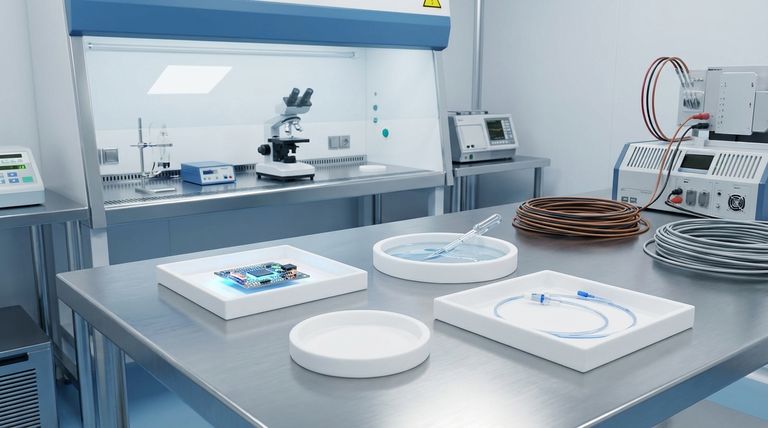
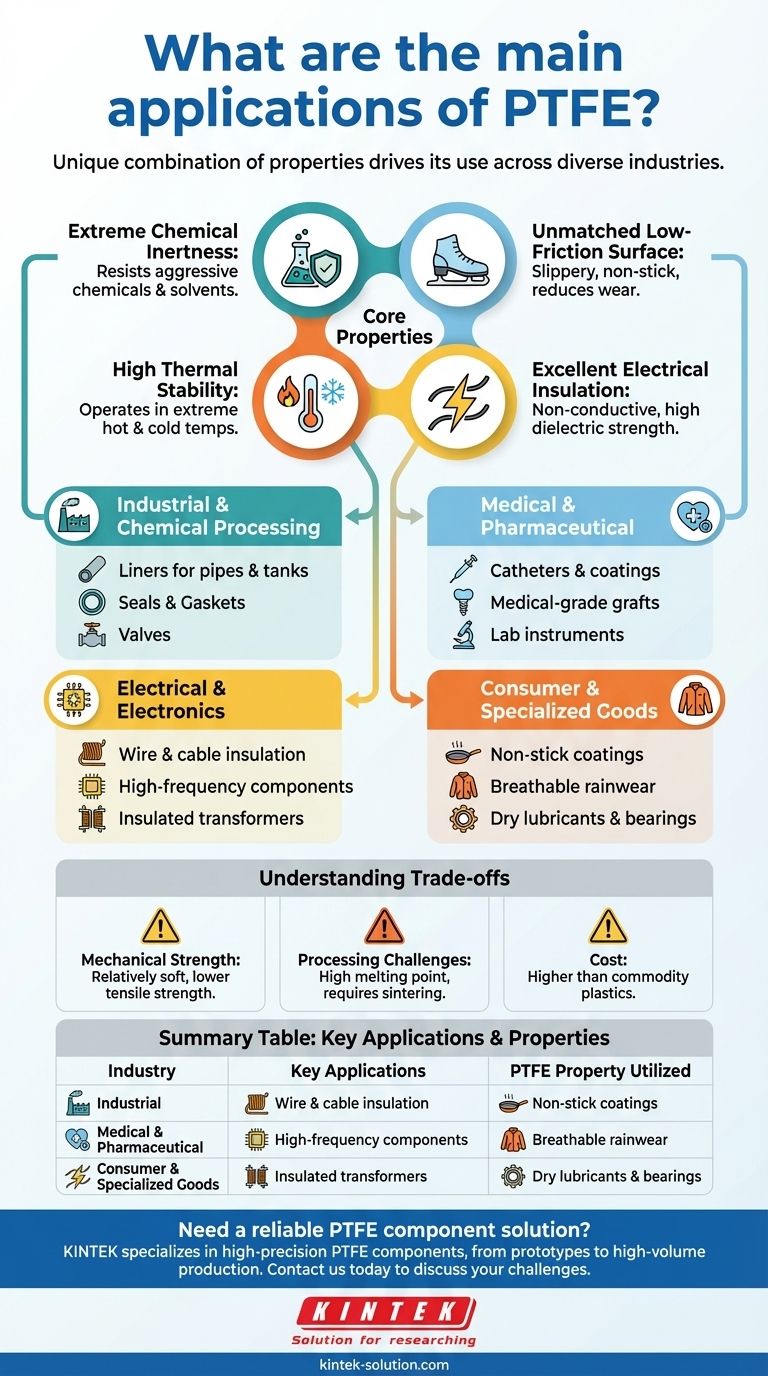
The primary applications of PTFE span a wide range of industries, including industrial chemical processing, medical devices, electronics, and consumer goods. Its use is almost always driven by its unique combination of properties: extreme chemical resistance, a very low-friction surface, high-temperature tolerance, and excellent electrical insulation.
The core reason for PTFE's widespread use is not just one of its properties, but its unique ability to combine them. It solves engineering challenges where materials must resist aggressive chemicals, reduce friction, and withstand high temperatures simultaneously.

Why PTFE is So Versatile: The Core Properties
The applications of Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) are a direct result of its fundamental material characteristics. Understanding these properties explains why it is the material of choice for so many demanding roles.
Extreme Chemical Inertness
PTFE is virtually non-reactive to almost all chemicals, solvents, and corrosive agents. This makes it an ideal material for containing or transporting aggressive substances.
This property is critical in chemical processing plants, laboratories, and pharmaceutical manufacturing where material purity and resistance to degradation are paramount.
Unmatched Low-Friction Surface
Famously known for its non-stick quality in cookware, PTFE has one of the lowest coefficients of friction of any solid material. This property is often compared to wet ice on wet ice.
This characteristic is essential for applications like low-friction bearings, seals, and non-stick surface coatings where reducing wear and preventing material adhesion are key objectives.
High Thermal Stability
PTFE can operate reliably over a very wide temperature range without degrading. This allows it to be used in high-temperature industrial processes as well as cryogenic applications.
Its durability under thermal stress makes it suitable for components like gaskets, expansion joints, and liners in environments that would destroy lesser polymers.
Excellent Electrical Insulation
PTFE is an exceptional electrical insulator with high dielectric strength. It does not conduct electricity, making it a perfect material for insulating wires and electronic components.
This is why it is commonly used for wire and cable insulation, particularly in high-performance applications where signal integrity and safety are critical.
Key Applications by Industry
Based on its core properties, PTFE has been adopted as a problem-solving material across numerous sectors.
Industrial and Chemical Processing
This is one of the largest application areas for PTFE. Its chemical resistance is leveraged in components like liners for pipes and tanks, seals, gaskets, valves, and expansion joints.
These components ensure the safe handling and transport of corrosive chemicals, preventing leaks and equipment failure in industries from petrochemicals to pharmaceuticals.
Medical and Pharmaceutical
PTFE's biocompatibility and inertness make it suitable for medical use. It complies with FDA regulations for many applications.
It is used to create medical-grade grafts, as a coating on catheters to prevent bacterial adhesion and reduce infections, and in various instruments and testing equipment where purity is essential.
Electrical and Electronics
Due to its superb insulating properties, PTFE is a go-to material for high-frequency electronics.
It is widely used for insulating wires and cables, especially in aerospace and computing, as well as for manufacturing insulated transformers and other critical components.
Consumer and Specialized Goods
The most well-known consumer application is non-stick coatings for cookware. However, a modified form (ePTFE) creates a microporous membrane used in high-performance, breathable rainwear and coats.
It is also used as a dry lubricant in machinery and as a component in bearings to reduce friction and improve efficiency.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While incredibly useful, PTFE is not the solution for every problem. A trusted advisor must acknowledge its limitations.
Mechanical Strength
PTFE is a relatively soft material. It has poor tensile strength and is not highly resistant to abrasion or wear compared to harder plastics or metals. In high-load applications, it is often reinforced with fillers like glass or carbon.
Processing Challenges
PTFE has a very high melting point and viscosity, which means it cannot be processed using conventional melt-processing techniques like injection molding. It is typically shaped through a process of compression and sintering, which can be more complex and costly.
Cost
As a high-performance polymer, PTFE is generally more expensive than common commodity plastics like polyethylene or polypropylene. Its use is typically justified by performance requirements that other materials cannot meet.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting a material depends entirely on the problem you need to solve. PTFE is the optimal choice when your primary challenge aligns with its core strengths.
- If your primary focus is handling aggressive chemicals: PTFE's unmatched chemical inertness makes it the safest and most reliable choice for seals, gaskets, and liners.
- If your primary focus is minimizing friction: PTFE's non-stick surface is ideal for creating low-wear bearings, self-lubricating parts, and non-stick coatings.
- If your primary focus is biocompatibility and purity: PTFE is a proven material for medical devices and food processing equipment where contamination must be avoided.
- If your primary focus is high-frequency electrical insulation: PTFE's excellent dielectric properties make it a superior choice for critical wiring and electronic components.
Ultimately, PTFE is a specialty material chosen when its unique combination of properties provides a level of performance and reliability that conventional materials cannot match.
Summary Table:
| Industry | Key Applications | PTFE Property Utilized |
|---|---|---|
| Industrial & Chemical | Liners, Seals, Gaskets, Valves | Extreme Chemical Resistance |
| Medical & Pharmaceutical | Catheters, Grafts, Instruments | Biocompatibility & Inertness |
| Electrical & Electronics | Wire Insulation, High-Frequency Components | Excellent Electrical Insulation |
| Consumer & Specialized Goods | Non-Stick Coatings, Breathable Fabrics | Low-Friction Surface & Thermal Stability |
Need a reliable PTFE component solution?
KINTEK specializes in manufacturing high-precision PTFE components—including seals, liners, and custom labware—for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. We combine expert custom fabrication with scalable production from prototypes to high-volume orders.
Contact us today to discuss how our PTFE expertise can solve your specific application challenges.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
People Also Ask
- What are the key advantages of PTFE as a solid lubricant? Clean, Stable Lubrication for Extreme Conditions
- What are the applications of PTFE laminated fabric in special apparel? A Guide to Advanced Protection & Comfort
- What are the benefits of using fillers in PTFE? Enhance Wear, Strength, and Performance
- What are the limitations of PTFE as a material? Key Mechanical Weaknesses to Consider
- What are some lesser-known facts about Teflon? Uncover Its Hidden Role in Tech and Industry
- How does the molecular structure of Nylon differ from PTFE? A Guide to Polymer Properties
- What are the main drawbacks of PEEK? Key Limitations for High-Performance Applications
- How can waste from PTFE manufacturing be reused? Transform Scrap into High-Performance Micropowder



















