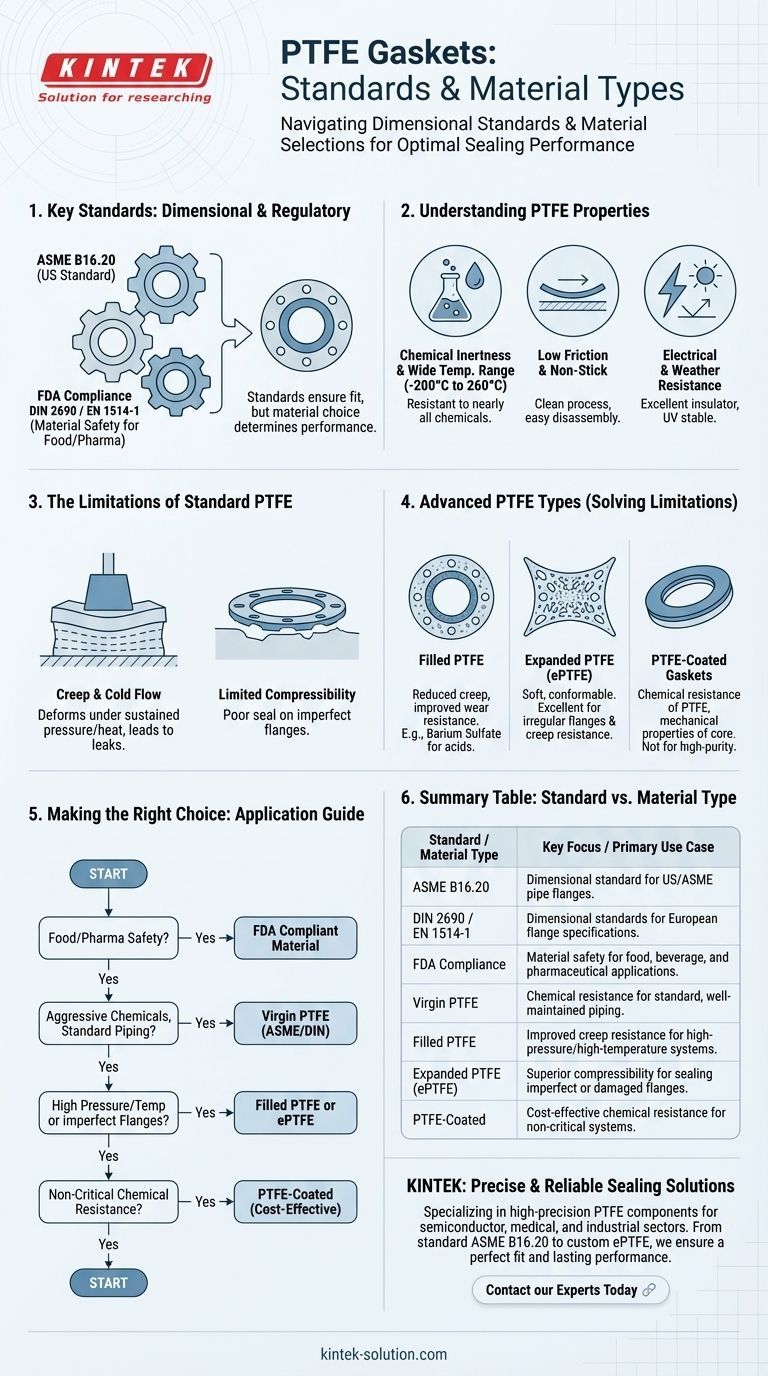
When selecting a PTFE gasket, it's crucial to understand that standards apply to both its physical dimensions and its material composition. The primary dimensional standards for pipe flanges are ASME B16.20, EN 1514-1, and DIN 2690, though custom sizes are also common. For applications in sensitive industries, ensuring the material complies with FDA regulations is equally important.
While dimensional standards like ASME and DIN ensure a gasket fits, they do not guarantee performance. The key to successful application is matching the specific type of PTFE material to the operational pressures, temperatures, and chemical environment of your system.

Understanding PTFE as a Gasket Material
Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is a synthetic fluoropolymer prized for a unique combination of properties. Understanding these is the first step in proper selection.
Unmatched Chemical Inertness
PTFE is resistant to nearly all industrial chemicals and solvents. This makes it a default choice for sealing systems that handle aggressive or corrosive media.
It also performs exceptionally well across a wide temperature range, typically from -200°C to 260°C (-328°F to 500°F).
Low Friction and Non-Stick Properties
The material has an extremely low coefficient of friction, giving it self-lubricating and non-stick characteristics. This prevents material from adhering to the gasket, ensuring a clean process and easier disassembly of flanged joints.
Electrical and Weather Resistance
PTFE is an excellent electrical insulator and is highly resistant to weathering and UV degradation, making it suitable for long-term outdoor or exposed applications.
Key Dimensional and Regulatory Standards
While the material properties are critical, gaskets must conform to established standards to ensure they fit correctly between standard flanges.
ASME B16.20
This is the standard from the American Society of Mechanical Engineers for metallic gaskets for pipe flanges. PTFE gaskets are frequently manufactured to these dimensional specifications for use in US-based or ASME-compliant systems.
DIN 2690 & EN 1514-1
These are the dominant European standards. DIN 2690 is a German standard for flange gaskets, while EN 1514-1 is a broader European standard. They define the dimensions for gaskets intended for use with flanges that follow DIN and EN specifications.
FDA Compliance
This is not a dimensional standard but a material safety regulation. If the gasket will be used in food, beverage, or pharmaceutical processing, it must be made from materials that are certified as safe for direct contact, as defined by the Food and Drug Administration.
The Critical Trade-offs of Standard PTFE
Virgin, or standard, PTFE is not a perfect sealing material. Its physical properties introduce significant limitations that must be managed.
Creep and Cold Flow
PTFE's most significant weakness is its tendency to creep, or gradually deform under sustained pressure (load). This is exacerbated at elevated temperatures, where it can exhibit cold flow, leading to a loss of bolt torque and potential leaks over time.
Limited Compressibility
Unlike more flexible elastomers, PTFE is a relatively rigid material. This lack of elasticity makes it difficult for a standard PTFE gasket to conform to and seal imperfect, scratched, or slightly warped flange surfaces.
Addressing PTFE's Limitations with Advanced Types
To overcome the weaknesses of virgin PTFE, manufacturers have developed several variations. Choosing the right one is essential for demanding applications.
Filled PTFE
To reduce creep and improve wear resistance, inert fillers like glass, graphite, or barium sulfate are added to the PTFE matrix. A barium sulfate-filled variant, for example, offers exceptional resistance to highly corrosive substances like hydrofluoric acid.
Expanded PTFE (ePTFE)
This material is created by rapidly stretching PTFE, resulting in a soft, highly compressible, and flexible gasket material. Biaxially expanded PTFE is excellent for sealing irregular or damaged flanges and has much better creep resistance than standard PTFE.
PTFE-Coated Gaskets
These are composite gaskets, typically with a rubber or metal core that is encapsulated in a thin layer of PTFE. They offer the chemical resistance of PTFE with the mechanical performance and compressibility of the core material, but are not suitable for high-purity applications.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct gasket requires moving beyond a simple standard and matching the material's properties to the system's demands.
- If your primary focus is food or pharmaceutical safety: Ensure the gasket material is explicitly certified as FDA compliant.
- If you are sealing aggressive chemicals in standard, well-maintained piping: Virgin PTFE gaskets conforming to the correct ASME or EN/DIN dimensional standard are often sufficient.
- If you are dealing with high pressures, high temperatures, or imperfect flanges: Specify a filled or expanded PTFE (ePTFE) gasket to mitigate creep and ensure a reliable seal.
- If you need chemical resistance on a non-critical system: A PTFE-coated gasket may offer a cost-effective solution, but avoid it for high-purity processes.
Ultimately, choosing the right standard is just the starting point; true reliability comes from selecting the right PTFE material for the specific demands of your application.
Summary Table:
| Standard / Material Type | Key Focus / Primary Use Case |
|---|---|
| ASME B16.20 | Dimensional standard for pipe flanges in US/ASME systems. |
| DIN 2690 / EN 1514-1 | Dimensional standards for European flange specifications. |
| FDA Compliance | Material safety for food, beverage, and pharmaceutical applications. |
| Virgin PTFE | Chemical resistance for standard, well-maintained piping. |
| Filled PTFE | Improved creep resistance for high-pressure/high-temperature systems. |
| Expanded PTFE (ePTFE) | Superior compressibility for sealing imperfect or damaged flanges. |
| PTFE-Coated | Cost-effective chemical resistance for non-critical systems. |
Ensure Your Sealing Solution is Precise and Reliable
Navigating PTFE gasket standards and material types is complex, but you don't have to do it alone. KINTEK specializes in manufacturing high-precision PTFE components, including seals and gaskets, for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors.
We prioritize precision production and offer custom fabrication—from prototypes to high-volume orders—to meet your exact dimensional and material requirements. Whether you need a standard ASME B16.20 gasket or a custom ePTFE solution for a challenging application, our expertise ensures a perfect fit and lasting performance.
Let's discuss your specific needs and build a sealing solution you can trust. Contact our experts today for a consultation.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
People Also Ask
- Why is PTFE considered cost-effective for plumbing applications? Maximize Long-Term Value & Reliability
- What are the long-term cost benefits of using PTFE expansion bellows? Invest in Durability to Slash Downtime & Maintenance Costs
- How are Teflon-encapsulated O-Rings utilized in heavy equipment and hydraulics? Achieve Superior Sealing and Reduce Downtime
- What are the benefits of using PTFE valves in the food processing industry? Ensure Safety, Purity, and Efficiency
- What are the benefits of PTFE guide strips? Achieve Smooth, Long-Lasting Motion Control
- How does PTFE's thermal expansion and contraction affect its machining and application? Master Dimensional Stability
- What lubrication benefits do PTFE bushes provide? Achieve Maintenance-Free, Low-Friction Performance
- What industries benefit from the use of PTFE? Solve Extreme Chemical, Thermal, and Purity Challenges



















