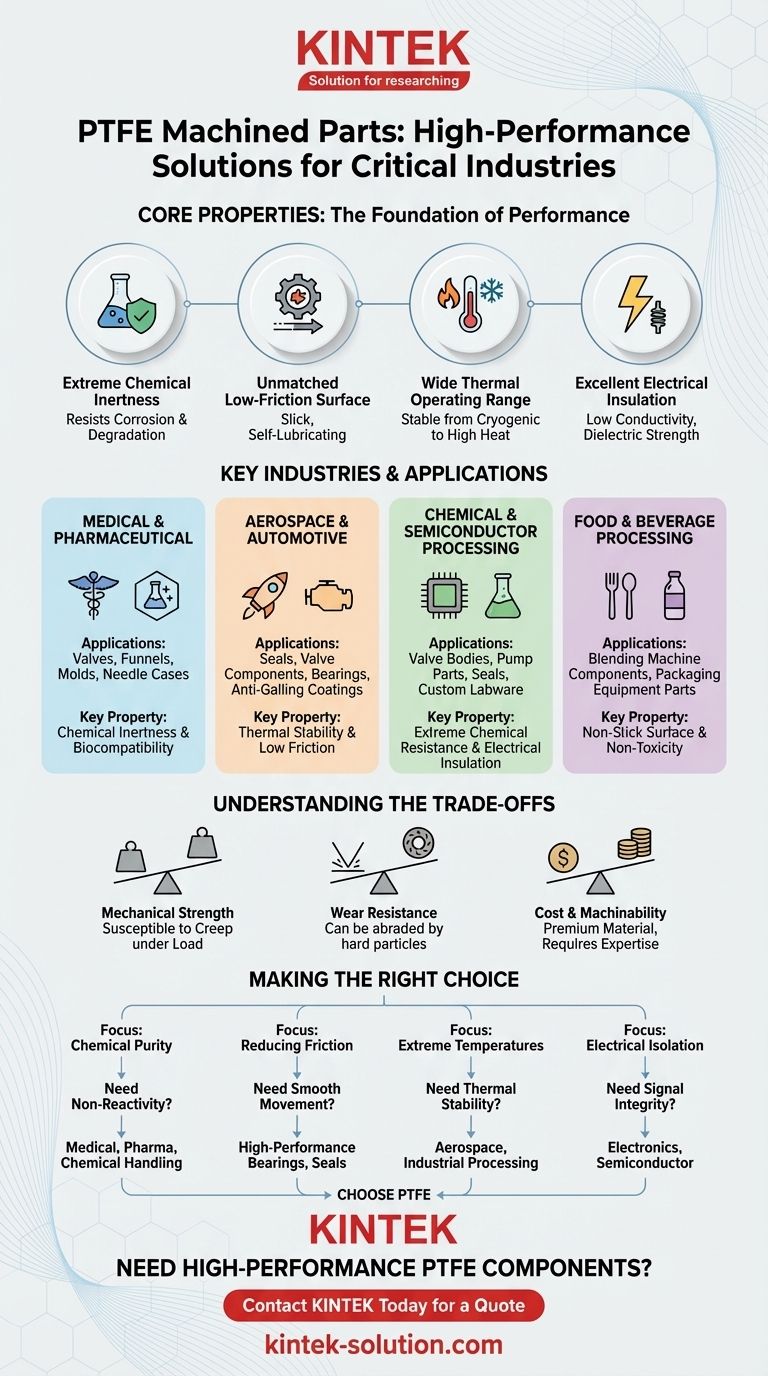
To put it simply, Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) machined parts are used across nearly every high-performance industry, including aerospace, medical, chemical processing, and food manufacturing. These sectors rely on PTFE for critical components like valves, seals, bearings, and insulators where extreme chemical resistance, low friction, and thermal stability are non-negotiable requirements.
The widespread adoption of PTFE is not due to a single feature, but its rare combination of three core properties: it is almost completely chemically inert, it has an incredibly low coefficient of friction, and it remains stable across a vast range of temperatures. This makes it an essential problem-solving material in demanding environments where other materials fail.

Why PTFE is the Material of Choice for Critical Applications
The value of machined PTFE parts comes from a unique set of intrinsic properties. Understanding these attributes is key to understanding its diverse applications.
Extreme Chemical Inertness
PTFE is one of the most non-reactive materials known. It resists corrosion and degradation from nearly all industrial chemicals, solvents, and acids.
This makes it indispensable for components that handle aggressive substances, ensuring the purity of the medium and the longevity of the part.
Unmatched Low-Friction Surface
Famously known by the brand name Teflon, PTFE has an extremely low coefficient of friction. Its surface is exceptionally slick and self-lubricating.
This property is ideal for applications requiring smooth movement with minimal resistance, such as in high-performance bearings, gears, and seals.
Wide Thermal Operating Range
PTFE performs reliably across a very broad temperature spectrum. It maintains its structural integrity and properties from cryogenic lows to high-temperature highs (up to its melting point).
This thermal stability is critical for parts used in aerospace, automotive engines, and industrial processing equipment.
Excellent Electrical Insulation
PTFE has very low electrical conductivity, making it an outstanding electrical insulator.
This dielectric strength is leveraged in the electronics and semiconductor industries for high-performance insulators, spacers, and connectors where signal integrity is paramount.
A Breakdown of Key Industrial Applications
The theoretical properties of PTFE translate directly into tangible solutions across several key sectors.
Medical and Pharmaceutical
In environments where biocompatibility and purity are critical, PTFE is a top choice. It is used for valves, funnels, molds, and needle cases.
Its non-reactive nature prevents contamination of sensitive biological or chemical compounds, a vital requirement in research and manufacturing.
Aerospace and Automotive
These industries demand materials that perform under extreme stress, temperature, and pressure. PTFE is used for seals, valve components, bearings, and anti-galling coatings.
Its self-lubricating properties reduce wear on moving parts, while its thermal stability ensures reliability in engines and flight systems.
Chemical and Semiconductor Processing
PTFE's resistance to aggressive chemicals makes it a default choice for this sector. It is machined into valve bodies, pump parts, seals, and custom labware.
In semiconductor manufacturing, its purity and electrical insulating properties are essential for tools and components that cannot risk process contamination or electrical interference.
Food and Beverage Processing
The non-stick and non-toxic properties of PTFE make it ideal for food-contact applications. It is commonly used for blending machine components and packaging equipment parts.
This ensures that equipment can be cleaned easily and does not contaminate the food products being processed.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While PTFE is a high-performance material, it's essential to understand its limitations to apply it correctly.
Mechanical Strength
Compared to metals or other engineering plastics, PTFE is a relatively soft material. It can be susceptible to "creep" or cold flow under sustained high loads.
Design considerations must account for its mechanical properties, especially in high-pressure sealing or load-bearing applications.
Wear Resistance
While its low friction reduces wear in many scenarios, PTFE can be abraded by hard, sharp particles. In such environments, filled grades of PTFE (mixed with glass, carbon, or other agents) are often used to enhance durability.
Cost and Machinability
As a premium performance material, PTFE is more costly than common plastics. Its unique properties can also present specific challenges that require expertise in machining to achieve tight tolerances and a fine finish.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting PTFE depends entirely on the problem you need to solve. Your primary engineering challenge should guide your material choice.
- If your primary focus is chemical purity and non-reactivity: PTFE is the gold standard for parts in medical, pharmaceutical, and aggressive chemical handling systems.
- If your primary focus is reducing friction and wear: Its self-lubricating surface makes it ideal for high-performance bearings, seals, and low-resistance sliding components.
- If your primary focus is performance in extreme temperatures: PTFE's stability from cryogenic conditions to high heat makes it a reliable choice for aerospace and industrial processing parts.
- If your primary focus is electrical isolation: Its dielectric strength is a key advantage for insulators and components in the electronics and semiconductor industries.
Ultimately, PTFE is chosen when the operational environment is too demanding for conventional materials to handle.
Summary Table:
| Industry | Key Applications | Primary PTFE Property Utilized |
|---|---|---|
| Medical & Pharmaceutical | Valves, funnels, molds, needle cases | Chemical inertness & biocompatibility |
| Aerospace & Automotive | Seals, valve components, bearings | Thermal stability & low friction |
| Chemical & Semiconductor | Valve bodies, pump parts, labware | Extreme chemical resistance & electrical insulation |
| Food & Beverage | Blending machine components, packaging parts | Non-stick surface & non-toxicity |
Need High-Performance PTFE Components?
When your application demands the unique combination of chemical inertness, low friction, and thermal stability that only PTFE can provide, you need a manufacturing partner with precision expertise.
KINTEK manufactures precision PTFE components—including seals, liners, valves, and custom labware—for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. We understand the critical tolerances and performance requirements of these demanding environments.
We offer custom fabrication from initial prototypes to high-volume production runs, ensuring you get the exact part you need, machined to the highest standards.
Contact KINTEB today to discuss your PTFE part requirements and get a quote.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Customizable PTFE Rods for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What makes PTFE butterfly valves special compared to other types? Unmatched Chemical & Thermal Performance
- What role do PTFE expansion bellows play in vibration isolation? Protect Piping Systems from Vibration Damage
- What are the benefits of PTFE's low friction coefficient in shaft seals? Boost Efficiency & Extend Equipment Life
- Why are PTFE seals preferred in press machinery in the pharmaceutical industry? Ensuring Purity and Performance
- What are the key properties of PTFE Teflon washers? Unlock Superior Chemical & Temperature Resistance
- What is the purpose of PTFE guide strips? Achieve Smooth, Reliable Motion in Your Systems
- How does the operating mechanism of PTFE lined butterfly valves work? A Guide to Corrosion-Resistant Flow Control
- Why is PTFE used for gaskets? Superior Sealing for Harsh Chemical & Temperature Environments



















