Beyond its famous non-stick surface, Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) possesses an exceptional and multifaceted profile. It is defined by its extreme chemical inertness, a vast operational temperature range, and superior performance as an electrical insulator. These core characteristics make it a critical material in demanding industrial, medical, and electronic applications.
PTFE's value comes from a unique combination of extreme properties—it is simultaneously one of the most chemically resistant, temperature-stable, and slippery materials known. However, these same strengths create significant limitations in mechanical strength and manufacturability that must be carefully considered.

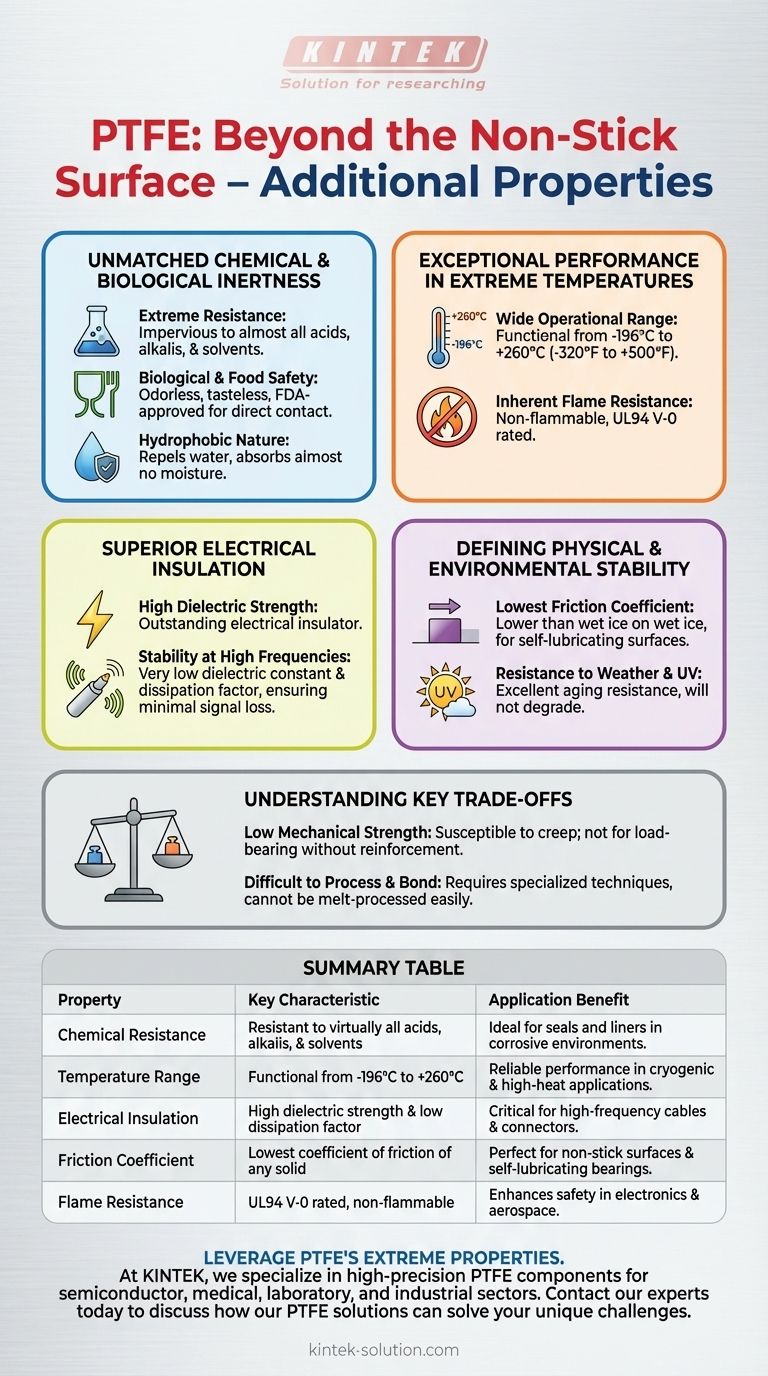
Unmatched Chemical and Biological Inertness
PTFE's performance in harsh chemical environments is legendary. Its molecular structure makes it almost universally resistant to chemical attack.
Extreme Chemical Resistance
PTFE is virtually impervious to almost all industrial chemicals, including aggressive acids, alkalis, and organic solvents. This makes it an ideal choice for seals, gaskets, and linings in corrosive environments.
Biological and Food Safety
The material is odorless, tasteless, and physiologically harmless up to high temperatures. It does not support the growth of fungi or microorganisms and is frequently FDA-approved for direct food contact.
Hydrophobic Nature
PTFE is profoundly hydrophobic, meaning it repels water and absorbs almost no moisture. This property contributes to its excellent performance as an insulator and ensures dimensional stability in humid environments.
Exceptional Performance in Extreme Temperatures
Few polymers can function across the wide temperature spectrum that PTFE can withstand, all while maintaining their core properties.
Wide Operational Temperature Range
PTFE remains functional and flexible across an incredibly broad temperature range, typically cited from -196°C to +260°C (-320°F to +500°F). It offers reliable performance in both cryogenic and high-heat applications.
Inherent Flame Resistance
PTFE is non-flammable and will not promote the spread of flames, earning it a UL94 V-0 flame rating. This is a critical safety feature for applications in electronics, aerospace, and construction.
Superior Electrical Insulation
PTFE's electrical properties are just as impressive as its chemical and thermal resistance, making it a first-choice material for high-performance electronics.
High Dielectric Strength
It is an outstanding electrical insulator with high dielectric strength and electrical resistance. This prevents the flow of electrical current, making it ideal for wire and cable insulation.
Stability at High Frequencies
PTFE has a very low dielectric constant and dissipation factor, even at high frequencies. This ensures minimal signal loss, a critical requirement for high-frequency coaxial cables, connectors, and printed circuit boards.
Defining Physical and Environmental Stability
The physical characteristics of PTFE are unique among solid materials, contributing to its specialized uses.
The Lowest Friction Coefficient
PTFE boasts the lowest coefficient of friction of any known solid material, even lower than wet ice on wet ice. This makes it the ultimate material for non-stick surfaces and self-lubricating bearings.
Resistance to Weather and UV
The material exhibits excellent resistance to weathering, UV radiation, and general aging. Parts made from PTFE will not degrade or become brittle even after years of exposure to the elements.
Understanding the Key Trade-offs
PTFE's unique advantages are directly linked to its limitations. An expert understands that no material is perfect, and PTFE's weaknesses are as defining as its strengths.
Low Mechanical Strength
Unfilled, or "virgin," PTFE is a relatively soft material. It is susceptible to creep, or deformation over time when under a constant load. It is not suitable for structural, load-bearing applications without reinforcement (e.g., glass or carbon fillers).
Difficult to Process and Bond
The very properties that make PTFE so useful—its chemical inertness and low-friction surface—also make it extremely difficult to work with. It cannot be processed using conventional melt-processing techniques and is notoriously difficult to bond to other materials without specialized surface treatments like chemical etching.
When to Choose PTFE for Your Application
Selecting the right material requires balancing technical requirements with practical limitations. Use these guidelines to determine if PTFE is the optimal choice.
- If your primary focus is chemical resistance and purity: PTFE is nearly unbeatable for seals, linings, and fluid-handling components in corrosive or high-purity systems.
- If your primary focus is low-friction and self-lubrication: It is the premier choice for bearings, slide plates, and non-stick coatings where smooth, effortless motion is critical.
- If your primary focus is high-frequency electrical insulation: Its exceptional dielectric properties make it ideal for demanding applications in telecommunications and electronics.
- If your primary focus is structural strength: You must consider filled grades of PTFE or alternative high-performance polymers, as pure PTFE will likely fail in load-bearing roles.
Understanding this balance between extreme performance and practical limitation is the key to successfully leveraging PTFE's remarkable capabilities.
Summary Table:
| Property | Key Characteristic | Application Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Resistance | Resistant to virtually all acids, alkalis, and solvents | Ideal for seals and liners in corrosive environments |
| Temperature Range | Functional from -196°C to +260°C | Reliable performance in cryogenic and high-heat applications |
| Electrical Insulation | High dielectric strength and low dissipation factor | Critical for high-frequency cables and connectors |
| Friction Coefficient | Lowest coefficient of friction of any solid | Perfect for non-stick surfaces and self-lubricating bearings |
| Flame Resistance | UL94 V-0 rated, non-flammable | Enhances safety in electronics and aerospace |
Leverage PTFE's extreme properties for your most demanding applications.
At KINTEK, we specialize in manufacturing high-precision PTFE components—including seals, liners, and custom labware—for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Whether you need prototypes or high-volume production, our expertise in custom fabrication ensures you get the exact performance your application requires.
Contact our experts today to discuss how our PTFE solutions can solve your unique challenges.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
- Custom PTFE Bottles for Diverse Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
People Also Ask
- How does PTFE react to common solvents? Discover Its Near-Total Chemical Immunity
- How was PTFE discovered and developed? From Lab Accident to Essential High-Performance Polymer
- What is Teflon and what is its chemical name? Unpacking the Science of PTFE
- What is PTFE commonly known as and what type of material is it? A Guide to High-Performance PTFE Properties
- What is Teflon and what are its alternative names? Understanding PTFE, the Material Behind the Brand



















