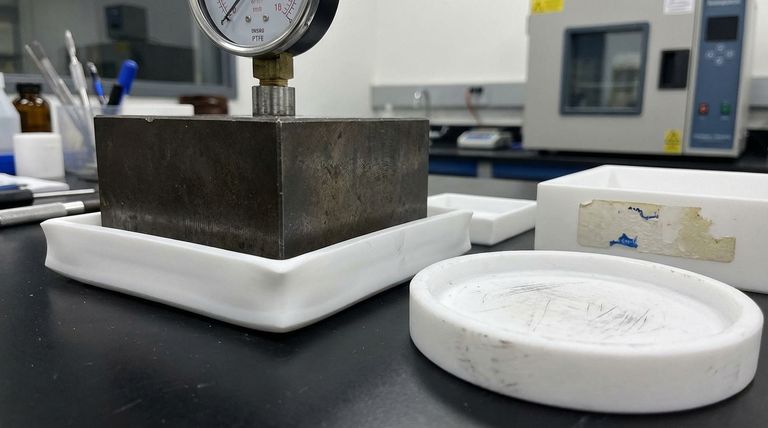
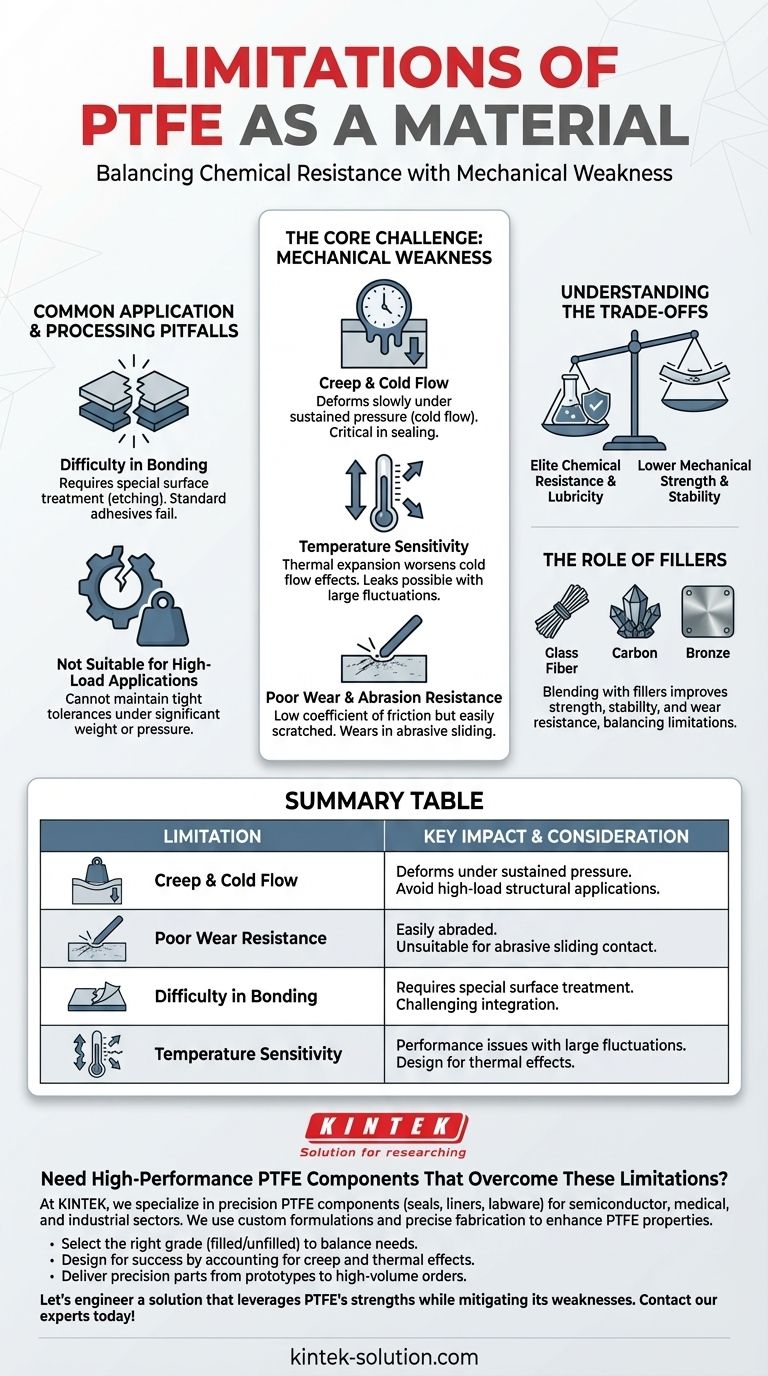
The primary limitations of Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) are mechanical in nature. While famous for its chemical and thermal resistance, PTFE is a relatively soft material subject to creep and cold flow, meaning it can deform over time under sustained pressure. This makes it unsuitable for high-load structural applications and requires careful design considerations in sealing environments, especially those with significant temperature fluctuations.
PTFE is a material of extremes. It offers world-class chemical inertness and low-friction properties, but this comes at the cost of poor mechanical strength and dimensional stability compared to other engineering plastics.

The Core Challenge: Mechanical Weakness
PTFE's most celebrated qualities—its inertness and slipperiness—stem from its molecular structure. However, this same structure is responsible for its most significant limitations.
Understanding Creep and Cold Flow
Creep, or "cold flow," is the tendency of a solid material to move slowly or deform permanently under the influence of persistent mechanical stress.
Because PTFE is a soft plastic, it will deform under a constant load, even at room temperature. This is especially critical in sealing applications, where a gasket might lose its sealing pressure over time, leading to leaks.
The Impact of Temperature Fluctuations
The references explicitly warn against using PTFE in environments with large temperature variations.
This is because thermal expansion and contraction can worsen the effects of cold flow. As the material expands and contracts, it can lose its original shape and fail to provide a consistent seal, requiring the use of high-pressure clamps to maintain integrity.
Low Wear and Abrasion Resistance
While PTFE has an exceptionally low coefficient of friction (making it very slippery), it is not inherently tough.
Unfilled PTFE can be easily scratched and has poor resistance to abrasive materials. In applications with sliding contact against a rough surface, it will wear away much faster than harder plastics.
Common Application and Processing Pitfalls
Beyond its inherent mechanical properties, PTFE presents challenges in how it is integrated into larger systems.
Difficulty in Bonding
The non-stick properties that make PTFE famous also make it extremely difficult to bond to other surfaces.
Special surface preparation techniques, like chemical etching, are required to create a bondable surface. Standard adhesives and cements will not work on untreated PTFE.
Not Suitable for High-Load Applications
The tendency to creep makes pure PTFE a poor choice for structural components or high-load bearings.
Without reinforcement, it cannot maintain the tight tolerances required for many mechanical parts and will deform under significant weight or pressure.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a material is always about balancing competing properties. PTFE is a perfect example of managing critical trade-offs.
The Friction vs. Strength Dilemma
The fundamental trade-off with PTFE is accepting lower mechanical performance in exchange for elite chemical resistance and lubricity.
For a static seal in a highly corrosive environment, it's an excellent choice. For a high-load gear or structural bracket, it is almost certainly the wrong one.
The Role of Fillers
To counteract its mechanical weaknesses, PTFE is often blended with fillers like glass fiber, carbon, or bronze.
These "filled" grades offer significantly improved strength, stability, and wear resistance. However, adding fillers can sometimes slightly reduce the chemical resistance or alter the electrical properties of the material.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
To use PTFE effectively, you must align its specific properties with the primary goal of your project.
- If your primary focus is ultimate chemical resistance: PTFE is an industry standard, but you must design for its tendency to creep by using appropriate high-pressure flanges and avoiding significant temperature cycles.
- If your primary focus is low-friction sliding: Unfilled PTFE is excellent for low-load bushings, sliders, and non-stick surfaces where wear from abrasion is not a concern.
- If your primary focus is mechanical strength or wear resistance: Pure PTFE is the wrong material. You must use a filled grade of PTFE or consider another engineering plastic entirely.
Ultimately, understanding a material's limitations is just as important as knowing its strengths.
Summary Table:
| Limitation | Key Impact | Application Consideration |
|---|---|---|
| Creep & Cold Flow | Deforms under sustained pressure | Avoid high-load structural applications |
| Poor Wear Resistance | Easily scratched and abraded | Unsuitable for abrasive sliding contact |
| Difficulty in Bonding | Requires special surface treatment | Challenging to integrate with other materials |
| Temperature Sensitivity | Performance issues with large fluctuations | Design for thermal expansion/contraction |
Need High-Performance PTFE Components That Overcome These Limitations?
At KINTEK, we specialize in manufacturing precision PTFE components (seals, liners, labware, etc.) for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. We understand these material challenges intimately and use advanced techniques—including custom filler formulations and precise fabrication—to enhance PTFE's mechanical properties for your specific application.
We help you:
- Select the right PTFE grade (filled or unfilled) to balance chemical resistance with mechanical strength.
- Design for success by accounting for creep and thermal effects from the start.
- Deliver precision parts from prototypes to high-volume orders that perform reliably.
Let's engineer a solution that leverages PTFE's strengths while mitigating its weaknesses. Contact our experts today for a consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Customizable PTFE Rods for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Volumetric Flasks for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Use
People Also Ask
- What is the temperature range for PTFE applications? Choose the Right Grade for Your High-Temp Needs
- What is PTFE and what are its key attributes? The Ultimate Guide to Its Properties & Uses
- What makes Teflon a versatile coating material? Unlock Superior Performance in Your Application
- What is the structure of Teflon? Unlocking the Secrets of PTFE's Unmatched Properties
- How do Teflon and UHMW compare in terms of applications and characteristics? Choose the Right High-Performance Polymer
- What are the key characteristics of polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE)? Unlocking High-Performance Material Properties
- What role does PTFE play in automotive manufacturing? Enhancing Vehicle Durability and Efficiency
- What distinguishes Virgin PTFE from Reprocessed PTFE? Choose the Right Material for Your Application



















