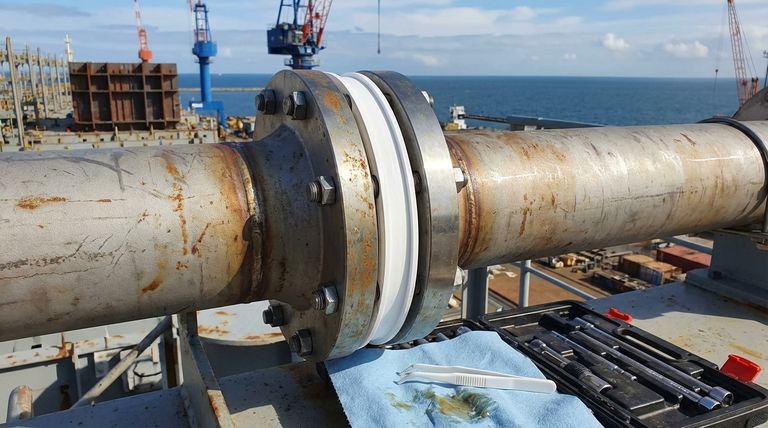
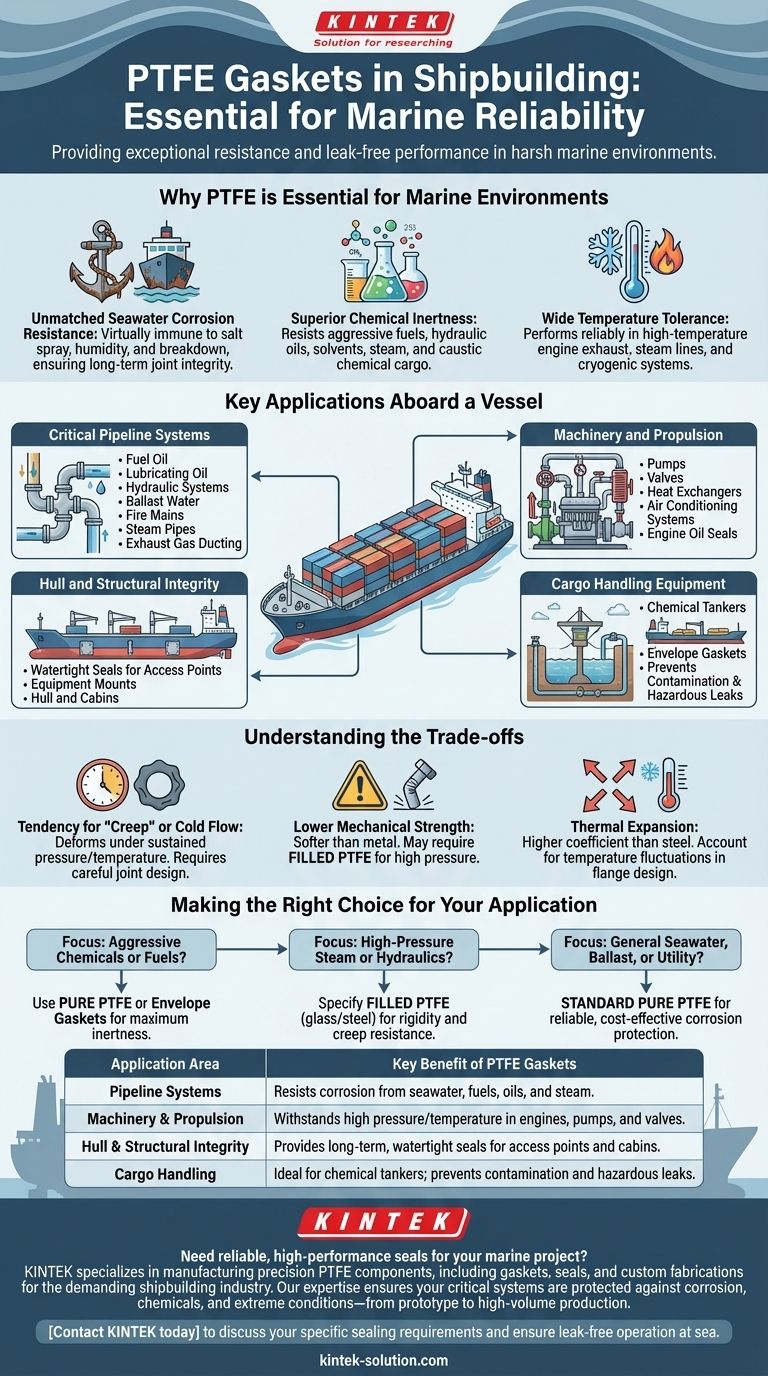
In the shipbuilding industry, PTFE gaskets are primarily used for sealing critical systems like hulls, cabins, and pipelines. Their value stems from an exceptional ability to withstand the harsh marine environment, offering superior resistance to seawater corrosion, aggressive chemicals, and extreme temperatures to ensure long-term, leak-free performance.
The core reason PTFE is so prevalent in shipbuilding is its chemical inertness. It provides a reliable seal in systems exposed to everything from corrosive saltwater and abrasive ballast to aggressive fuels, oils, and chemical cargo, where lesser materials would quickly degrade and fail.

Why PTFE is Essential for Marine Environments
To understand the specific applications of PTFE gaskets on a vessel, we must first appreciate the material's fundamental properties. A ship is a self-contained system operating in one of the most corrosive environments on earth, and its components must be exceptionally resilient.
Unmatched Seawater Corrosion Resistance
PTFE is virtually immune to saltwater corrosion. Unlike metal or many elastomeric gaskets, it will not degrade, rust, or break down when constantly exposed to seawater, salt spray, and high humidity, ensuring the long-term integrity of sealed joints.
Superior Chemical Inertness
A modern vessel handles a wide array of aggressive media. PTFE's ability to resist chemical attack makes it the ideal choice for sealing pipes and equipment containing fuels, hydraulic oils, solvents, steam, and even the most caustic chemical cargo.
Wide Temperature Tolerance
Shipboard systems operate at a huge range of temperatures. PTFE gaskets perform reliably in high-temperature applications like engine exhaust and steam lines, as well as in cryogenic systems for liquefied gas carriers or refrigeration circuits.
Key Applications Aboard a Vessel
Based on its core properties, PTFE is deployed in numerous critical locations throughout a ship.
Critical Pipeline Systems
This is the most common application. PTFE gaskets are used to seal flanged connections in pipes for fuel oil, lubricating oil, hydraulic systems, ballast water, and fire mains. They are also used in steam pipes and exhaust gas ducting from the engine room.
Machinery and Propulsion
Within the engine room and machinery spaces, PTFE gaskets and seals are indispensable. They are used in pumps, valves, heat exchangers, air conditioning systems, and as engine oil seals to prevent leaks in high-pressure, high-temperature conditions.
Hull and Structural Integrity
PTFE gaskets contribute to the vessel's watertight integrity. They are used in sealing various access points, equipment mounts on the deck, and connections in the hull and cabins to prevent water ingress.
Cargo Handling Equipment
For chemical tankers and vessels carrying specialized cargo, PTFE is critical. Envelope gaskets, which have a PTFE outer layer protecting a different core material, are often used to seal cargo lines, ensuring no contamination or leaks of hazardous substances.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While highly effective, no material is perfect. A clear understanding of PTFE's limitations is crucial for proper application.
Tendency for "Creep" or Cold Flow
PTFE has a tendency to deform or "creep" over time under sustained pressure, especially at elevated temperatures. This requires careful consideration in joint design and bolt torque specifications to maintain a long-term seal.
Lower Mechanical Strength
Compared to metallic gaskets, PTFE is much softer. In extremely high-pressure systems, a standard PTFE gasket may be extruded from the flange. In these cases, filled PTFE (compounded with materials like glass fiber or steel) is used to improve rigidity and creep resistance.
Thermal Expansion
PTFE has a higher coefficient of thermal expansion than steel. In systems with wide temperature fluctuations, this difference must be accounted for in the flange and bolt design to prevent the joint from loosening as temperatures change.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct gasket is about matching the material to the specific demands of the system.
- If your primary focus is sealing aggressive chemical cargo or fuel systems: Use pure PTFE or PTFE envelope gaskets for maximum chemical inertness.
- If your primary focus is high-pressure steam or hydraulic lines: Specify a filled PTFE gasket (e.g., glass or stainless steel filled) to mitigate cold flow and ensure seal integrity.
- If your primary focus is general seawater, ballast, or utility systems: Standard, pure PTFE gaskets provide a reliable and cost-effective solution against corrosion.
PTFE's unique combination of resistances makes it a cornerstone material for ensuring the safety, reliability, and operational readiness of modern marine vessels.
Summary Table:
| Application Area | Key Benefit of PTFE Gaskets |
|---|---|
| Pipeline Systems | Resists corrosion from seawater, fuels, oils, and steam. |
| Machinery & Propulsion | Withstands high pressure/temperature in engines, pumps, and valves. |
| Hull & Structural Integrity | Provides long-term, watertight seals for access points and cabins. |
| Cargo Handling | Ideal for chemical tankers; prevents contamination and hazardous leaks. |
Need reliable, high-performance seals for your marine project?
KINTEK specializes in manufacturing precision PTFE components, including gaskets, seals, and custom fabrications for the demanding shipbuilding industry. Our expertise ensures your critical systems are protected against corrosion, chemicals, and extreme conditions—from prototype to high-volume production.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss your specific sealing requirements and ensure leak-free operation at sea.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Customizable PTFE Seals Filter Holders for Versatile Applications
People Also Ask
- What are the best practices for achieving tight tolerances in Teflon (PTFE) machining? Master Precision for Demanding Applications
- What industries use PTFE machined parts and for what applications? Critical Components for Demanding Environments
- How does PTFE contribute to low friction and wear resistance? Achieve Superior Performance with Advanced Materials
- What are the key advantages of PTFE? Unmatched Performance for Extreme Environments
- What are the main advantages of using PTFE parts in industrial applications? Unlock Unmatched Chemical Resistance and Reliability



















