At its core, PTFE is a uniquely versatile material defined by four exceptional properties: near-total chemical resistance, an extremely low coefficient of friction, excellent stability across a wide temperature range, and high-performance electrical insulation. This powerful combination allows it to perform reliably in harsh environments where most other plastics would fail.
The true power of Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) lies not in any single property, but in its rare combination of extreme chemical inertness, thermal resilience, and a near-frictionless surface. This unique trifecta allows it to solve engineering challenges that few other materials can address.
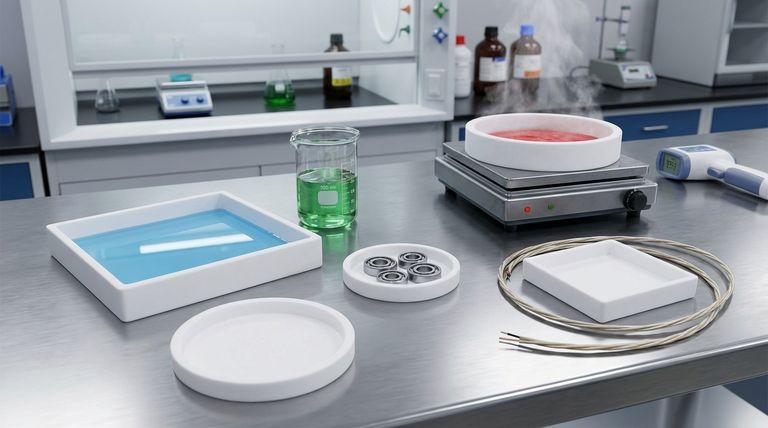

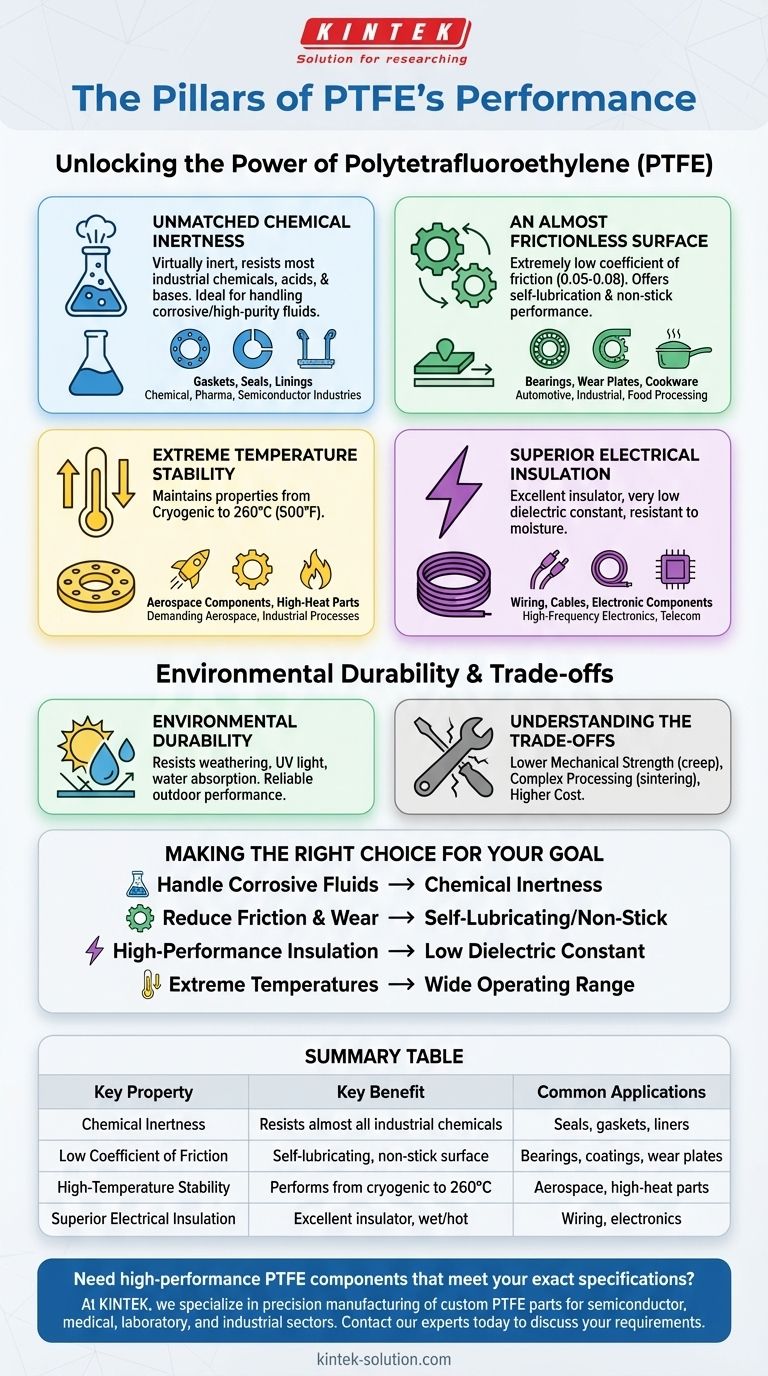
The Pillars of PTFE's Performance
To understand why PTFE is so widely adopted across industries like aerospace, chemical processing, and electronics, we must examine its foundational characteristics and the problems they solve.
Unmatched Chemical Inertness
PTFE is virtually inert and does not react with the vast majority of industrial chemicals, acids, and bases. This makes it an ideal material for handling corrosive or high-purity fluids.
This property is the primary reason it's specified for gaskets, seals, and linings in chemical pipes and valves used in the petrochemical, pharmaceutical, and semiconductor industries.
An Almost Frictionless Surface
PTFE has one of the lowest coefficients of friction of any solid material, with values around 0.05 to 0.08. This gives it two distinct advantages: self-lubrication and non-stick performance.
As a self-lubricating material, it is used for bearings and wear plates in automotive and industrial applications. Its non-stick, or anti-adhesion, quality is essential for non-stick cookware, food processing equipment, and even waterproof, breathable fabrics.
Extreme Temperature Stability
PTFE maintains its properties across an exceptionally broad temperature range, typically from cryogenic levels up to 260°C (500°F).
This thermal resilience ensures it remains stable and reliable in demanding high-heat aerospace applications or in industrial processes that involve significant temperature fluctuations.
Superior Electrical Insulation
PTFE is an excellent electrical insulator with a very low dielectric constant, even in hot and wet conditions. It effectively resists the flow of electricity.
This makes it a critical material for high-frequency electronics, serving as insulation for wiring and cables in aerospace, computing, and telecommunications equipment where signal integrity is paramount.
Environmental Durability
Beyond its primary characteristics, PTFE also exhibits strong resistance to weathering, UV light, and water absorption. It does not degrade with environmental exposure, ensuring long-term performance and reliability in outdoor or harsh settings.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No material is perfect, and making an informed decision requires acknowledging PTFE's limitations. Its unique properties come with specific mechanical and processing trade-offs.
Lower Mechanical Strength
Compared to other engineering plastics, PTFE is relatively soft. It has lower tensile strength and is susceptible to "creep," meaning it can deform over time when under a sustained load. This makes it unsuitable for high-load structural applications without reinforcement.
Processing and Fabrication
PTFE cannot be processed using conventional melt techniques like injection molding. It must be compressed and sintered—a process that is often slower and more complex. This can impact the final cost and design possibilities of a component.
Higher Relative Cost
Due to its complex manufacturing process and raw material costs, PTFE is generally more expensive than many commodity and even some engineering plastics. Its use is typically justified by performance requirements that other materials cannot meet.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting PTFE is a decision driven by the need to solve a specific, often extreme, engineering challenge. Its properties make it the ideal choice when performance cannot be compromised.
- If your primary focus is handling corrosive fluids: PTFE's chemical inertness makes it the definitive choice for linings, seals, and gaskets.
- If your primary focus is reducing friction and wear: Its self-lubricating, non-stick surface is ideal for bearings, low-friction coatings, and release surfaces.
- If your primary focus is high-performance electrical insulation: Its low dielectric constant and moisture resistance make it perfect for critical wiring and electronic components.
- If your primary focus is performance in extreme temperatures: Its wide and stable operating range ensures reliability in both cryogenic and high-heat environments.
Ultimately, understanding these core properties allows you to leverage PTFE not just as a material, but as a strategic solution to complex engineering problems.
Summary Table:
| Key Property | Key Benefit | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Inertness | Resists almost all industrial chemicals | Seals, gaskets, liners in chemical processing |
| Low Coefficient of Friction | Self-lubricating, non-stick surface | Bearings, non-stick coatings, wear plates |
| High-Temperature Stability | Performs from cryogenic to 260°C (500°F) | Aerospace components, high-heat industrial parts |
| Superior Electrical Insulation | Excellent insulator, even in wet/hot conditions | Wiring, cables, and components for electronics |
Need high-performance PTFE components that meet your exact specifications?
At KINTEK, we specialize in the precision manufacturing of custom PTFE parts—including seals, liners, and labware—for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. We combine expert material knowledge with advanced fabrication techniques to deliver solutions that leverage PTFE's full potential, from prototypes to high-volume production.
Contact our experts today to discuss how our PTFE components can solve your most challenging application requirements.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Customizable PTFE Rods for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Volumetric Flasks for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Use
People Also Ask
- How was Teflon (PTFE) discovered? The Accidental Invention That Revolutionized Industry
- What are the environmental and safety considerations for Teflon and UHMW? Ensure Safe Material Selection
- What are the limitations of PTFE as a material? Key Mechanical Weaknesses to Consider
- What are the key properties that make Teflon widely applicable? Unlock Unmatched Chemical & Thermal Resistance
- What makes PTFE valuable for electrical applications? Unlocking Superior Insulation and Signal Integrity
- Is PTFE safe for use in electrical environments? Achieve Superior Insulation & Reliability
- Why are PTFE laminated membrane filters preferred for solvent filtration? Unmatched Chemical Resistance & Hydrophobicity
- How is PTFE utilized in printing and packaging? Enhance Efficiency with Nonstick Solutions



















