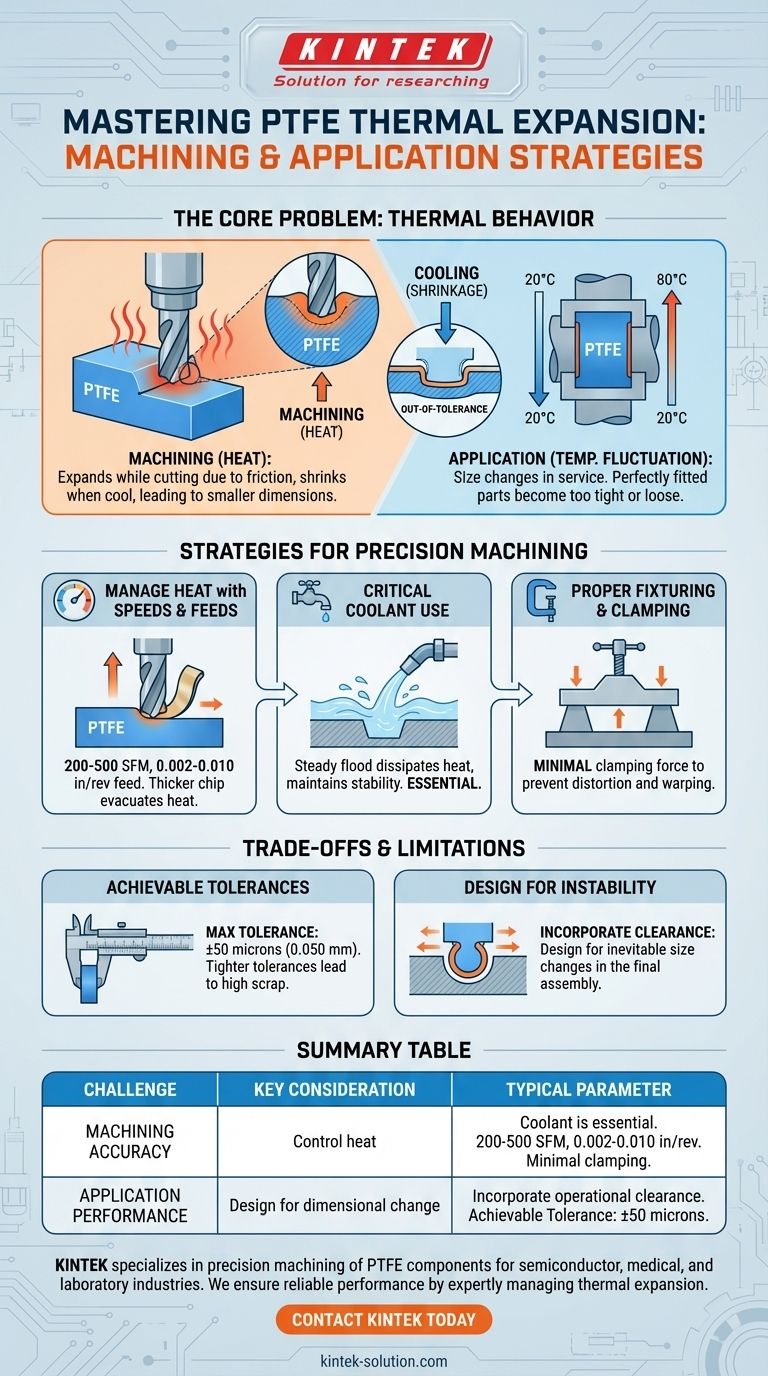
The primary challenge in working with PTFE is its exceptionally high rate of thermal expansion and contraction. This property directly impacts the material's dimensional stability, creating significant hurdles during the machining process and requiring careful consideration in the final application design to prevent part failure.
Success with PTFE hinges on a dual strategy: you must aggressively manage heat during machining to achieve dimensional accuracy, and simultaneously design the final part to accommodate the inevitable size changes it will experience in its service environment.
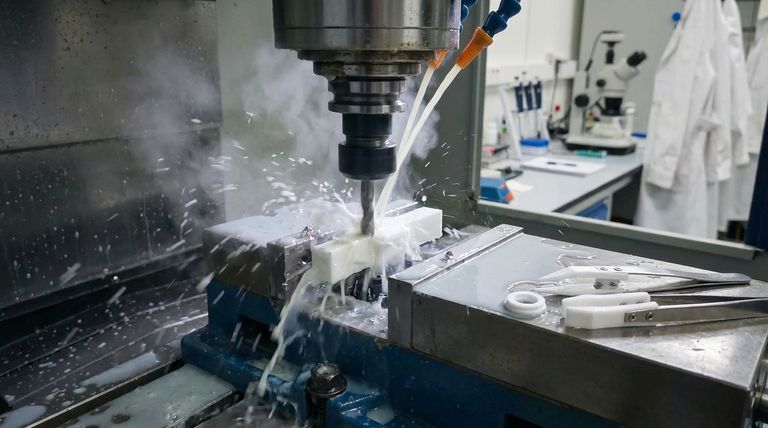

The Core Problem: PTFE's Thermal Behavior
Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) changes size with temperature far more dramatically than metals or even most other plastics. Understanding this is the first step toward controlling it.
What This Means During Machining
The friction from a cutting tool generates significant heat. As the PTFE warms up, it expands while being cut.
Once the machining is complete and the part cools to ambient temperature, it shrinks. This results in a final part that is smaller than the intended dimensions, leading to out-of-tolerance components.
What This Means in Application
A perfectly machined PTFE component will still expand and contract based on its operating temperature. A part that fits perfectly at 20°C may become too tight or too loose at 80°C.
This must be accounted for in the design phase, especially for seals, bearings, or wear plates that interface with more stable materials like steel.
Strategies for Precision Machining
Controlling the dimensional accuracy of PTFE requires a proactive approach to mitigate heat buildup and material stress.
Managing Heat with Speeds and Feeds
The goal is to create a clean cut that evacuates heat quickly with the chip. This requires a balanced approach.
Recommended cutting speeds are generally between 200 to 500 surface feet per minute (SFM).
Combine this with relatively high feed rates, from 0.002 to 0.010 inches per revolution, to create a thicker chip that carries heat away from the workpiece.
The Critical Role of Coolant
Using a coolant is essential for maintaining thermal stability. A steady flood of coolant dissipates heat from the cutting zone before it can cause the material to expand significantly.
This single step is one of the most effective ways to prevent thermal expansion from ruining part accuracy.
Proper Fixturing and Clamping
PTFE is a soft material that deforms easily under pressure. Excessive clamping force will distort the workpiece before a single cut is made.
Use minimal clamping pressure and fixtures designed to support the part broadly without pinching it. This prevents physical warping that would compound the thermal inaccuracies.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
Even with perfect technique, PTFE has inherent characteristics that must be respected in the design and manufacturing process.
Achievable Tolerances
While challenging, PTFE can be machined to precise dimensions. A maximum tolerance of 50 microns (0.050 mm) is considered achievable with proper process control.
Demanding tighter tolerances than this often leads to high scrap rates and costs.
Designing for Instability
The most critical factor for application success is to design for movement. Assume the part will change size and incorporate appropriate clearances or expansion joints.
Forgetting this step is a common reason for the failure of PTFE components in assemblies that experience temperature fluctuations.
Avoiding Stress and Warping
Beyond heat, it is critical to avoid excessive tool pressure and vibration. These forces can induce internal stresses in the material, leading to warping over time.
Using sharp tools and rigid machine setups ensures a smooth surface finish and a dimensionally stable final part.
How to Apply This to Your Project
Your strategy should be guided by whether your immediate challenge is manufacturing accuracy or long-term application performance.
- If your primary focus is achieving tight machining tolerances: Your strategy must revolve around aggressive heat management through coolants, optimized feed rates, and minimal, supportive clamping pressure.
- If your primary focus is long-term performance in a variable temperature environment: Your design must account for the material's natural thermal expansion and contraction by incorporating sufficient operational clearance.
By mastering these thermal and mechanical considerations, you can reliably produce dimensionally stable and high-performing PTFE components.
Summary Table:
| Challenge | Key Consideration | Typical Parameter |
|---|---|---|
| Machining Accuracy | Control heat from cutting tools | Coolant use is essential |
| Optimize cutting parameters | 200-500 SFM, 0.002-0.010 in/rev feed | |
| Use proper fixturing | Minimal clamping pressure | |
| Application Performance | Design for dimensional change | Incorporate operational clearance |
| Achievable Tolerance | ±50 microns (0.050 mm) |
Struggling with PTFE's dimensional instability? KINTEK specializes in precision machining of PTFE components (seals, liners, labware) for the semiconductor, medical, and laboratory industries. We expertly manage thermal expansion during fabrication to deliver parts that perform reliably in your application, from prototypes to high-volume orders.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss your PTFE project requirements and ensure long-term performance.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Customizable PTFE Rods for Advanced Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What are the key advantages of PTFE? Unmatched Performance for Extreme Environments
- What industries use PTFE machined parts and for what applications? Critical Components for Demanding Environments
- Why is CNC machining preferred for Teflon parts over other methods? Unlock Precision & Complex Designs
- Why is PTFE rod suitable for automotive applications? Boost Vehicle Performance & Durability
- What are the future considerations for machining Teflon? Mastering Material Challenges with Smart Tech



















