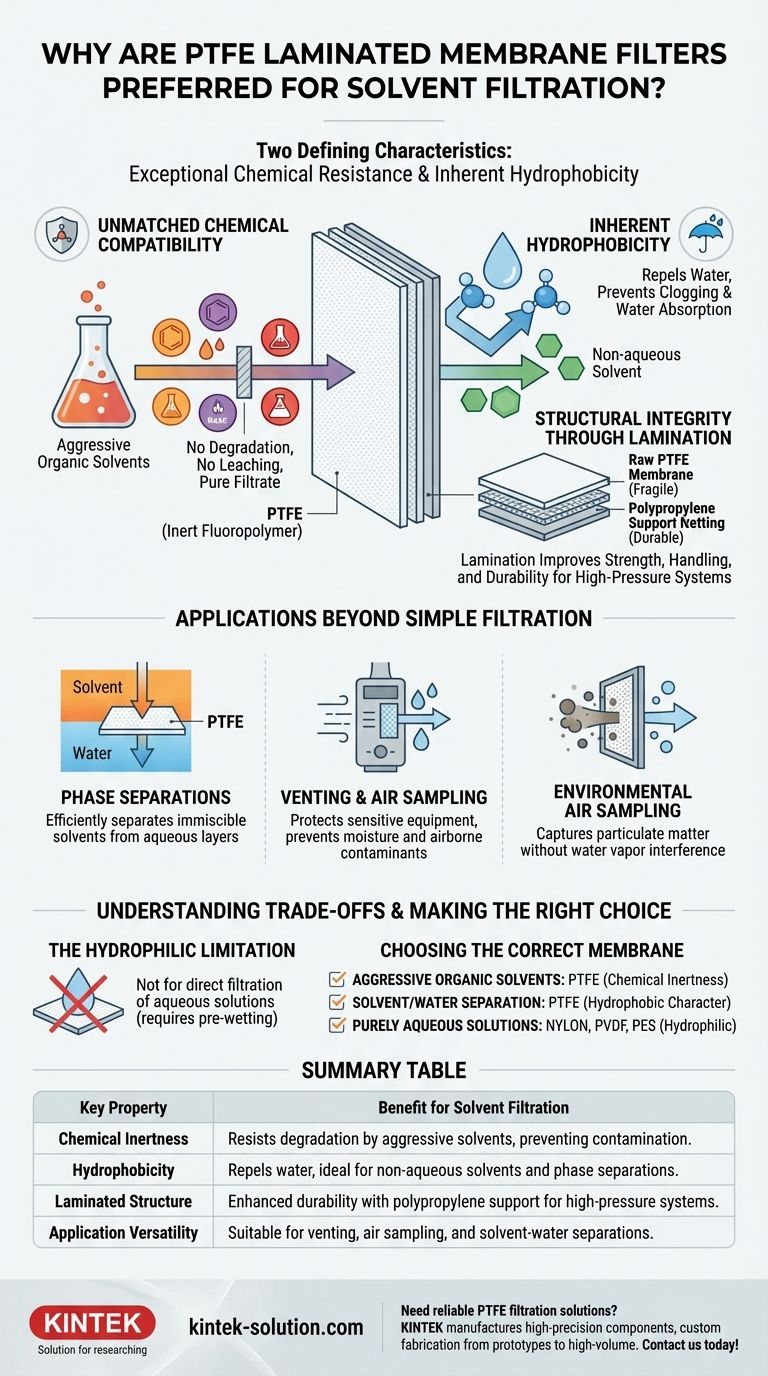
At their core, Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) laminated membrane filters are preferred for solvent filtration because of two defining characteristics: their exceptional chemical resistance and their inherent hydrophobicity. This combination ensures the filter will not degrade when exposed to aggressive solvents and will actively repel any water, resulting in pure, efficient filtration of non-aqueous liquids.
The critical insight is that PTFE's value isn't just its durability. Its hydrophobic (water-repelling) nature is the key feature that prevents water absorption, guaranteeing the integrity and purity of the solvent being filtered.

The Core Properties of PTFE Filters
To understand why PTFE is the material of choice, we need to examine its fundamental properties and how they directly benefit solvent-based applications.
Unmatched Chemical Compatibility
PTFE is a highly inert fluoropolymer. This means it has a broad chemical compatibility and does not react with or degrade when exposed to a vast range of chemicals, including aggressive organic solvents, acids, and bases.
This inertness is critical because it prevents the filter itself from becoming a source of contamination. The filter will not leach impurities into the solvent, ensuring the final filtrate is pure.
The Critical Role of Hydrophobicity
PTFE is a hydrophobic material, which literally means "water-fearing." Its surface actively repels water molecules while allowing non-aqueous, organic-based solvents to pass through freely.
This property is essential for two reasons. First, it prevents the filter membrane from becoming saturated and clogged by any ambient humidity or trace water in the solvent. Second, it ensures excellent water repellency, which is vital for applications requiring the separation of solvents from aqueous mixtures.
Structural Integrity and Lamination
A raw PTFE membrane can be fragile. To overcome this, these filters are often laminated onto a polypropylene support netting.
This lamination significantly improves the filter's strength and handling characteristics. It provides the durability needed to withstand the pressure of filtration systems without tearing or compromising the membrane's integrity.
Applications Beyond Simple Filtration
The unique properties of PTFE make it versatile for several specialized laboratory and industrial tasks beyond just clarifying solvents.
Phase Separations
Because PTFE allows organic solvents to pass through while blocking water, it is an ideal medium for phase separations. It can be used to efficiently separate an immiscible organic solvent from an aqueous layer without the need for a traditional separatory funnel.
Venting and Air Sampling
The hydrophobic nature of PTFE allows gases and air to pass through easily while blocking water droplets and aerosols. This makes it perfect for venting applications, such as protecting sensitive electronic equipment or sterile containers from moisture and airborne contaminants.
It is also used in environmental air sampling to capture particulate matter while preventing water vapor from affecting the sample.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While highly effective, PTFE filters are not a universal solution. Understanding their primary limitation is crucial for proper application.
The Hydrophilic Limitation
The key trade-off for PTFE's hydrophobicity is that it cannot be used to filter aqueous (water-based) solutions directly. Water will not readily pass through the membrane due to surface tension and the material's repellent nature.
To filter an aqueous solution with a PTFE filter, the membrane must first be "pre-wetted" with a low-surface-tension solvent like methanol or isopropanol. This pre-wetting step can add complexity to a workflow.
Cost and Specialization
PTFE is a premium, high-performance polymer. Filters made from it are often more expensive than alternatives like nylon or cellulose. Its use is typically reserved for applications where its superior chemical resistance and hydrophobic properties are a strict requirement.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct membrane filter is essential for achieving accurate and repeatable results. Your choice should be dictated by the chemical nature of your sample.
- If your primary focus is filtering aggressive organic solvents: PTFE is the safest and most reliable choice due to its unparalleled chemical inertness.
- If your primary focus is separating a solvent from a water-based solution: PTFE's hydrophobic character makes it exceptionally effective for this type of phase separation.
- If your primary focus is filtering purely aqueous solutions: A naturally hydrophilic membrane, such as nylon, PVDF, or polyethersulfone (PES), is a more direct and efficient choice.
Ultimately, matching the membrane's properties to your solvent's chemistry is the key to successful and reliable filtration.
Summary Table:
| Key Property | Benefit for Solvent Filtration |
|---|---|
| Chemical Inertness | Resists degradation by aggressive solvents, preventing contamination. |
| Hydrophobicity | Repels water, ideal for non-aqueous solvents and phase separations. |
| Laminated Structure | Enhanced durability with polypropylene support for high-pressure systems. |
| Application Versatility | Suitable for venting, air sampling, and solvent-water separations. |
Need reliable PTFE filtration solutions for your specialized applications? KINTEK manufactures high-precision PTFE components, including laminated membrane filters, seals, liners, and labware for semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. We offer custom fabrication from prototypes to high-volume orders, ensuring chemical compatibility and performance. Contact us today to discuss your solvent filtration needs and achieve purity with precision!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- PTFE Chemical Solvent Sampling Spoon
- Customizable PTFE Seals Filter Holders for Versatile Applications
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What factors should be considered when choosing between Nylon and PTFE? Select the Right Material for Your Application
- What are the main applications of PTFE type Teflon? Unlock Its Versatility for Your Industry
- What fabrication services are available for PTFE? Shearing, Stamping, Laser Cutting, Molding & Machining
- What challenges arise when machining PTFE (Teflon)? Overcome Softness, Heat, and Instability
- What design considerations are important for custom PTFE parts? Design for Performance & Reliability



















