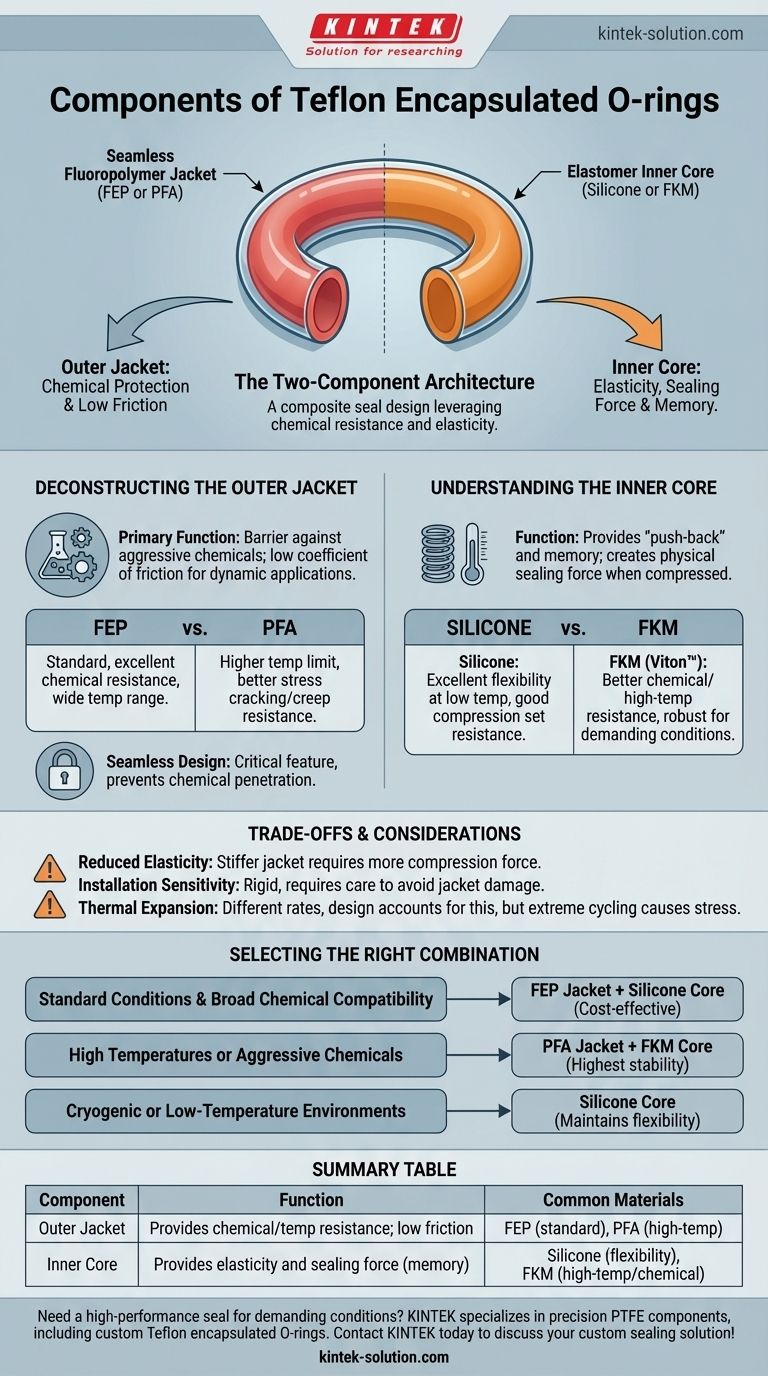
At its core, a Teflon encapsulated O-ring is a composite seal made of two distinct components. It features a solid elastomer inner core, which is completely enclosed within a seamless outer jacket made of a high-performance fluoropolymer like Teflon™ FEP or PFA.
This dual-component design leverages the best of both worlds: it combines the superior chemical and temperature resistance of a fluoropolymer jacket with the flexibility and compressive memory of an elastomer core, creating a seal that is both resilient and exceptionally robust.
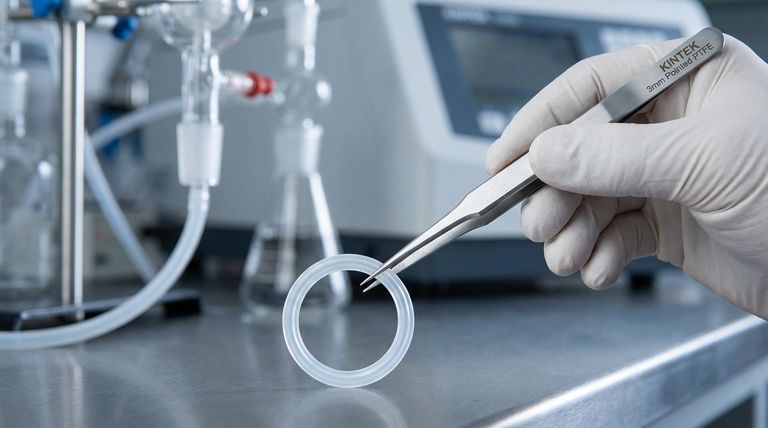

The Two-Component Architecture
A key point of understanding is that an encapsulated O-ring is not a single, uniform material. It is an engineered solution where each component serves a specific and critical function to achieve a sealing capability that neither material could provide on its own.
The inner core provides the physical force for the seal, while the outer jacket provides the chemical protection.
Deconstructing the Outer Jacket
The outer jacket is the component that directly contacts the process media, making its properties paramount for seal integrity and longevity.
The Role of the Fluoropolymer Jacket
The primary function of the jacket is to provide a barrier against aggressive chemicals. Fluoropolymers like FEP and PFA are virtually inert to most industrial chemicals and solvents.
This jacket also offers a very low coefficient of friction, which is beneficial in dynamic applications and helps prevent sticking during assembly.
Common Jacket Materials: FEP vs. PFA
The seamless jacket is typically made from one of two materials:
- FEP (Fluorinated Ethylene Propylene): This is the standard material, offering excellent chemical resistance and a wide service temperature range.
- PFA (Perfluoroalkoxy): PFA offers a higher temperature limit and better resistance to stress cracking and creep (permanent deformation under load) compared to FEP, making it suitable for more demanding applications.
The Importance of a Seamless Design
The "seamless" nature of the jacket is a critical design feature. It ensures there are no join lines or potential weak points that could allow chemicals to penetrate and attack the more vulnerable inner core.
Understanding the Inner Core
While protected by the jacket, the inner core is the engine of the seal. It provides the elasticity and resilience necessary to maintain a constant sealing force.
The Function of the Elastomer Core
The core's job is to provide the O-ring's "memory" or "push-back." When compressed in a groove (gland), the elastomer core deforms and exerts a force against the mating surfaces, creating the physical seal.
The core material dictates the O-ring's ability to rebound after compression and its performance across a temperature range.
Common Core Materials: Silicone vs. FKM
Two elastomers dominate as core materials:
- Silicone: Known for its excellent flexibility at low temperatures and a wide overall temperature range. It has good compression set resistance, meaning it rebounds well after being compressed for long periods.
- FKM (Fluoroelastomer): Often known by its trade name, Viton™, FKM provides better chemical resistance and higher temperature performance than silicone. This makes it a more robust choice for demanding thermal or chemical environments.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While highly effective, the composite nature of encapsulated O-rings introduces specific considerations.
Reduced Elasticity
The fluoropolymer jacket is significantly stiffer than a standard elastomer. This means encapsulated O-rings require more force to compress and are less forgiving of surface imperfections or improper gland design.
Installation Sensitivity
Because of their rigidity, encapsulated O-rings can be more difficult to install than standard O-rings. Stretching them over shafts must be done with extreme care to avoid damaging the outer jacket.
Thermal Expansion Differences
The jacket and the core materials have different rates of thermal expansion. This factor is accounted for in the design, but extreme temperature cycling can stress the seal over its lifetime.
Selecting the Right Combination for Your Application
Choosing the correct jacket and core combination is critical for reliable performance.
- If your primary focus is broad chemical compatibility in standard conditions: A standard FEP jacket with a Silicone core is often the most cost-effective and reliable choice.
- If your application involves high temperatures or aggressive chemicals: A PFA jacket with an FKM core provides the highest level of thermal and chemical stability.
- If your system operates in cryogenic or low-temperature environments: A Silicone core is essential for maintaining flexibility and proper sealing force.
Understanding these two core components empowers you to select an engineered seal perfectly matched to your operational demands.
Summary Table:
| Component | Function | Common Materials |
|---|---|---|
| Outer Jacket | Provides chemical/temperature resistance; low friction | FEP (standard), PFA (high-temp) |
| Inner Core | Provides elasticity and sealing force (memory) | Silicone (flexibility), FKM (high-temp/chemical) |
Need a high-performance seal for demanding conditions?
KINTEK specializes in manufacturing precision PTFE components, including custom Teflon encapsulated O-rings. We combine expert material selection with precision production to deliver seals that meet the exact requirements of the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors.
Whether you need prototypes or high-volume orders, we ensure your seals provide reliable chemical resistance and sealing force. Contact KINTEK today to discuss your custom sealing solution!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- Why is CNC machining preferred for Teflon parts over other methods? Unlock Precision & Complex Designs
- What are the main advantages of using PTFE parts in industrial applications? Unlock Unmatched Chemical Resistance and Reliability
- What are the best practices for achieving tight tolerances in Teflon (PTFE) machining? Master Precision for Demanding Applications
- What are the future considerations for machining Teflon? Mastering Material Challenges with Smart Tech
- What are the key considerations when machining Teflon? Master Precision Machining for Soft Polymers



















