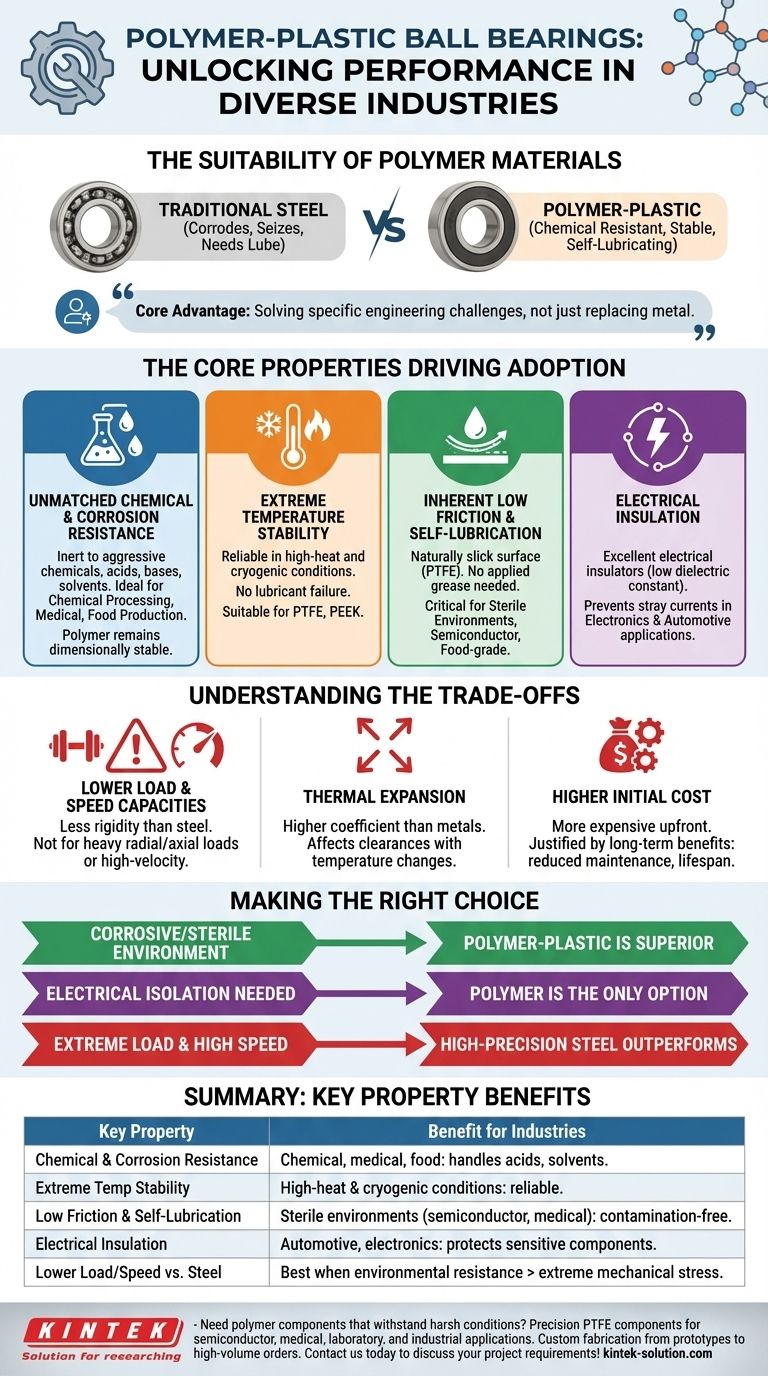
The suitability of polymer-plastic ball bearings stems directly from their material composition. Unlike steel, materials like PTFE (Polytetrafluoroethylene), PPS, and PEEK possess inherent properties such as exceptional chemical resistance, broad temperature stability, and low-friction surfaces. These characteristics allow them to function reliably in environments where traditional metal bearings would quickly corrode, seize, or fail.
The core advantage of polymer bearings isn't replacing metal in all scenarios, but rather solving specific engineering challenges. They excel in applications where corrosion, chemical exposure, electrical conductivity, or the need for lubrication-free operation makes steel an impractical choice.
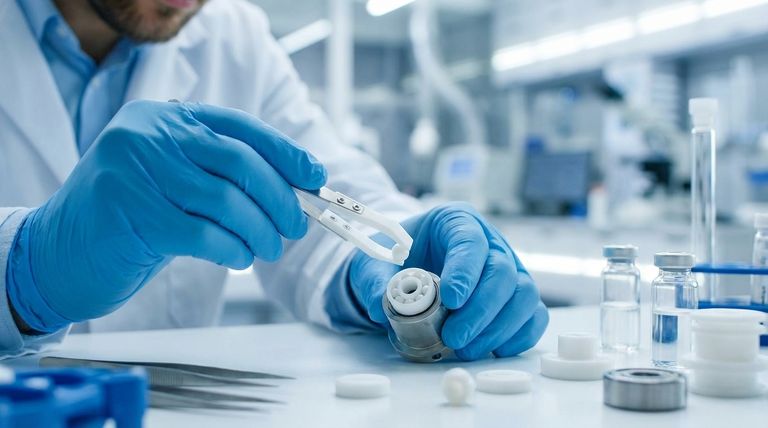

The Core Properties Driving Adoption
To understand their value, we must look beyond a simple comparison to steel and analyze the specific properties that make polymers a unique solution for certain industries.
Unmatched Chemical and Corrosion Resistance
Polymers are inherently inert to a wide range of aggressive chemicals, including acids, bases, and solvents. This makes them indispensable in industries like chemical processing, medical device manufacturing, and food production.
Where a steel bearing would rust or degrade upon contact with cleaning agents or process fluids, a polymer bearing remains dimensionally stable and operationally sound.
Extreme Temperature Stability
High-performance polymers like PTFE have outstanding thermal stability, functioning reliably in both high-heat and cryogenic conditions.
In these temperature extremes, traditional grease lubricants would either burn off or freeze, causing catastrophic failure in a metal bearing. Polymer bearings, however, often require no external lubrication.
Inherent Low Friction and Self-Lubrication
The molecular structure of materials like PTFE provides a naturally slick, non-stick surface. This results in a very low coefficient of friction without the need for applied grease or oil.
This self-lubricating property is critical for applications where contamination is a major concern, such as in medical equipment, semiconductor manufacturing, or food-grade machinery.
Electrical Insulation
Unlike conductive metal bearings, polymers are excellent electrical insulators, a property measured by their low dielectric constant.
This feature is essential in electronics and automotive applications where bearings must prevent the flow of stray electrical currents, which could otherwise damage sensitive components or cause system failures.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While their properties offer significant advantages, it is crucial to recognize the limitations of polymer bearings. They are not a universal replacement for their metal counterparts.
Lower Load and Speed Capacities
As a general rule, polymers do not possess the same rigidity and hardness as steel. This means they cannot withstand the same heavy radial and axial loads as comparably sized steel bearings.
Similarly, their maximum rotational speeds are typically lower. High-stress, high-velocity applications remain the domain of precision-engineered steel.
Thermal Expansion
Polymers have a higher coefficient of thermal expansion than metals. Engineers must account for this, as significant temperature fluctuations can cause the bearing to expand or contract more than its housing, affecting critical clearances and performance.
Higher Initial Cost
Specialized, high-performance polymers can be more expensive upfront than standard chrome or stainless steel bearings. The decision to use them must be justified by the long-term benefits of reduced maintenance, increased component lifespan in harsh environments, and prevention of costly system failures.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
The selection process is not about which material is "better," but which is right for the specific operational demands of your project.
- If your primary focus is operating in a corrosive or sterile environment: Polymer bearings are the superior choice due to their chemical inertness and lack of need for contaminating lubricants.
- If your primary focus is electrical isolation: The inherent non-conductive properties of plastic make it the only viable option for preventing electrical arcing or interference between components.
- If your primary focus is extreme load and high-speed rotation: A traditional, high-precision steel bearing will almost always outperform a polymer-plastic alternative in these mechanically demanding roles.
Ultimately, selecting a polymer bearing is a strategic decision to solve environmental and operational challenges that are beyond the capabilities of conventional metal components.
Summary Table:
| Key Property | Benefit for Industries |
|---|---|
| Chemical & Corrosion Resistance | Ideal for chemical processing, medical, and food production where exposure to acids, bases, and solvents is common. |
| Extreme Temperature Stability | Functions reliably in high-heat and cryogenic conditions without lubrication failure. |
| Low Friction & Self-Lubrication | Prevents contamination in sterile environments like semiconductor manufacturing and medical devices. |
| Electrical Insulation | Protects sensitive electronics in automotive and industrial applications by preventing stray currents. |
| Lower Load/Speed vs. Steel | Best for applications where environmental resistance outweighs the need for extreme mechanical stress. |
Need polymer components that withstand harsh conditions? KINTEK specializes in precision PTFE components (seals, liners, labware, and more) for semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial applications. Our custom fabrication—from prototypes to high-volume orders—ensures your equipment operates reliably in corrosive, high-purity, or electrically sensitive environments. Contact us today to discuss your project requirements!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
People Also Ask
- What tips can improve Teflon machining results? Master Sharp Tools, Heat Control, and Rigid Support
- What are the future considerations for machining Teflon? Mastering Material Challenges with Smart Tech
- What are the key considerations when machining Teflon? Master Precision Machining for Soft Polymers
- What are the key advantages of PTFE? Unmatched Performance for Extreme Environments
- Why is PTFE rod suitable for automotive applications? Boost Vehicle Performance & Durability



















