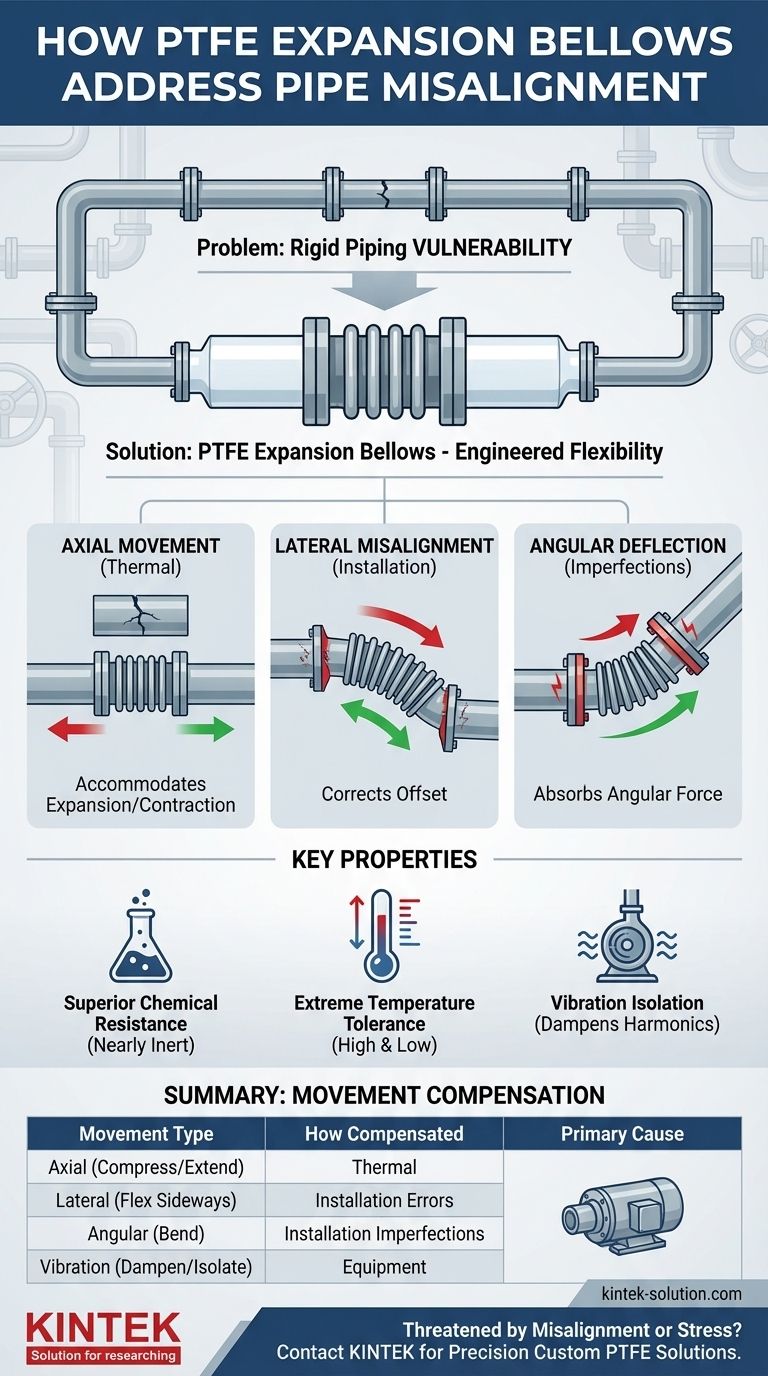
To address pipe misalignment, PTFE expansion bellows act as highly flexible joints within a rigid piping system. Their key function is to absorb three distinct types of movement—axial, lateral, and angular—thereby compensating for pipes that are not perfectly aligned and preventing the transfer of stress that could lead to system failure.
The fundamental problem with rigid piping is that it cannot tolerate stress from misalignment, thermal changes, or vibration. PTFE expansion bellows solve this by introducing a point of engineered flexibility that safely absorbs these forces, ensuring the system's long-term integrity.

Why Misalignment is a Threat to Piping Systems
Rigid pipes are excellent for transporting fluids, but their lack of flexibility makes them vulnerable. Any force that attempts to bend, stretch, or compress the pipe concentrates at its weakest points, such as flanges and connections.
The Problem of Thermal Expansion
As temperatures fluctuate, pipes expand and contract. This movement, known as axial movement, can generate immense stress, potentially causing pipes to crack or connections to leak.
The Challenge of Mechanical Vibration
Pumps, motors, and other equipment introduce vibrations into a piping system. A rigid system transmits these vibrations directly, leading to metal fatigue and eventual failure.
The Reality of Installation Imperfections
Perfect alignment during installation is often difficult and costly to achieve. This can result in pipes that are slightly offset (lateral misalignment) or connected at an incorrect angle (angular misalignment).
How PTFE Bellows Provide the Solution
PTFE expansion bellows are designed with convolutions (the "accordion" shape) that allow them to move in multiple directions without compromising their seal. This flexibility is the core of how they protect the system.
Accommodating Axial Movement
When a pipe expands or contracts due to temperature changes, the bellows simply compress or extend along the pipe's axis. This action absorbs the change in length and neutralizes the stress.
Correcting Lateral Misalignment
For pipes that are parallel but offset, the bellows can flex sideways. This allows a secure connection to be made between two misaligned points without inducing dangerous bending forces on the pipe itself.
Absorbing Angular Deflection
If two pipes meet at a slight angle, the bellows can bend to accommodate the difference. This ensures a leak-proof seal while preventing the angular force from stressing the flange bolts and gaskets.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Key Properties
While their primary function is to handle misalignment, the material properties of PTFE are what make these bellows suitable for demanding industrial applications.
Superior Chemical Resistance
PTFE is nearly inert, making it resistant to corrosion from a vast range of aggressive chemicals. This ensures the bellows do not become a point of failure in chemically harsh environments.
Extreme Temperature Tolerance
As noted in pharmaceutical applications, PTFE can withstand extreme temperature ranges. This includes high-temperature sterilization processes and cryogenic applications without becoming brittle or losing its flexibility.
Vibration Isolation
The inherent flexibility of the bellows dampens mechanical vibrations. By placing a bellow near a pump, you effectively isolate the rest of the piping system from damaging harmonic forces.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To select the correct bellow, you must first identify the primary force you need to manage.
- If your primary focus is thermal expansion: You need a bellow rated for the specific amount of axial movement your system will experience between its lowest and highest operating temperatures.
- If your primary focus is correcting installation errors: Measure the lateral and angular offset between the pipe ends to select a bellow that can accommodate that specific misalignment.
- If your primary focus is vibration damping: Install a bellow as close as possible to the vibration source to effectively isolate it from the wider piping network.
Ultimately, by introducing engineered flexibility, PTFE expansion bellows transform a vulnerable rigid system into a resilient and durable one.
Summary Table:
| Movement Type | How PTFE Bellows Compensate | Primary Cause |
|---|---|---|
| Axial | Compress or extend along the pipe's axis | Thermal expansion/contraction |
| Lateral | Flex sideways to connect offset pipes | Installation errors |
| Angular | Bend to accommodate incorrect angles | Installation imperfections |
| Vibration | Dampen and isolate harmonic forces | Pumps, motors, and equipment |
Is misalignment, thermal stress, or vibration threatening your piping system? KINTEK specializes in manufacturing high-precision, custom PTFE components, including expansion bellows, for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Our bellows are engineered to absorb movement, resist harsh chemicals, and withstand extreme temperatures, ensuring your system's long-term integrity and performance. From prototype to high-volume production, we deliver the reliability you need.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss your specific application and receive a solution tailored to your goals.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Customizable PTFE Rods for Advanced Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What are the unique properties of PTFE? Unlock Unmatched Performance in Demanding Applications
- What industrial benefits do PTFE-machined parts offer? Achieve Peak Performance in Demanding Applications
- What are the unique properties of PTFE? The 3 Pillars Driving Demand for High-Performance Parts
- What factors should be considered when choosing between Nylon and PTFE? Select the Right Material for Your Application
- What fabrication services are available for PTFE? Shearing, Stamping, Laser Cutting, Molding & Machining



















