PTFE grade is defined by the limitations of its filler:
- Glass: A common, cost-effective filler. However, it can be attacked by strong alkalis and hydrofluoric acid.
- Carbon/Graphite: Offers excellent chemical resistance that is very close to that of Virgin PTFE, with few exceptions. It enhances thermal conductivity and wear resistance.
- Bronze: A metal alloy filler that greatly increases strength and thermal conductivity. However, it is susceptible to attack by acids and oxidizing agents.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Ultimately, material selection must be driven by the precise demands of the operating environment.
- If your primary focus is absolute chemical purity or the broadest possible resistance: Choose Virgin PTFE. This is the only safe choice for high-purity services (semiconductor, pharmaceutical) or when the full range of potential chemical exposure is unknown.
- If your primary focus is mechanical performance in a known chemical environment: Choose a Filled PTFE with a compatible filler. For a pump bearing running in sulfuric acid, a carbon-filled PTFE is a far better choice than a bronze-filled or virgin grade.
- If your primary focus is avoiding electrical conductivity: You must use Virgin PTFE or a glass-filled grade, as carbon and bronze fillers will make the material conductive.
Matching the specific grade of PTFE to its intended service environment is the key to successful application.
Summary Table:
| Material Type | Chemical Resistance | Key Advantage | Common Filler Vulnerabilities |
|---|---|---|---|
| Virgin PTFE | Nearly universal inertness | Gold standard for purity & broadest resistance | N/A |
| Glass-Filled PTFE | Excellent, but filler can be attacked | Improved wear resistance, cost-effective | Strong alkalis, hydrofluoric acid |
| Carbon-Filled PTFE | Excellent, very close to Virgin PTFE | Superior wear & creep resistance, thermal conductivity | Few exceptions |
| Bronze-Filled PTFE | Good, but metal filler is vulnerable | High compressive strength, thermal conductivity | Acids, oxidizing agents |
Unsure which PTFE grade is right for your demanding chemical environment?
At KINTEK, we specialize in manufacturing high-performance PTFE components—from seals and liners to custom labware—for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Our expertise ensures you get a component with the perfect balance of chemical resistance and mechanical properties for your specific application.
We offer custom fabrication from prototypes to high-volume orders, prioritizing precision to meet your exact specifications. Let our experts help you select the optimal material. Contact KINTEK today for a consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Bottles for Diverse Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
People Also Ask
- Why is PTFE rod suitable for automotive applications? Boost Vehicle Performance & Durability
- How does PTFE contribute to low friction and wear resistance? Achieve Superior Performance with Advanced Materials
- What are the best practices for achieving tight tolerances in Teflon (PTFE) machining? Master Precision for Demanding Applications
- What are the key considerations when machining Teflon? Master Precision Machining for Soft Polymers
- What are the key advantages of PTFE? Unmatched Performance for Extreme Environments



















