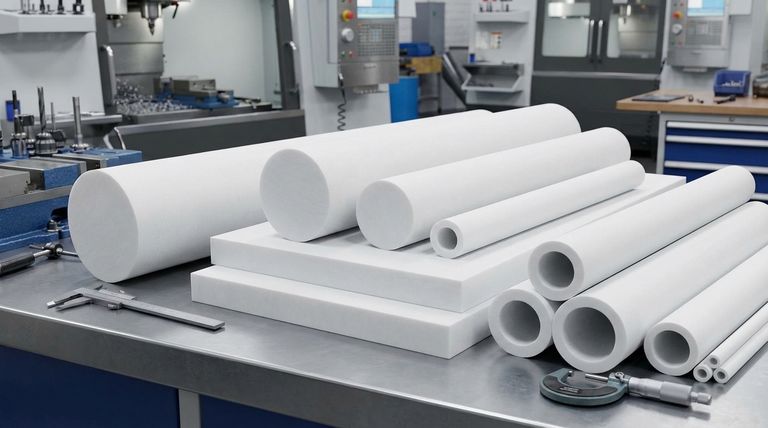
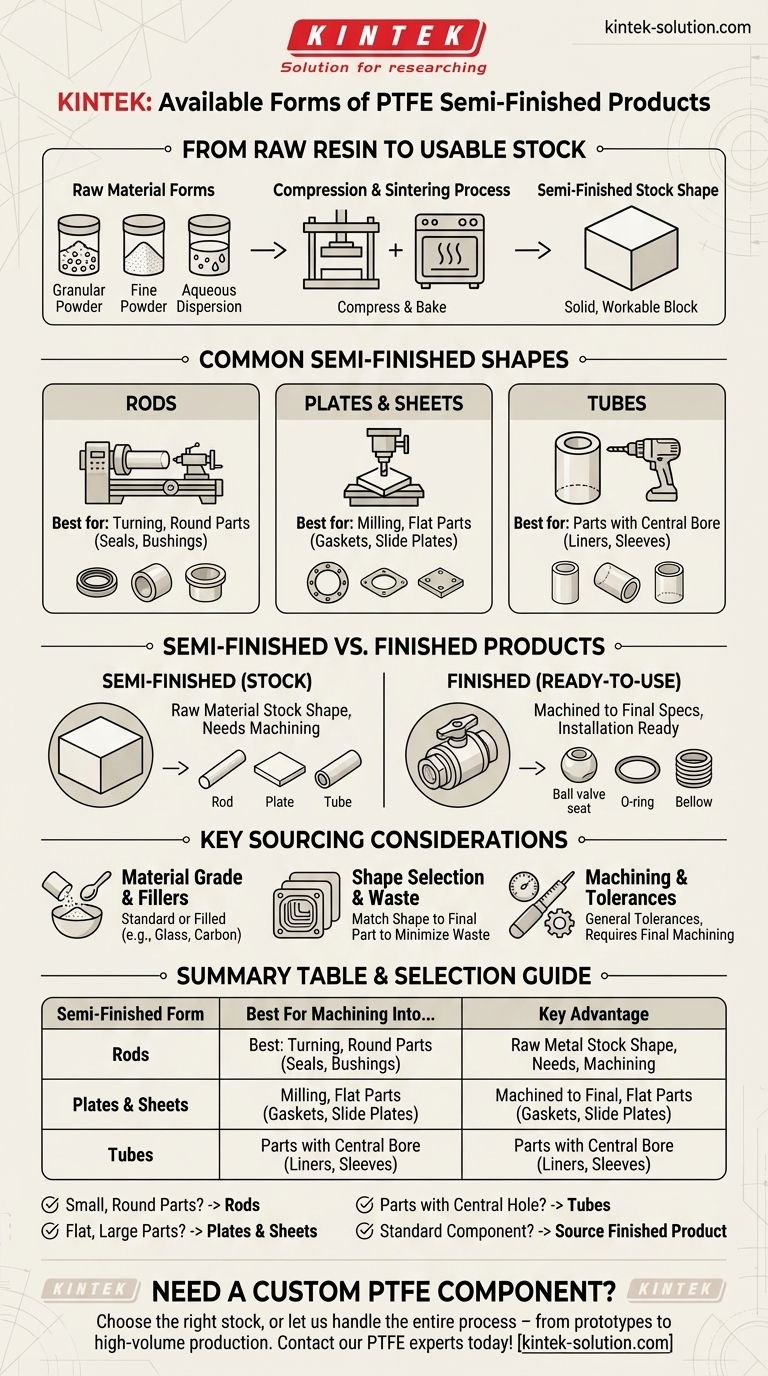
At its core, the most common semi-finished forms of Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) are stock shapes intended for machining, such as plates and rods. These forms are created by compressing one of the three raw PTFE material types—granular powder, fine powder, or aqueous dispersion—into a solid, workable block or cylinder.
The key is to understand the manufacturing chain: raw PTFE resin is converted into a semi-finished stock shape (like a plate or rod), which you then machine into a finished product (like a seal or bushing). Choosing the right semi-finished form is the first step in creating a custom PTFE component.

From Raw Resin to Usable Stock
To understand semi-finished products, it's helpful to see where they come from. The process begins with raw PTFE resin and ends with a solid shape ready for the machine shop.
The Raw Material Forms
PTFE is not melted and injection molded like many common plastics. Instead, it starts as one of three primary forms:
- Granular PTFE: A powder used for compression molding larger, simpler shapes.
- Fine Powder PTFE: Used for a process called paste extrusion, often for wire coatings or thin-walled tubing.
- Aqueous Dispersion: A milky liquid where PTFE particles are suspended in water, primarily used for coatings.
The Compression and Sintering Process
To create a semi-finished shape, granular PTFE powder is compressed under high pressure in a mold (e.g., a large cylinder or a rectangular block). This "green" preform is then sintered—baked at a high temperature below its melting point—to fuse the particles into a solid, dense material.
Common Semi-Finished Shapes
This process results in standard stock shapes that can be easily sourced and machined.
- Rods: Solid cylinders of PTFE, ideal for turning on a lathe to create round parts like seals, bushings, and insulators.
- Plates & Sheets: Large, flat blocks of PTFE. These are used for milling custom shapes, creating gaskets, or as slide plates.
- Tubes: Hollow cylinders that are efficient for parts with a central bore, as they reduce machining time and material waste compared to drilling a solid rod.
Semi-Finished vs. Finished Products
A frequent point of confusion is the difference between a semi-finished shape and a finished product. The distinction is based on intent and readiness for use.
What Defines a Semi-Finished Product?
A semi-finished product is a raw material stock shape. It is not intended for a final application in its "as-is" form. It is produced with the expectation that it will be cut, drilled, turned, or milled into something else.
What Defines a Finished Product?
A finished product is a component that has already been machined to final specifications and is ready for installation or direct use. Examples from the references are excellent illustrations:
- Ball valve seats
- O-rings and custom seals
- Guide rings and bushings
- Electrical insulators
- Bellows
Key Considerations for Sourcing PTFE
Choosing the right semi-finished product involves more than just picking a shape. You must consider the material grade and manufacturing efficiency.
Material Grade and Fillers
Standard, "virgin" PTFE can be modified with fillers to enhance specific properties. You can source semi-finished products made from filled grades, such as glass-filled PTFE for improved wear resistance or carbon-filled PTFE for increased compressive strength and conductivity.
Choosing Shape to Minimize Waste
The logic is simple: match the stock shape to the final part geometry. Using a tube instead of a rod for a hollow part, or a thin sheet instead of a thick plate for a gasket, significantly reduces material cost and machining time.
Machining and Tolerances
Remember that semi-finished products are made to general tolerances. The final, precise dimensions required for your application must be achieved through your own machining process.
Selecting the Right Form for Your Application
Use your end goal to guide your sourcing decision.
- If your primary focus is machining small, round components: Start with PTFE rods, as they are perfectly suited for lathe operations.
- If your primary focus is creating flat parts, gaskets, or large non-symmetrical components: Begin with PTFE plates or sheets to provide the necessary surface area.
- If your primary focus is a part with a central hole: Choose PTFE tubing to minimize drilling operations and material waste.
- If you need a standard, ready-to-use component like a valve seat or seal: You are looking for a finished product, which you should source directly from a specialized supplier.
Choosing the correct semi-finished material is the first and most critical step toward efficiently manufacturing a high-performance PTFE component.
Summary Table:
| Semi-Finished Form | Best For Machining Into... | Key Advantage |
|---|---|---|
| Rods | Seals, bushings, insulators (round parts) | Ideal for lathe turning |
| Plates & Sheets | Gaskets, slide plates, large custom shapes | Provides a large surface area for milling |
| Tubes | Parts with a central bore (liners, sleeves) | Reduces waste vs. drilling a solid rod |
Need a custom PTFE component?
Choosing the right semi-finished PTFE stock is the first step to a successful, cost-effective part. At KINTEK, we specialize in manufacturing high-precision PTFE components for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors.
We can provide the semi-finished stock you need or handle the entire process—from custom fabrication of prototypes to high-volume production of finished parts like seals, liners, and labware.
Let's discuss your project requirements and get you a quote.
Contact our PTFE experts today!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Customizable PTFE Rods for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What is the importance of selecting the right ball valve seat materials? Ensure a Leak-Proof Seal
- How does CAD/CAM software enhance the precision of CNC machined PTFE parts? Master Digital Machining for Flawless Components
- What are the primary materials used for oil seals? NBR vs. PTFE for Your Application
- What is the coefficient of friction for Pure Teflon? Unlock Superior Low-Friction Performance
- What are the available sizes and thicknesses for PTFE sheets? A Guide for Engineers & Designers
- Why are PTFE O-rings suitable for food production machinery? Ensuring Purity and Performance
- Can PTFE butterfly valves be used for all types of fluids? Maximize Chemical Resistance and Purity
- Are Teflon PTFE sheets safe for food-related uses? Ensuring Food Safety with Pure PTFE



















