To be clear, PTFE lined ball valves are specifically engineered to handle a wide range of highly corrosive and aggressive media. Their primary strength lies in providing a chemically inert barrier for fluids such as acids, bases, salts, oxidants, and various organic solvents, making them a cornerstone in industries where fluid purity and corrosion prevention are critical.
The core principle to understand is that while PTFE offers near-universal chemical resistance, its physical softness is its primary limitation. These valves excel with clean, corrosive liquids but are fundamentally unsuitable for any media containing hard particles, crystals, or abrasive impurities that can mechanically damage the lining.
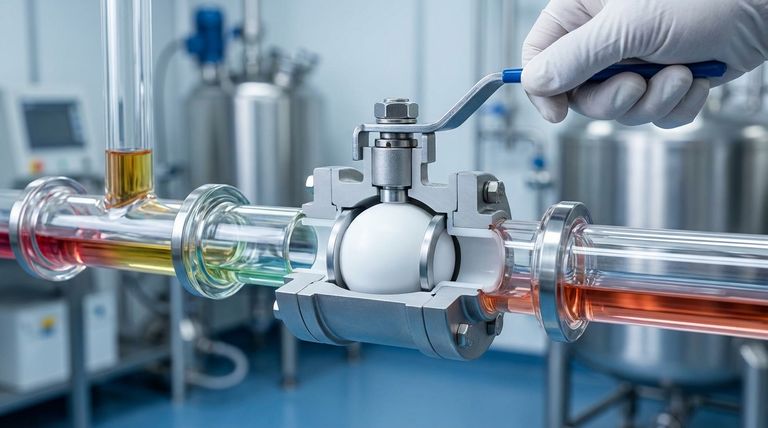

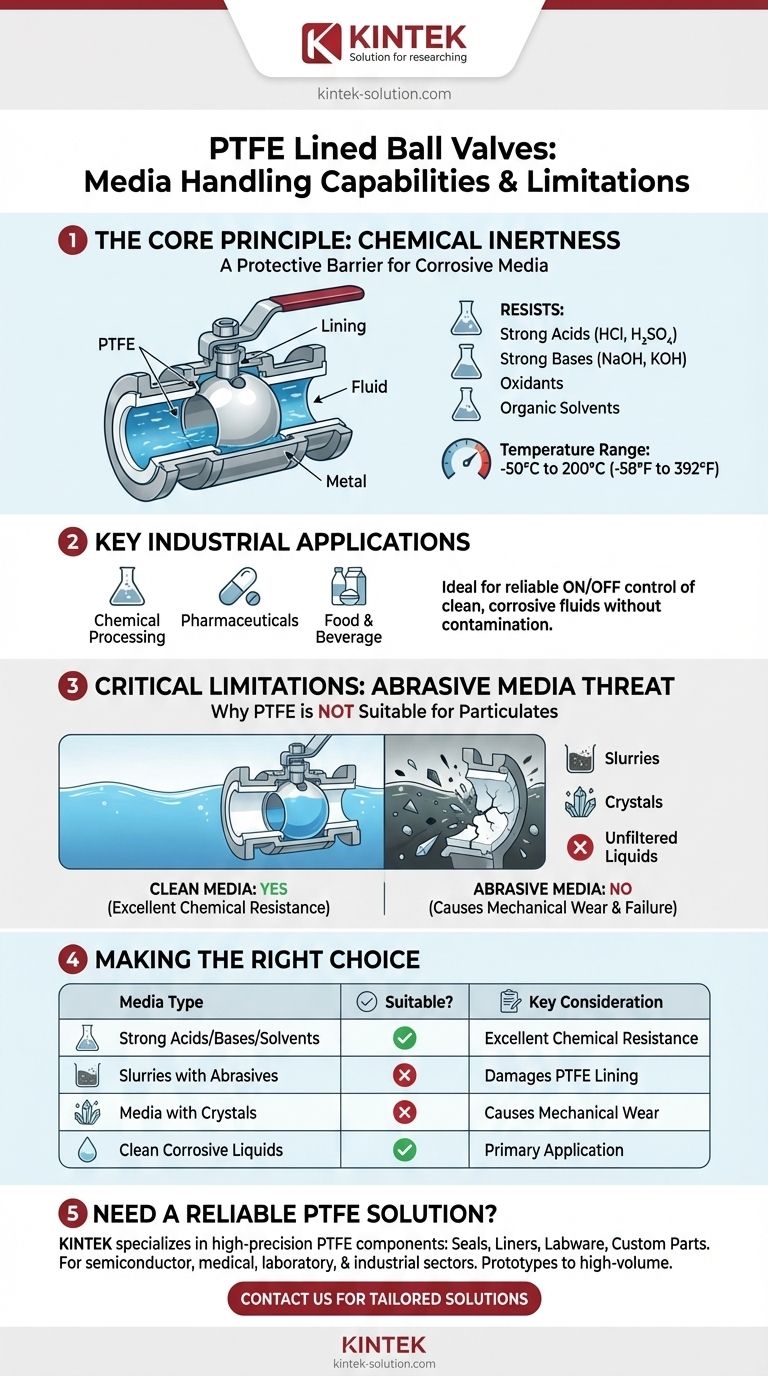
The Principle of Chemical Inertness
The effectiveness of a PTFE lined valve stems from a simple, powerful concept: isolating the process media from the structural metal of the valve body. This design prevents chemical attack and ensures fluid purity.
A Protective Barrier
The valve's interior surfaces are completely lined with Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE). This lining acts as a robust barrier, ensuring the corrosive fluid only ever comes into contact with the chemically resistant PTFE, not the carbon or stainless steel body.
Broad Spectrum Resistance
This design makes the valve suitable for an extensive list of aggressive substances commonly found in demanding industrial environments. This includes strong acids, alkalis, corrosive salts, and powerful oxidizing agents.
Key Industrial Applications
Because of this resistance, these valves are standard equipment in sectors like chemical processing, pharmaceuticals, and food and beverage. They provide reliable ON/OFF control for corrosive fluid transport without risk of contamination or valve degradation.
Stable Across Temperatures
PTFE linings maintain their integrity across a wide temperature spectrum, typically from -50°C to 200°C (-58°F to 392°F). This stability makes them suitable for both cryogenic and elevated temperature applications without compromising performance.
Critical Limitations: Understanding the Trade-offs
The primary weakness of PTFE is mechanical, not chemical. Understanding this trade-off is essential to prevent valve failure and ensure system reliability.
The Threat of Abrasive Media
The most significant restriction is that the media must be free of hard particles, crystals, or impurities. PTFE is a relatively soft material. Abrasive elements in the fluid will physically scour and wear down the lining during operation.
How Failure Occurs
As the valve opens and closes, any suspended particles will grind against the PTFE on the ball and the valve seats. This mechanical wear quickly erodes the lining, compromising the valve's sealing capability.
The Result: Reduced Performance and Lifespan
Once the lining is damaged, the valve will no longer provide a tight shut-off. More critically, the corrosive media can then penetrate the compromised lining and attack the metal body, leading to catastrophic valve failure and a potential safety hazard.
Making the Right Choice for Your Media
Selecting the correct valve requires evaluating both the chemical and physical properties of your process fluid.
- If your primary focus is handling clean but highly corrosive liquids (e.g., pure acids, solvents, or caustics): A PTFE lined ball valve is an excellent and reliable choice for safe and long-term service.
- If your primary focus is handling fluids with suspended solids (e.g., slurries, media with crystals, or unfiltered liquids): You must avoid PTFE lined valves and consider alternatives designed for abrasion, such as metal-seated or ceramic ball valves.
Ultimately, matching the valve's material properties to the complete profile of your media is the fundamental principle of reliable system design.
Summary Table:
| Media Type | Suitable for PTFE Lined Valve? | Key Consideration |
|---|---|---|
| Strong Acids (e.g., HCl, H2SO4) | Yes | Excellent chemical resistance |
| Strong Bases (e.g., NaOH, KOH) | Yes | Ideal for caustic solutions |
| Organic Solvents | Yes | Maintains fluid purity |
| Slurries with Abrasive Particles | No | Particles will damage PTFE lining |
| Media with Crystals | No | Causes mechanical wear and failure |
| Clean Corrosive Liquids | Yes | Primary application for these valves |
Need a reliable PTFE component solution for corrosive applications?
At KINTEK, we specialize in manufacturing high-precision PTFE components—including seals, liners, labware, and custom parts—for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Whether you require prototypes or high-volume orders, our expertise ensures your equipment handles aggressive media safely and efficiently.
Contact us today to discuss your specific requirements and get a tailored solution that guarantees performance and longevity.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
People Also Ask
- What is the function of check valves in water pump systems? Protect Your Pump and Prevent Backflow
- What key factors contribute to long-term savings when using Teflon gland packing? Reduce Downtime and Maintenance Costs
- What are symptoms of temperature-induced PTFE lip seal failure? Identify the Cause of Your Leaks
- What are the operational benefits of the PTFE seat butterfly valve? Superior Control for Corrosive & Sensitive Media
- What are some common products made from PTFE? Discover Versatile Solutions for Harsh Environments
- What factors should be considered when choosing between O-rings, square rings, quad rings, or flat gaskets? Optimize Your Seal Selection
- What are typical applications of Teflon/PTFE machined parts? Key Uses in Aerospace, Medical & Chemical Processing
- How do PTFE expansion bellows address pipe misalignment? Protect Your Piping System from Stress and Failure



















