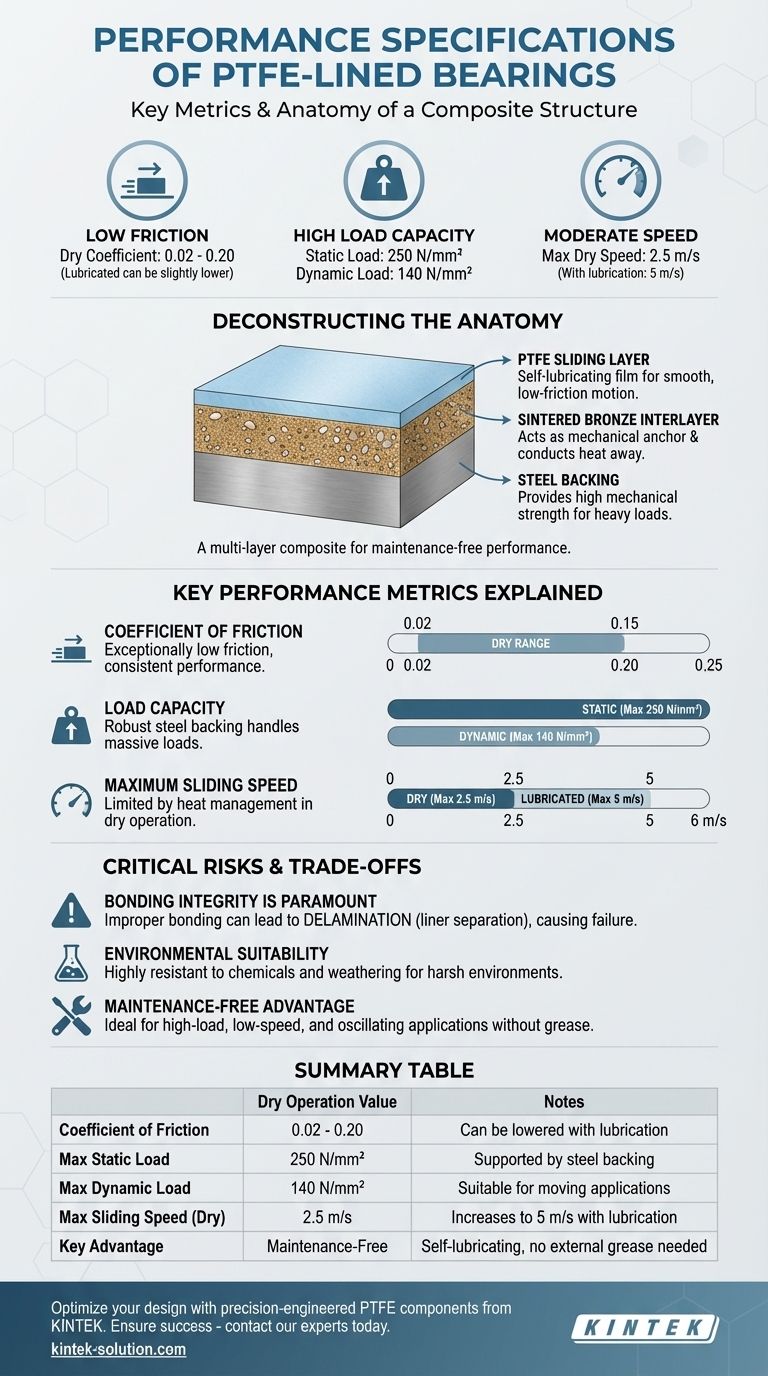
The performance specifications of PTFE-lined bearings are defined by their impressively low friction, high load capacity, and moderate speed capabilities. These self-lubricating bearings typically have a dry coefficient of friction between 0.02 and 0.20, a maximum dry sliding speed of 2.5 m/s, and can handle immense static loads up to 250 N/mm² and dynamic loads of 140 N/mm².
The key to understanding these specifications is recognizing that a PTFE-lined bearing is not a single material, but a composite structure. This design achieves maintenance-free, low-friction performance by combining the slipperiness of a polymer liner with the high strength of a metal backing.
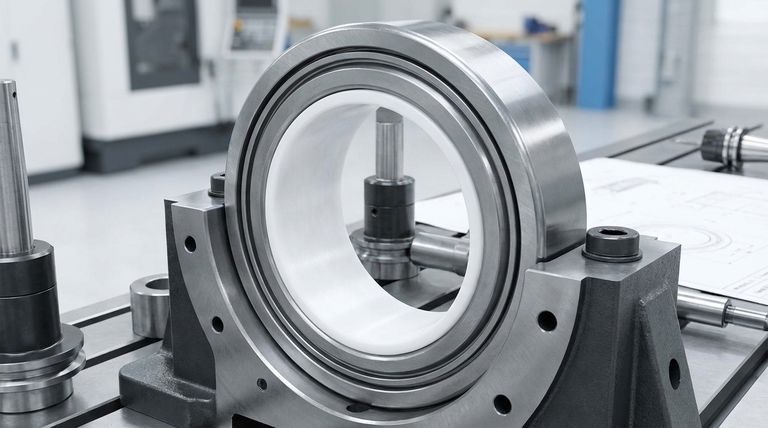

Deconstructing the Bearing's Anatomy
The performance numbers are a direct result of the bearing's multi-layer construction. Each layer serves a distinct and critical purpose.
The Steel Backing
The foundation of the bearing is a steel backing. This layer provides the mechanical strength and rigidity necessary to support extremely high static and dynamic loads.
The Sintered Bronze Interlayer
Bonded to the steel is a thin, porous layer of sintered bronze powder. This layer performs two vital functions: it acts as a mechanical anchor for the PTFE liner and efficiently conducts heat away from the sliding surface to prevent overheating.
The PTFE Sliding Layer
The final layer is a PTFE (polytetrafluoroethylene) polymer mixture that is impregnated into the bronze interlayer. During initial operation, a thin film of this material transfers to the mating surface, creating a highly effective, solid-lubricant film that enables smooth, low-friction motion.
Key Performance Metrics Explained
Understanding the headline specifications requires looking at the context in which they are measured.
Coefficient of Friction
The coefficient of friction is exceptionally low, ranging from 0.02 to 0.20 in dry conditions. The addition of a lubricant like oil can slightly lower the maximum value to 0.15, ensuring consistent performance.
Load Capacity
The robust steel backing allows for a massive static load capacity of 250 N/mm². For moving applications, the dynamic load capacity is 140 N/mm², a figure that still positions these bearings for heavy-duty use.
Maximum Sliding Speed
The speed limit is primarily a function of heat management. In dry operation, the maximum recommended speed is 2.5 m/s. With external lubrication to help dissipate heat, this can be increased to 5 m/s.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Critical Risks
While powerful, PTFE-lined bearings are not without limitations. Their composite nature introduces a critical point of failure that must be understood.
The Critical Nature of the Bonding Process
The single most important factor in a bearing's reliability is the bond between the PTFE liner and the bronze interlayer. Improper bonding can lead to liner separation, also known as delamination.
This failure mode is catastrophic, as the low-friction surface is stripped away, causing a rapid increase in friction, heat generation, and complete failure of the bearing.
The Importance of Manufacturer Expertise
Because the bonding process is so sensitive, selecting a manufacturer with proven experience is paramount. Global standards like BS:5400 and AASHTO provide design guidance, but the quality of execution ultimately determines the bearing's lifespan and safety.
Environmental Suitability
PTFE's inherent properties make these bearings highly resistant to chemicals and weathering. This makes them exceptionally well-suited for applications where they may be exposed to harsh or corrosive environments.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the right bearing depends entirely on your primary engineering goal.
- If your primary focus is maintenance-free operation in high-load, low-speed systems: The self-lubricating and high static load capacity of PTFE-lined bearings make them an ideal choice.
- If your primary focus is smooth, low-friction motion under oscillating or intermittent movement: The solid lubricant film excels in these conditions, preventing the stick-slip phenomenon common with traditionally lubricated bearings.
- If your application involves consistently high speeds above 5 m/s: You may need to consider alternative bearing technologies, as managing the thermal load becomes the primary engineering challenge.
Ultimately, understanding the composite structure of these bearings is the key to leveraging their unique advantages in your design.
Summary Table:
| Specification | Dry Operation Value | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Coefficient of Friction | 0.02 - 0.20 | Can be lowered with lubrication |
| Max Static Load Capacity | 250 N/mm² | Supported by steel backing |
| Max Dynamic Load Capacity | 140 N/mm² | Suitable for moving applications |
| Max Sliding Speed | 2.5 m/s | Can increase to 5 m/s with lubrication |
| Key Advantage | Maintenance-Free | Self-lubricating, no external grease needed |
Optimize your design with precision-engineered PTFE components from KINTEK.
PTFE-lined bearings deliver exceptional performance, but their reliability hinges on expert manufacturing and a flawless bonding process to prevent delamination. As a trusted manufacturer of high-performance PTFE seals, liners, and labware for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors, KINTEK prioritizes precision production and robust quality control.
We offer custom fabrication from prototypes to high-volume orders, ensuring your PTFE components meet exact specifications for maintenance-free operation, high load capacity, and chemical resistance.
Ensure your application's success — contact our experts today to discuss your specific requirements and receive a tailored solution.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Customizable PTFE Rods for Advanced Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What makes PTFE butterfly valves special compared to other types? Unmatched Chemical & Thermal Performance
- What temperature range can PTFE-lined valves operate within? Key Limits for Safe & Reliable Performance
- How are PTFE O-ring seals used in the automotive industry? Critical Sealing Solutions for High-Performance Vehicles
- What are the key performance capabilities of spring energized PTFE seals? Conquer Extreme Environments
- What are the desirable properties of PTFE as a sealing material? Unlock Superior Performance in Extreme Conditions
- What are the temperature limitations of Teflon packing? Ensure Sealing Integrity from -200°C to 260°C
- What factors should engineers consider when selecting a PTFE rotary seal? Ensure Long-Term Reliability for Your System
- What are the advantages and disadvantages of virgin PTFE diaphragms? Achieve Optimal Performance in Critical Applications



















