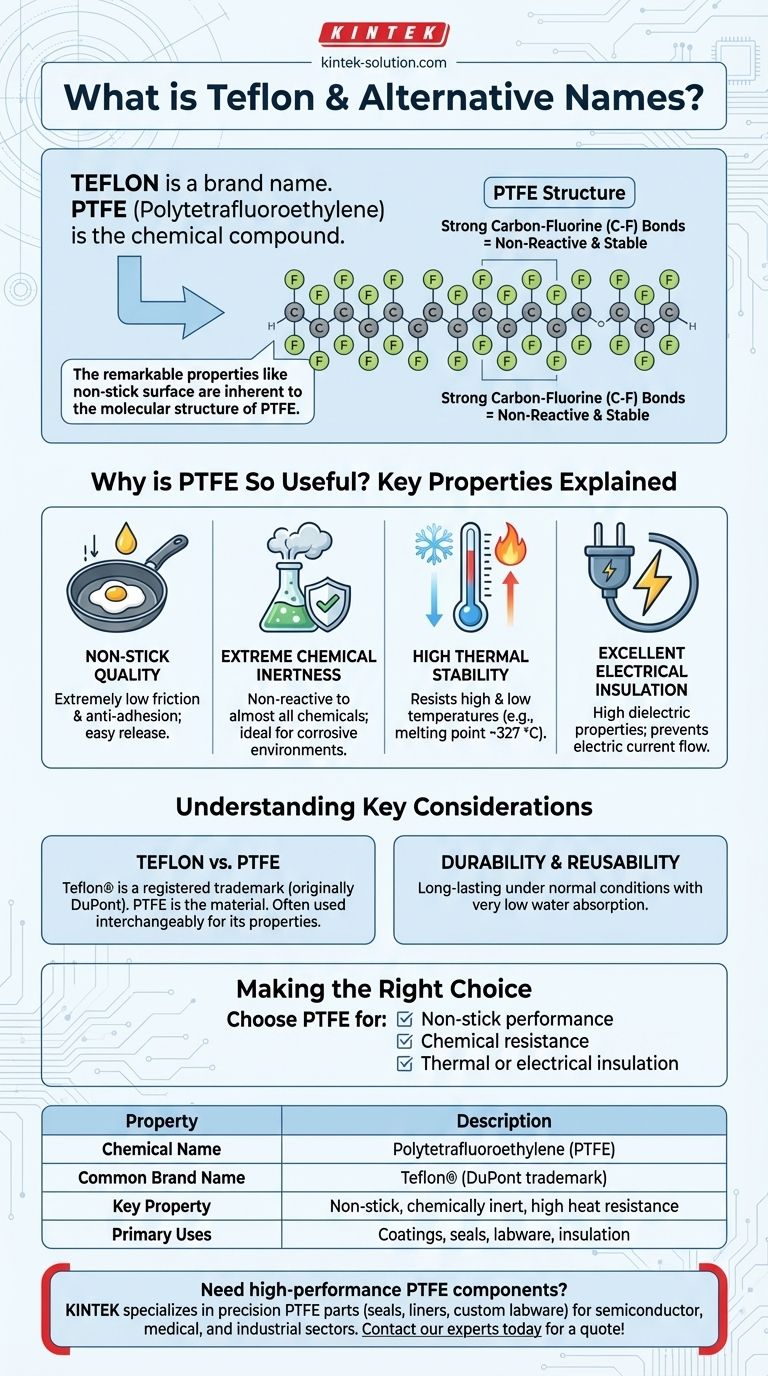
In short, Teflon is the well-known brand name for a synthetic fluoropolymer whose chemical name is Polytetrafluoroethylene, most commonly abbreviated as PTFE. It is a semi-crystalline thermoplastic created by polymerizing tetrafluoroethylene. While "Teflon" is the household name, the material itself is PTFE.
The key takeaway is that "Teflon" is a registered trademark, while Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is the actual chemical compound. Understanding this distinction is crucial because the remarkable properties people associate with Teflon—like its non-stick surface—are inherent to the molecular structure of PTFE.

What is Teflon at a Chemical Level?
Teflon, or PTFE, is a synthetic polymer valued for its unique and robust characteristics. Its properties are a direct result of its simple but powerful molecular composition.
The Building Blocks: Carbon and Fluorine
At its core, PTFE is composed primarily of a long chain of carbon atoms, with each carbon atom bonded to two fluorine atoms. This material is produced through a process called polymerization, which links together many individual tetrafluoroethylene molecules.
The Resulting Structure
The bond between carbon and fluorine is exceptionally strong and stable. This creates a molecular structure that is dense, non-reactive, and resistant to being broken down by other chemicals.
Key Physical Characteristics
At room temperature, PTFE is a white solid compound with a density of approximately 2.2 g/cm³. It has a high melting point of around 600 K (327 °C or 620 °F), contributing to its excellent heat resistance.
Why is PTFE So Useful? Key Properties Explained
The molecular structure of PTFE gives rise to a combination of properties that make it incredibly versatile and useful in a wide range of applications, from cookware to industrial components.
The Signature Non-Stick Quality
PTFE has an extremely low coefficient of friction and powerful anti-adhesion properties. This means other substances find it very difficult to stick to its surface, making it the ideal material for non-stick coatings.
Extreme Chemical Inertness
The strong carbon-fluorine bonds make PTFE non-reactive to almost all chemicals. It is only known to be affected by certain alkali metals, making it highly valuable for use in corrosive environments.
High Thermal Stability
This material demonstrates excellent resistance to both high and low temperatures. It maintains its structural integrity and properties across a wide thermal range without degrading.
Excellent Electrical Insulation
PTFE possesses very good dielectric properties and high bulk resistivity. This makes it an exceptional electrical insulator, preventing the flow of electric current.
Understanding the Key Considerations
While the terms are often used interchangeably, understanding the distinction and the material's nature is important for practical application.
Teflon is a Brand, PTFE is the Material
The name Teflon is a registered trademark, originally created by the company DuPont. While it is the most famous brand of PTFE, other companies also manufacture PTFE. Functionally, people use the names interchangeably to refer to the material's properties.
Durability and Reusability
PTFE is a durable and reusable material that can last for many years under normal conditions. It also has a very low water absorption capacity, which adds to its longevity and stability.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Understanding the core properties of PTFE allows you to identify when it is the right material for a specific need.
- If your primary focus is non-stick performance: You are looking for PTFE, a material prized for its exceptionally low friction and anti-adhesion surface.
- If your primary focus is chemical resistance: You need a fluoropolymer like PTFE, which is non-reactive to nearly all substances due to its strong molecular bonds.
- If your primary focus is thermal or electrical insulation: PTFE's ability to withstand extreme temperatures and resist electrical current makes it an excellent choice.
Ultimately, recognizing Teflon as the brand name for PTFE empowers you to understand the fundamental science behind one of the world's most versatile synthetic materials.
Summary Table:
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Chemical Name | Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) |
| Common Brand Name | Teflon® (DuPont trademark) |
| Key Property | Non-stick, chemically inert, high heat resistance |
| Primary Uses | Non-stick coatings, seals, labware, electrical insulation |
Need high-performance PTFE components for your application?
At KINTEK, we specialize in the precision manufacturing of PTFE parts—including seals, liners, and custom labware. Whether you're in the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, or industrial sector, our expertise in custom fabrication from prototypes to high-volume orders ensures you get components that deliver superior chemical resistance, non-stick performance, and thermal stability.
Contact our experts today to discuss your specific requirements and get a quote!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
People Also Ask
- How does PTFE's coefficient of friction compare to other plastics? Unmatched Low-Friction Performance
- Can PTFE be recycled and what are the challenges? Navigating the Complexities of PTFE Sustainability
- What forms is PTFE available in besides sheets and rods? Discover the Full Range of PTFE Options
- Why is virgin PTFE preferred for certain applications? Ensuring Absolute Purity for Sensitive Industries
- How does the friction of Teflon compare to other materials? Discover the Benchmark for Low Friction
- What are the different grades of PTFE and their uses? A Guide to Selecting the Right Material
- Why can't PTFE be processed using conventional polymer techniques? Discover the Sintering Solution
- What makes PTFE versatile for various industrial uses? Discover the Key Properties Driving Its Success



















