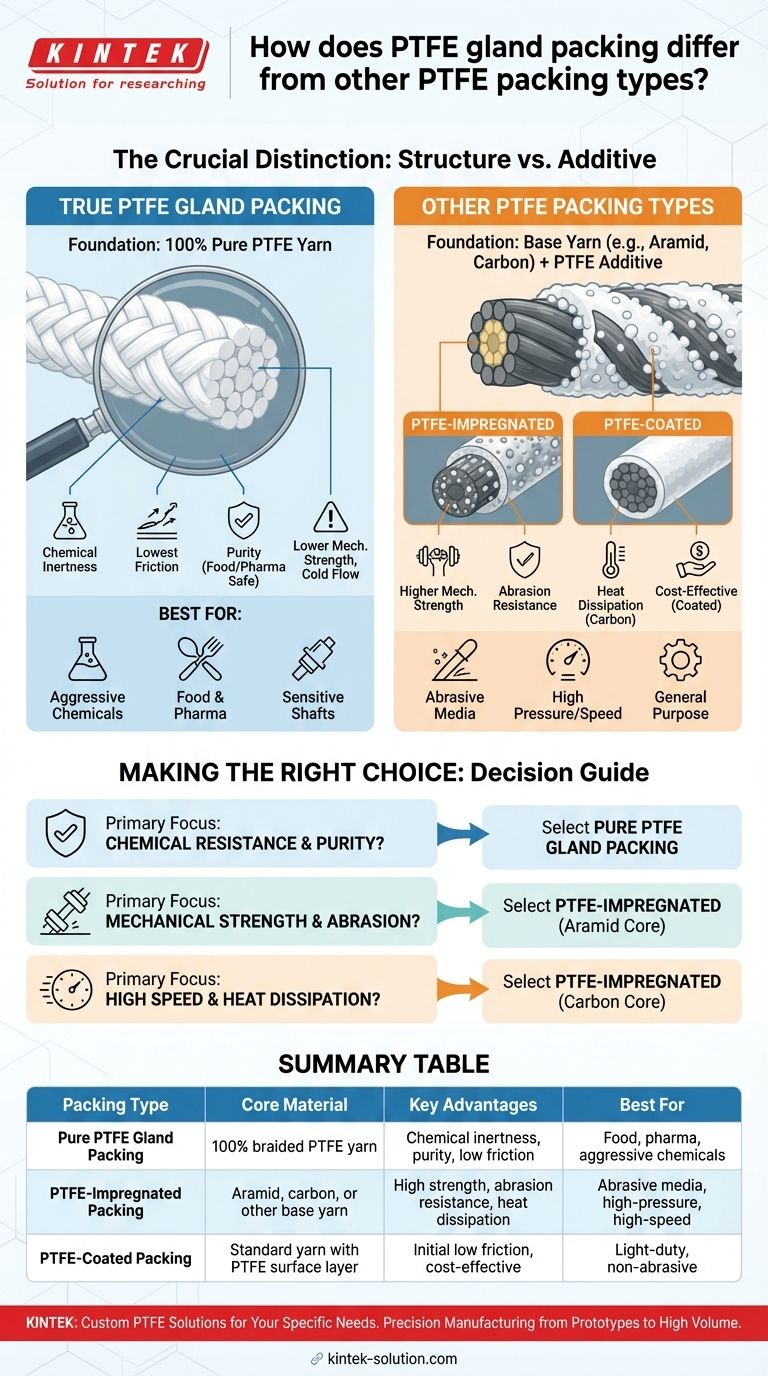
At its core, PTFE gland packing is a specific construction type made entirely from pure, braided PTFE yarns. This distinguishes it from the broader category of "PTFE packing," which can refer to any packing material that is merely coated or impregnated with PTFE, but whose core structure is made from a different material.
The crucial distinction is not the presence of PTFE, but its role. In true PTFE gland packing, PTFE is the structural foundation. In other PTFE packings, it serves as a performance-enhancing coating or lubricant for a different base yarn.

What Defines True PTFE Gland Packing?
True PTFE gland packing is valued for its unique combination of material purity and structural integrity, making it a specialized solution for demanding sealing environments.
A Foundation of Pure PTFE Yarns
This packing is constructed from 100% pure Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) yarns. There is no other base material; the PTFE itself provides the packing's entire substance and structure.
The Braided Construction
The pure PTFE yarns are braided into a flexible, rope-like form. This braiding provides the mechanical stability and resilience needed to create a tight, consistent seal when compressed within a gland.
Key Properties: Low Friction and Chemical Inertness
Because it is pure PTFE, this packing has an extremely low coefficient of friction. This minimizes wear on rotating shafts and valve stems. Its chemical inertness also means it can withstand highly aggressive substances like acids and solvents without degrading.
Exploring the Broader "PTFE Packing" Category
The term "PTFE packing" is an umbrella that includes materials where PTFE is an additive rather than the core component. These composite materials leverage the properties of a base yarn enhanced by PTFE.
Type 1: PTFE-Impregnated Packing
This type uses a base yarn made of a different material, such as aramid or carbon fiber, which is then impregnated with fine PTFE particles and often a lubricant. The PTFE fills the voids in the braid, reducing friction and improving chemical resistance, while the base yarn provides primary characteristics like high tensile strength or heat dissipation.
Type 2: PTFE-Coated Packing
This is a standard yarn that has been dipped in a PTFE solution. This process applies a thin surface layer of PTFE to the packing. While this provides some initial low-friction benefits, the coating is less durable than impregnation and can wear away over time, especially in abrasive applications.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing the right packing requires understanding the advantages and limitations of each construction type. No single packing is superior for all applications.
When Pure PTFE Gland Packing Excels
Pure PTFE gland packing is the ideal choice for applications where purity and chemical resistance are non-negotiable. This includes pumps and valves in the food processing, pharmaceutical, and aggressive chemical industries. Its low-friction nature is also critical for preventing scoring on sensitive equipment shafts.
The Limits of Pure PTFE
The primary limitation of pure PTFE is its relatively low mechanical strength and tendency to "cold flow" (deform under sustained pressure). It is not well-suited for very high-pressure applications or for sealing against abrasive slurries, which can quickly wear down the soft material.
The Advantage of Composite Packings
PTFE-impregnated packings offer a balanced solution. An aramid yarn with PTFE impregnation, for example, delivers far greater abrasion resistance and mechanical strength than pure PTFE, making it suitable for sealing abrasive media. A carbon fiber yarn with PTFE offers superior heat dissipation for high-speed shaft applications.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct packing material is essential for maximizing seal life and preventing equipment damage. Your decision should be guided by the specific demands of the operating environment.
- If your primary focus is maximum chemical resistance and purity: Choose pure, braided PTFE gland packing for its complete inertness.
- If your primary focus is mechanical strength and abrasion resistance: Select a PTFE-impregnated packing with a durable core yarn like aramid.
- If your primary focus is high-speed rotation and heat dissipation: Use a PTFE-impregnated packing with a thermally conductive core like carbon or graphite fiber.
By understanding the distinction between pure, impregnated, and coated materials, you can ensure you select a seal that optimizes both performance and equipment longevity.
Summary Table:
| Packing Type | Core Material | Key Advantages | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pure PTFE Gland Packing | 100% braided PTFE yarn | Chemical inertness, purity, low friction | Food, pharma, aggressive chemicals |
| PTFE-Impregnated Packing | Aramid, carbon, or other base yarn | High strength, abrasion resistance, heat dissipation | Abrasive media, high-pressure, high-speed applications |
| PTFE-Coated Packing | Standard yarn with PTFE surface layer | Initial low friction, cost-effective | Light-duty, non-abrasive environments |
Need a Custom PTFE Packing Solution?
Choosing the right gland packing is critical for your equipment's performance and longevity. At KINTEK, we specialize in manufacturing high-precision PTFE components, including custom gland packing tailored to your specific industry needs—whether for semiconductor, medical, laboratory, or industrial applications.
Our expertise in precision production and custom fabrication ensures you get a seal that offers optimal chemical resistance, durability, and efficiency—from prototypes to high-volume orders.
Let us help you optimize your sealing system. Contact our experts today for a consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
- Customizable PTFE Seals Filter Holders for Versatile Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
People Also Ask
- What is the temperature range for PTFE expansion bellows? From -200°C to 260°C for Extreme Applications
- What are the main advantages of PTFE diaphragm valves in the pharmaceutical industry? Ensure Purity, Sterility, and Reliability
- What are the available forms of PTFE semi-finished products? A Guide to Stock Shapes for Machining
- What are the advantages of using PTFE bushes? Low-Friction, Chemical-Resistant Performance
- What is the process of CNC machining Teflon? A Guide to Mastering Precision with PTFE
- What are the main components of a PTFE sliding pad? A Simple Two-Part System for Low-Friction Movement
- What makes PTFE gland packings suitable for demanding sealing conditions? Unmatched Chemical & Thermal Resistance
- Why are PTFE washers commonly used in sealing applications? Unlock Superior Chemical & Thermal Resistance



















