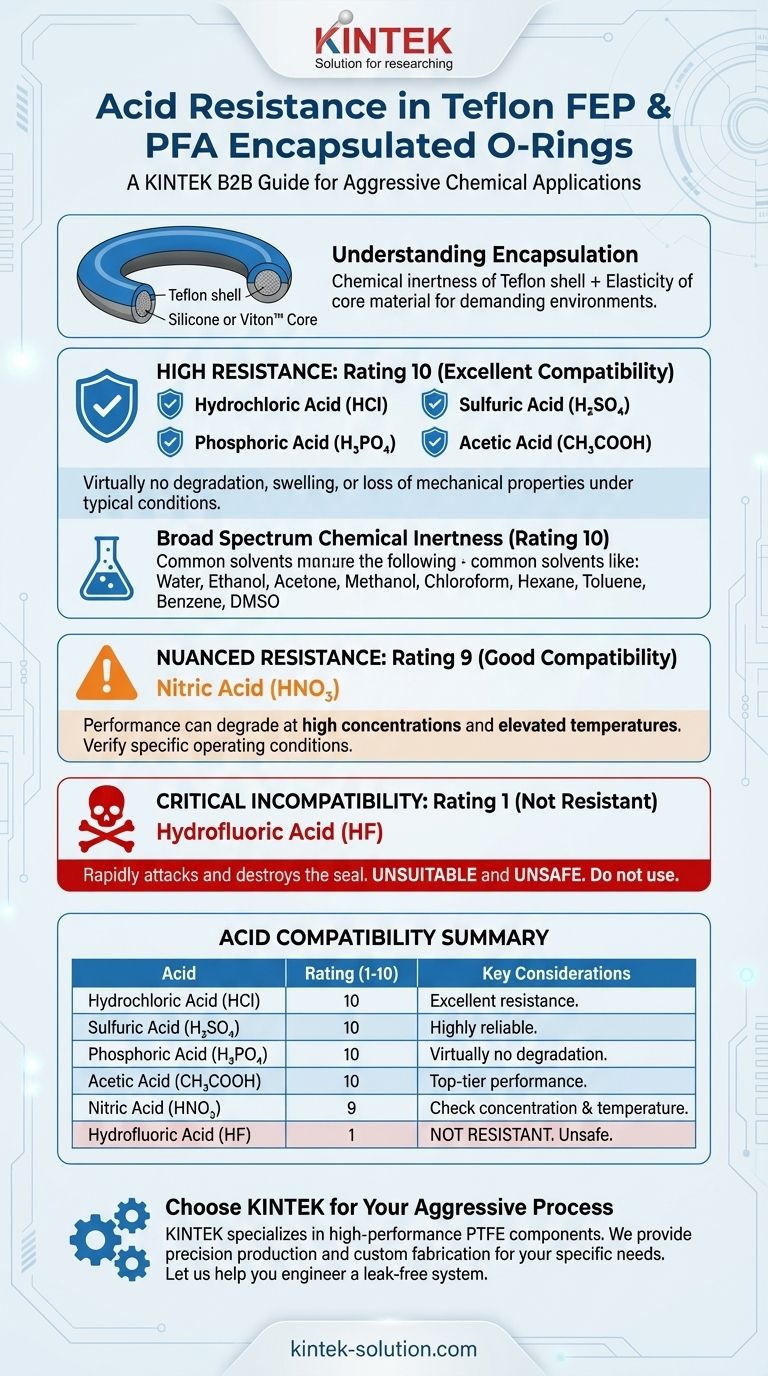
For applications demanding exceptional chemical resilience, Teflon FEP and PFA encapsulated O-rings provide high resistance to several common and aggressive acids. These materials achieve the highest compatibility rating (10) with hydrochloric acid, sulfuric acid, phosphoric acid, and acetic acid.
While Teflon FEP and PFA encapsulation creates a nearly inert seal against most common acids, successful application hinges on understanding its specific limitations. Performance can be compromised by certain chemicals like hydrofluoric acid and by extreme operating conditions with others, such as nitric acid.

Understanding High-Resistance Acids
Teflon encapsulated O-rings combine the chemical inertness of a Teflon shell with the elasticity of a core material like silicone or Viton™. This design makes them uniquely suited for aggressive chemical environments where standard elastomers would fail.
The Core Group of Compatible Acids
Hydrochloric acid, sulfuric acid, phosphoric acid, and acetic acid all receive the highest possible resistance rating of 10 when used with Teflon FEP and PFA encapsulated O-rings.
This top-tier rating indicates that these acids cause virtually no degradation, swelling, or loss of mechanical properties in the sealing material under typical operating conditions.
The Nuance of Nitric Acid
Nitric acid shows good resistance and is generally considered compatible, with a high rating of 9.
However, this is not an unconditional approval. Its performance can be negatively affected by high concentrations and elevated temperatures, which may lead to premature degradation of the seal.
Broad Spectrum Chemical Inertness
The resilience of these O-rings extends beyond acids. They also exhibit the highest resistance rating (10) to a wide array of common solvents.
This list includes water, ethanol, acetone, methanol, chloroform, hexane, toluene, benzene, and dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO), highlighting the material's broad utility in diverse chemical processes.
Critical Pitfalls and Chemical Incompatibilities
No material is universally impervious. Understanding the specific, known weaknesses of Teflon encapsulation is critical for preventing catastrophic seal failure, equipment damage, and safety hazards.
The Critical Exception: Hydrofluoric Acid (HF)
Teflon FEP and PFA encapsulated O-rings are not resistant to hydrofluoric acid.
HF receives the lowest possible resistance rating of 1. This incompatibility is especially pronounced with concentrated solutions, which will rapidly attack and destroy the seal.
The Impact of Temperature and Concentration
The case of nitric acid provides a crucial lesson: chemical compatibility is not always a simple yes-or-no answer.
Even for chemicals rated as "good" or "high" in resistance, extreme operating conditions can push a material past its limits. Always factor in the specific concentration and temperature of your process when evaluating material suitability.
Making the Right Choice for Your Acid Application
Use these guidelines to ensure you select a safe and reliable seal for your specific needs.
- If your primary focus is hydrochloric, sulfuric, phosphoric, or acetic acid: These O-rings offer a highly reliable and safe sealing solution across a wide range of conditions.
- If you are working with nitric acid: You must verify your operating temperature and concentration, as seal performance can degrade under extreme conditions.
- If your process involves hydrofluoric acid (HF) at any concentration: You must select a different sealing material, as Teflon encapsulation is an unsuitable and unsafe choice.
By understanding these specific chemical compatibilities and limitations, you can confidently engineer a durable and leak-free system.
Summary Table:
| Acid | Compatibility Rating (1-10) | Key Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| Hydrochloric Acid (HCl) | 10 | Excellent resistance across a wide range of conditions. |
| Sulfuric Acid (H₂SO₄) | 10 | Highly reliable and safe sealing solution. |
| Phosphoric Acid (H₃PO₄) | 10 | Virtually no degradation under typical use. |
| Acetic Acid (CH₃COOH) | 10 | Top-tier performance with no swelling or loss of properties. |
| Nitric Acid (HNO₃) | 9 | Good resistance, but performance can degrade with high concentration and elevated temperature. |
| Hydrofluoric Acid (HF) | 1 | Not resistant. Unsuitable and unsafe choice; will rapidly destroy the seal. |
Need a Reliable Seal for Your Aggressive Chemical Process?
KINTEK specializes in manufacturing high-performance PTFE components, including custom Teflon FEP and PFA encapsulated O-rings. We understand the critical need for chemical inertness and durability in demanding applications.
We provide:
- Precision Production: Ensuring consistent quality and reliable performance for your semiconductor, medical, laboratory, or industrial equipment.
- Custom Fabrication: From prototype development to high-volume orders, we tailor solutions to meet your exact specifications and operating conditions.
Let us help you engineer a leak-free system. Contact KINTEK today to discuss your specific requirements and get a quote for your project.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
People Also Ask
- What is PTFE and what class of plastics does it belong to? A Guide to High-Performance Fluoropolymers
- What is Teflon and what are its alternative names? Understanding PTFE, the Material Behind the Brand
- What environmental resistances does PTFE offer? Unmatched Durability for Harsh Conditions
- How does PTFE react to common solvents? Discover Its Near-Total Chemical Immunity
- What are the additional properties of PTFE? Beyond Non-Stick: Extreme Chemical, Thermal & Electrical Performance



















