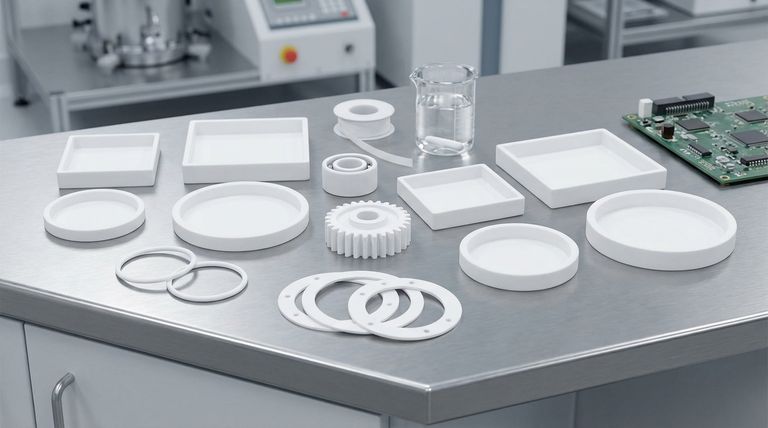
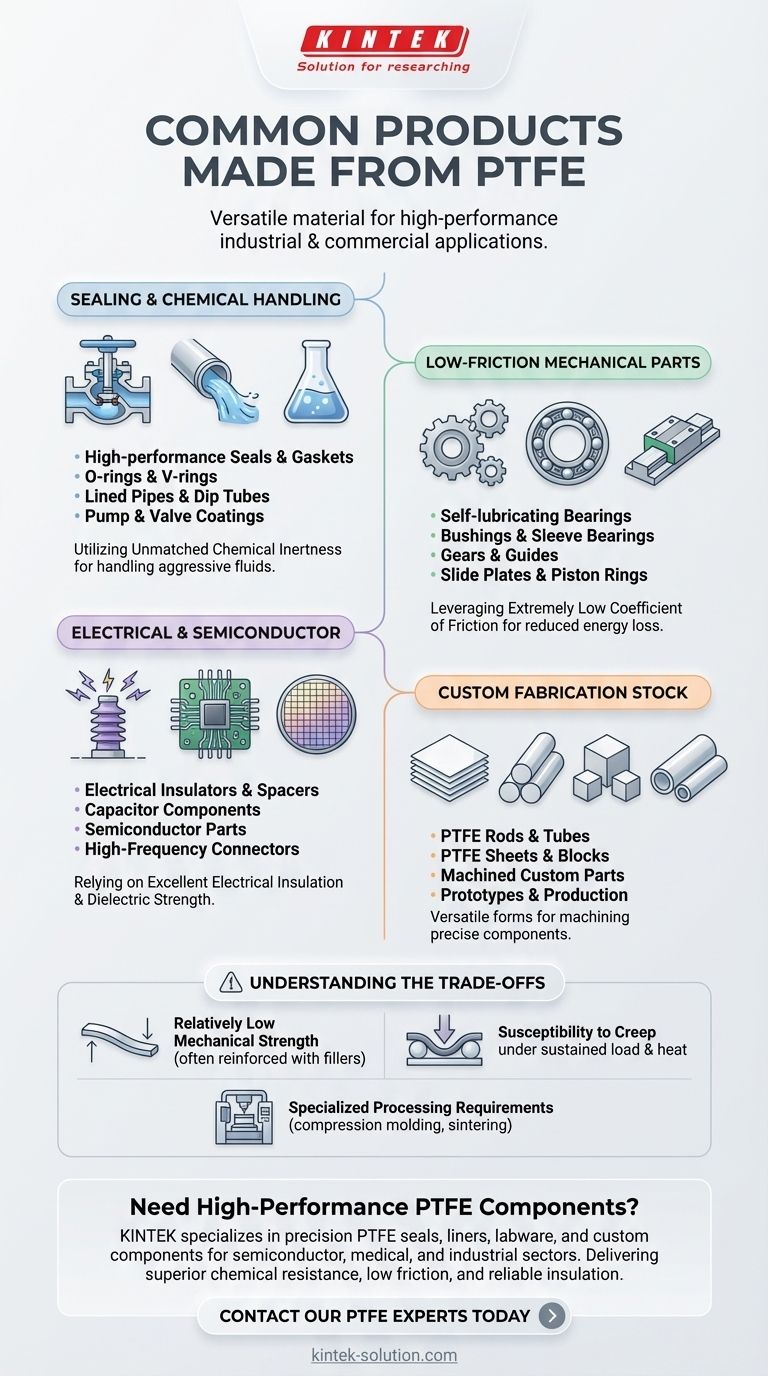
In short, Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is manufactured into a vast range of industrial and commercial products. The most common applications are high-performance seals, gaskets, and O-rings; low-friction mechanical components like bearings and gears; and critical electrical insulators and parts for chemical processing equipment.
The versatility of PTFE does not stem from a single property, but from its unique combination of extreme chemical inertness, an exceptionally low coefficient of friction, and excellent dielectric strength. This makes it a premier problem-solving material for harsh or demanding engineering environments.

The Core Properties Driving PTFE Applications
To understand why PTFE is used in so many products, you must first understand the core material properties that engineers leverage. Each unique characteristic makes it the ideal choice for a specific category of applications.
Unmatched Chemical Inertness
PTFE is famously non-reactive and resistant to nearly all industrial chemicals and solvents. This makes it indispensable for handling corrosive materials.
This property is why you see PTFE used for seals, gaskets, and O-rings in chemical pumps and valves. It's also formed into lined pipes, dip tubes, and coatings for pump interiors to protect metal components from aggressive fluids.
Extremely Low Coefficient of Friction
PTFE has one of the lowest friction coefficients of any known solid material, often compared to wet ice on wet ice. This allows for the creation of self-lubricating parts that reduce energy loss and wear.
This low-friction nature is the reason PTFE is machined into bearings, bushings, gears, and guides. These components can operate smoothly without external lubrication, which is critical in clean environments or hard-to-service machinery.
Excellent Electrical Insulation
PTFE is an exceptional electrical insulator with high dielectric strength, meaning it can withstand a strong electric field without breaking down. It also maintains these properties across a wide range of frequencies and temperatures.
Because of this, PTFE is a primary material for electrical insulators, semiconductor components, and spacers in capacitors. Its reliability is crucial for high-performance electronics.
High-Performance Stock Materials
Due to its versatility, PTFE is often produced in standard shapes for custom fabrication. Engineers can then machine the precise component they need for a specific application.
These common stock forms include PTFE rods, sheets, blocks, and tubes. They are the starting point for creating many of the custom gaskets, insulators, and mechanical parts previously mentioned.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While its properties are impressive, PTFE is not a universal solution. Understanding its limitations is critical for proper material selection.
Relatively Low Mechanical Strength
Compared to other engineering polymers, PTFE is a relatively soft material. It has low tensile strength and is not suitable for high-load structural applications on its own. It is often reinforced with fillers like glass or carbon to improve its mechanical properties.
Susceptibility to Creep
Under a sustained load, especially at elevated temperatures, PTFE can slowly deform or "creep." This must be accounted for in the design of components like seals and gaskets, which are under constant compression.
Specialized Processing Requirements
PTFE cannot be melt-processed like common thermoplastics such as nylon or polycarbonate. It must be formed using specialized and often more costly techniques like compression molding, sintering, or paste extrusion, which can affect the final price of the component.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting PTFE is about matching its unique strengths to your specific engineering challenge.
- If your primary focus is sealing against aggressive chemicals: Use PTFE for gaskets, O-rings, V-rings, and lined pipes to ensure long-term integrity.
- If your primary focus is creating low-friction, self-lubricating parts: Specify PTFE for bearings, slide plates, gears, and piston rings where maintenance is difficult and cleanliness is key.
- If your primary focus is isolating high-voltage or high-frequency electronics: Choose PTFE for its superior dielectric properties in insulators, spacers, and semiconductor manufacturing components.
Ultimately, PTFE is chosen when other materials fail to provide the necessary combination of chemical, thermal, and electrical resistance.
Summary Table:
| Application Category | Common PTFE Products | Key PTFE Property Utilized |
|---|---|---|
| Sealing & Chemical Handling | Seals, Gaskets, O-rings, Lined Pipes, Dip Tubes | Unmatched Chemical Inertness |
| Low-Friction Mechanical Parts | Bearings, Bushings, Gears, Slide Plates, Piston Rings | Extremely Low Coefficient of Friction |
| Electrical & Semiconductor | Insulators, Spacers, Capacitor Components, Semiconductor Parts | Excellent Electrical Insulation & Dielectric Strength |
| Custom Fabrication Stock | Rods, Sheets, Blocks, Tubes (for machining custom parts) | Versatility & Machinability |
Need high-performance PTFE components tailored to your specific requirements?
At KINTEK, we specialize in manufacturing precision PTFE seals, liners, labware, and custom components for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Whether you need prototypes or high-volume production, our expertise in PTFE fabrication ensures you get parts that deliver superior chemical resistance, low friction, and reliable electrical insulation.
Contact our PTFE experts today to discuss your project and receive a custom solution that meets your exact specifications.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- When and by whom was PTFE discovered? A Tale of Accidental Innovation
- What is the temperature range that PTFE can withstand? From -200°C to +260°C for Demanding Applications
- What is the hardness range of PTFE on the Shore D scale? Leveraging Its Softness for Superior Performance
- How is PTFE used in industrial processes? Maximize Safety and Efficiency
- Why is dimensional stability a concern when machining PTFE? Ensure Accurate, Stable PTFE Components



















