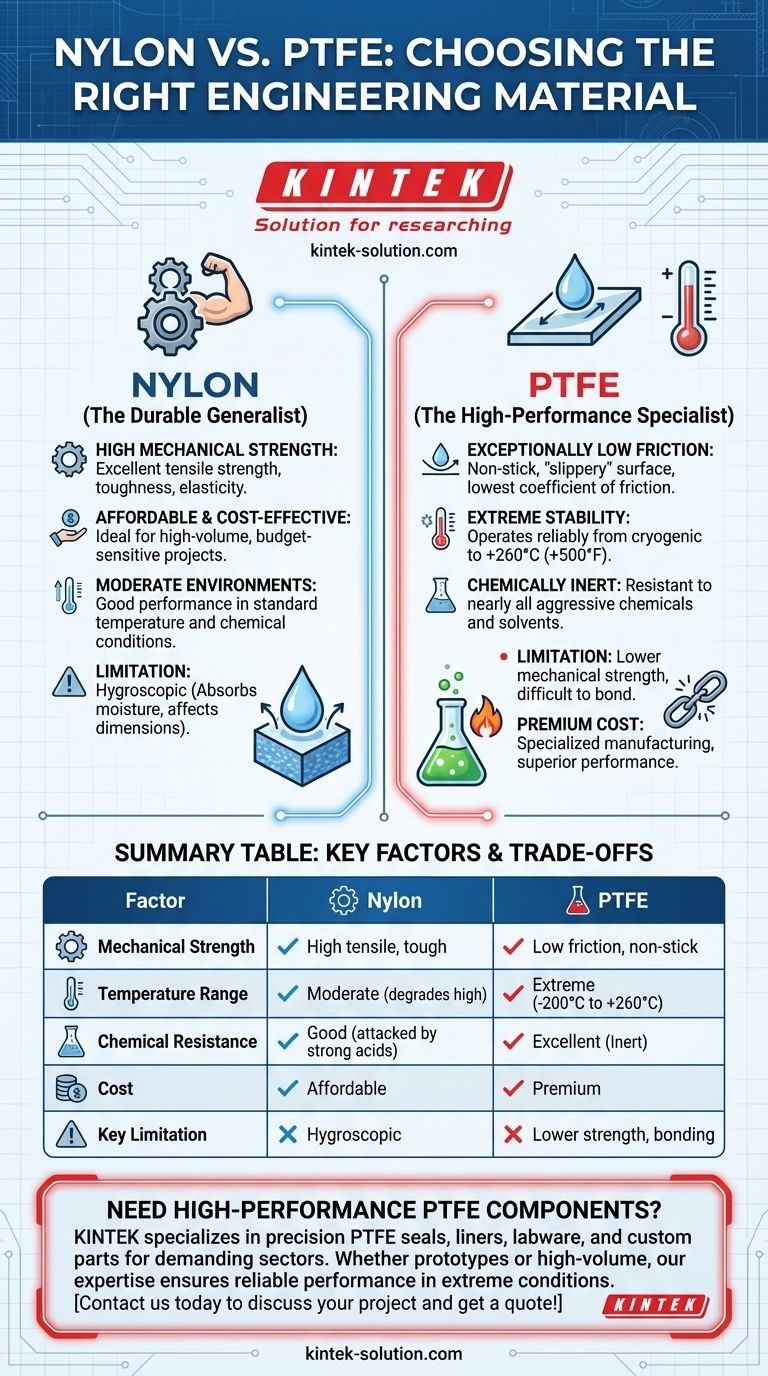
The choice between Nylon and PTFE is a classic engineering decision that hinges on three primary factors: mechanical requirements, environmental conditions, and budget. Nylon is valued for its mechanical strength and affordability, making it a versatile workhorse. In contrast, PTFE is a specialized material chosen for its extreme temperature stability, chemical inertness, and exceptionally low friction.
Your decision is fundamentally a choice between a durable, cost-effective generalist (Nylon) and a high-performance specialist (PTFE). The specific demands of your application—not the materials themselves—should dictate the right answer.
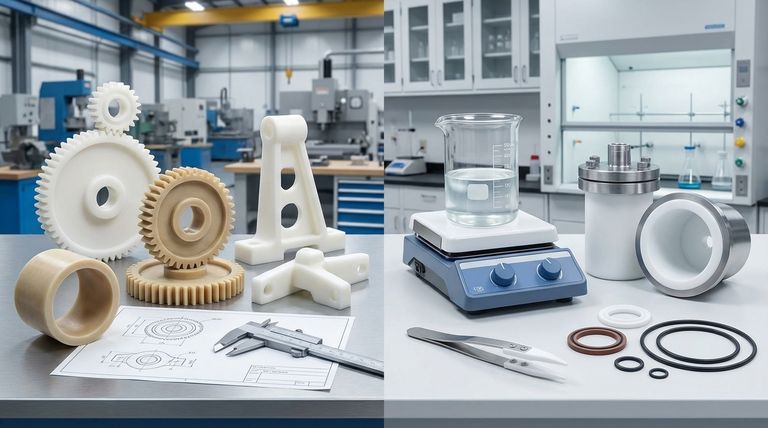

Analyzing Core Mechanical Properties
The most significant distinction between these two materials lies in their mechanical behavior. One offers structural integrity, while the other provides unparalleled surface performance.
Nylon: The Case for Strength and Durability
Nylon is known for its impressive tensile strength, toughness, and elasticity. This makes it an excellent choice for components that must withstand significant mechanical stress.
It is frequently used for gears, bearings, and structural parts where durability and wear resistance are paramount.
PTFE: The Standard for Low Friction
PTFE (Polytetrafluoroethylene), widely known by the brand name Teflon, has one of the lowest coefficients of friction of any solid material. Its value lies in its non-stick, "slippery" surface.
This property is critical for applications like non-stick coatings, seals, and bushings where reducing friction is the primary engineering goal.
Evaluating Environmental Resistance
How a material performs under thermal and chemical stress is often the deciding factor. Here, PTFE has a clear and significant advantage.
Temperature Stability: Where PTFE Excels
PTFE can operate reliably across an extremely wide temperature range, from cryogenic lows to highs of around 260°C (500°F).
Nylon, while robust, is suitable for more moderate temperature environments and can degrade or lose its properties at the extremes where PTFE thrives.
Chemical Inertness: PTFE's Key Advantage
PTFE is chemically inert and resistant to nearly all chemicals and solvents. This makes it the default choice for seals, linings, and components used in aggressive chemical processing.
Nylon has good chemical resistance to many common substances but can be attacked by strong acids and oxidizing agents.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a material is never just about its strengths; it's also about understanding its limitations and costs.
The Cost Equation: Affordability vs. Performance
Nylon is a significantly more affordable material, making it ideal for cost-sensitive projects and high-volume production.
PTFE is a premium material. Its higher cost is a direct result of its specialized manufacturing process and superior performance characteristics in harsh environments.
Practical Limitations to Consider
While strong, Nylon is hygroscopic, meaning it absorbs moisture from the environment. This absorption can cause dimensional changes and a reduction in mechanical properties, which must be accounted for in precise applications.
PTFE has lower mechanical strength compared to Nylon and can be more difficult to bond to other surfaces due to its non-stick nature.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your final decision should be guided by the single most important requirement of your project.
- If your primary focus is mechanical strength and cost-efficiency: Choose Nylon for its excellent balance of durability and affordability in moderate environments.
- If your primary focus is performance in extreme temperatures or aggressive chemical environments: PTFE is the only reliable choice.
- If your primary focus is creating a low-friction or non-stick surface: PTFE's unique properties make it the clear winner for these applications.
By clearly defining your application's non-negotiable needs, you can confidently select the material that provides the best performance and value.
Summary Table:
| Factor | Nylon | PTFE |
|---|---|---|
| Mechanical Strength | High tensile strength, tough, elastic | Low friction, non-stick surface |
| Temperature Range | Moderate (degrades at high temps) | Extreme (-200°C to +260°C) |
| Chemical Resistance | Good, but attacked by strong acids | Excellent, inert to nearly all chemicals |
| Cost | Affordable, cost-effective | Premium, higher cost |
| Key Limitation | Hygroscopic (absorbs moisture) | Lower mechanical strength, difficult to bond |
Need High-Performance PTFE Components?
At KINTEK, we specialize in manufacturing precision PTFE seals, liners, labware, and custom components for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Whether you require prototypes or high-volume orders, our expertise ensures your parts meet the demanding requirements of extreme temperatures and aggressive chemical environments.
Contact us today to discuss your project and get a quote!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Customizable PTFE Rods for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What are the key advantages of PTFE? Unmatched Performance for Extreme Environments
- What are the key considerations when machining Teflon? Master Precision Machining for Soft Polymers
- What industries use PTFE machined parts and for what applications? Critical Components for Demanding Environments
- Why is PTFE rod suitable for automotive applications? Boost Vehicle Performance & Durability
- What are the future considerations for machining Teflon? Mastering Material Challenges with Smart Tech



















