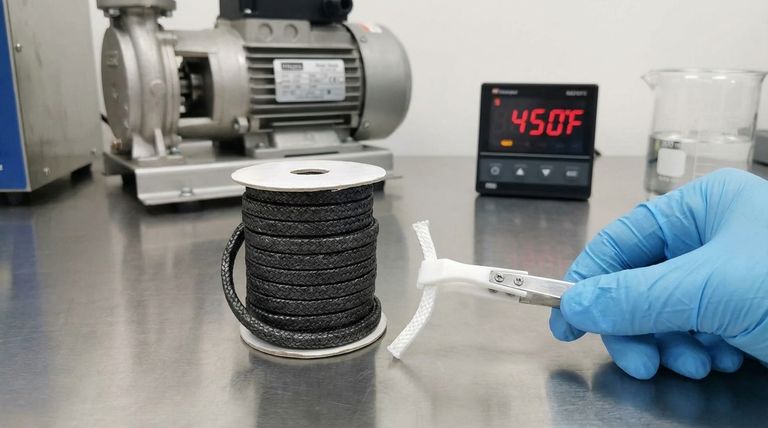
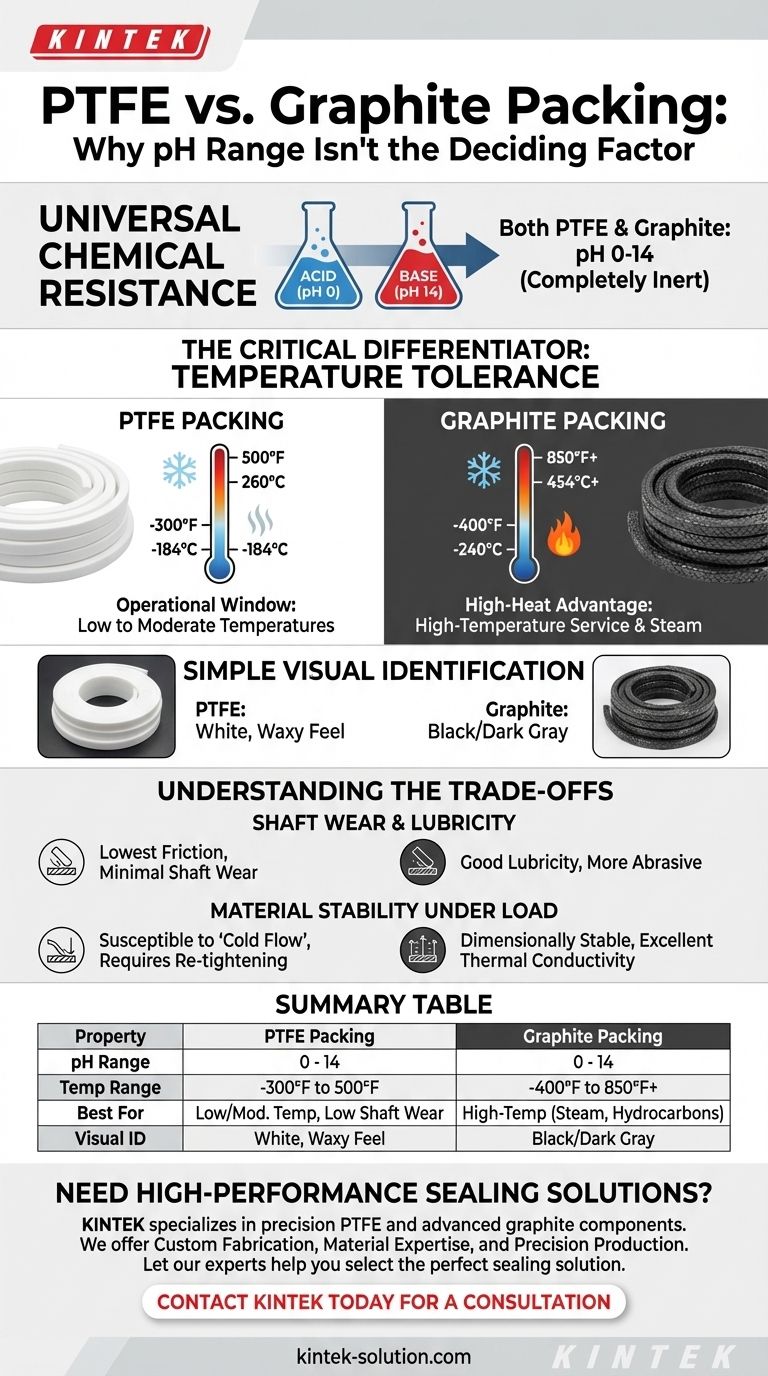
When selecting packing for extreme chemical environments, both PTFE and graphite packing offer the maximum possible chemical resistance. They each have an operational pH range of 0-14, making them completely inert to the most corrosive acids and caustic bases.
While their identical pH range makes them seem interchangeable from a chemical standpoint, the correct choice between PTFE and graphite packing is almost always determined by the application's operating temperature.

Why pH Range Isn't the Deciding Factor
The shared pH range of 0-14 for both materials is a testament to their exceptional chemical inertness. This shared strength means you must look at other properties to make an informed decision for your specific equipment, such as a pump or valve.
Universal Chemical Resistance
A pH range of 0-14 signifies that a material is unaffected by virtually all process fluids. Whether you are pumping sulfuric acid (pH 0) or sodium hydroxide (pH 14), neither PTFE nor graphite will degrade chemically.
Different Origins, Different Properties
The core difference between these materials lies in their composition. PTFE (polytetrafluoroethylene) is a synthetic fluoropolymer, known for its low-friction surface. Graphite, on the other hand, is a naturally occurring, inorganic form of pure carbon.
These distinct origins give rise to vastly different physical properties, particularly when it comes to thermal stability.
The Critical Differentiator: Temperature Tolerance
While chemically similar in resilience, their performance under heat is what truly separates PTFE and graphite packing.
PTFE's Operating Window
PTFE packing is highly effective in a temperature range from approximately -300°F to 500°F (-184°C to 260°C). This makes it a superb choice for cryogenic services and a vast number of general industrial applications operating at low to moderate temperatures.
Graphite's High-Heat Advantage
Graphite packing excels where PTFE cannot. It maintains its integrity in temperatures from -400°F up to 850°F (-240°C to 454°C) in oxidizing environments like air, and even higher in non-oxidizing conditions. This makes it the default standard for high-temperature steam, hydrocarbon, and other demanding process applications.
Simple Visual Identification
You can typically tell the materials apart at a glance. PTFE packing is characteristically white and has a waxy feel. Graphite packing is braided from black carbon yarn and is typically black or dark gray.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Beyond temperature, a few other performance characteristics are important to consider for ensuring long-term reliability and minimizing maintenance.
Shaft Wear and Lubricity
PTFE is one of the lowest-friction materials known, resulting in very little wear on rotating shafts. While modern graphite packing is often engineered to minimize friction, it can be inherently more abrasive than PTFE, a factor to consider for high-speed pumps.
Material Stability Under Load
Graphite is dimensionally stable and has excellent thermal conductivity, helping it dissipate heat away from the shaft. PTFE, being a polymer, can be susceptible to "cold flow" or creep over time, which may require periodic re-tightening of the gland follower.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct packing material prevents premature failure and ensures the safety and efficiency of your equipment. Base your decision on the primary operational demand.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature service (above 500°F): Graphite packing is the necessary choice due to its superior thermal stability.
- If your application involves moderate temperatures (below 500°F): PTFE packing is an excellent and often less abrasive option for the equipment shaft.
- If your only concern is chemical compatibility: Both materials are equally suitable from a pH perspective, so your final decision must be based on the thermal and pressure demands of the system.
Ultimately, understanding that temperature is the key differentiator empowers you to select the correct packing for long-term reliability.
Summary Table:
| Property | PTFE Packing | Graphite Packing |
|---|---|---|
| pH Range | 0 - 14 | 0 - 14 |
| Temperature Range | -300°F to 500°F (-184°C to 260°C) | -400°F to 850°F+ (-240°C to 454°C+) |
| Best For | Low to moderate temperatures, low shaft wear | High-temperature service (steam, hydrocarbons) |
| Visual ID | White, waxy feel | Black/Dark Gray |
Need High-Performance Sealing Solutions?
Choosing the right packing material is critical for the safety and efficiency of your equipment. KINTEK specializes in manufacturing precision PTFE and advanced graphite components for the most demanding applications in the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors.
We offer:
- Custom Fabrication: From prototypes to high-volume orders.
- Material Expertise: Ensuring optimal performance for your specific temperature and chemical environment.
- Precision Production: Guaranteeing reliability and long service life.
Let our experts help you select the perfect sealing solution. Contact KINTEK today for a consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Customizable PTFE Seals Filter Holders for Versatile Applications
People Also Ask
- What are the main features of PTFE bushings? Unlock Superior Performance in Harsh Environments
- What applications do PTFE gaskets have in the shipbuilding industry? Ensure Leak-Free Performance in Harsh Marine Environments
- What material properties make polymer-plastic ball bearings suitable for diverse industries? Solve Harsh Environment Challenges
- How do PTFE lip seals compare to traditional elastomer lip seals? A Guide to High-Performance Sealing
- Why is the PTFE ball valve considered a popular choice in various industries? Unmatched Reliability in Demanding Environments
- Which acids show high resistance with Teflon FEP and PFA encapsulated O-rings? Ensure Leak-Free Performance in Aggressive Chemical Environments
- What are PTFE balls made of and what are their key properties? Unlock Superior Chemical & Thermal Performance
- What should be considered when milling Teflon? Master Machining for Precision PTFE Parts



















