Yes, manufacturing waste from Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) can be effectively reused. The primary method involves reprocessing scrap material, such as shavings and off-cuts from cutting processes, into a fine micropowder. This recycled powder is then used either for molding new products or as a high-performance additive in other materials like lubricants and inks.
The core principle of PTFE recycling is not about melting it down like metal, but about mechanically grinding clean manufacturing scrap into a fine powder. This process transforms waste into a valuable raw material with specific industrial applications, reducing waste and maximizing material use.
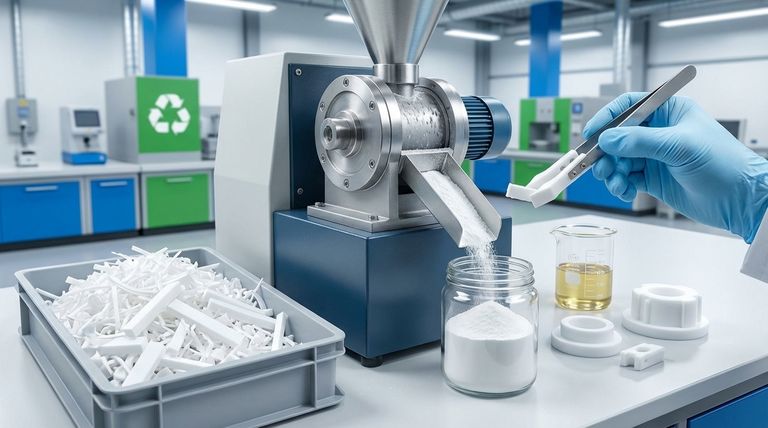

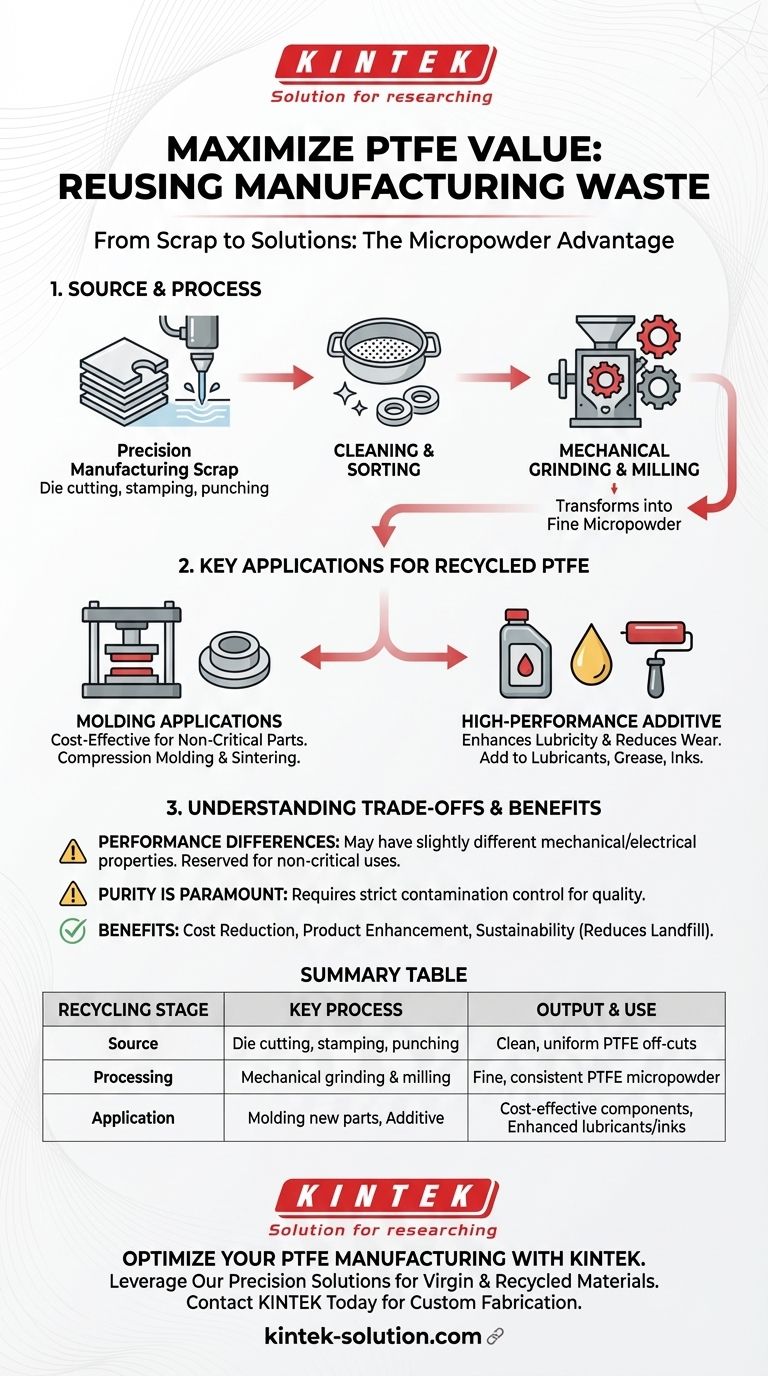
The Source and Process of PTFE Recycling
To understand its reuse, we must first look at how the waste is generated and processed. The goal is to convert clean, uniform scrap into a consistent, usable format.
From Precision Manufacturing Scrap
PTFE waste suitable for recycling typically originates from mechanical fabrication processes. These are not post-consumer, contaminated materials, but clean industrial off-cuts.
Common sources include scrap from die cutting, stamping, punching, and water jet cutting. This ensures the raw waste is of a known quality and free from external contaminants.
The Conversion to Micropowder
The recycling journey from solid scrap to usable powder involves a few key steps.
- Cleaning and Sorting: The process begins by ensuring the scrap is clean and consists only of PTFE. Any impurities would compromise the quality of the final product.
- Mechanical Grinding: The sorted scrap is then subjected to a specialized grinding or milling process. This mechanically breaks down the material into a fine, consistent powder, often referred to as a micropowder.
The resulting powder is a recycled-grade PTFE, ready to be reintegrated into new manufacturing applications.
Key Applications for Recycled PTFE
The reprocessed PTFE powder has two primary destinations, each leveraging the material's inherent properties like low friction and chemical resistance.
Use in Molding Applications
The most direct form of reuse is incorporating the recycled powder into the molding of new PTFE components.
This is typically done through compression molding, where the powder is pressed into a desired shape and then sintered (heated) to fuse the particles together. These parts are often used in less demanding applications where the ultimate performance of virgin PTFE is not required.
As a High-Performance Additive
A very common and high-value application is using the PTFE micropowder as an additive to other materials.
By mixing it into lubricants, oils, greases, and inks, it imparts its signature low-friction characteristic. This enhances lubricity and reduces wear in the host material, improving the performance and lifespan of the final product.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While recycling PTFE is highly beneficial, it's important to be aware of the practical limitations and considerations. This is not a one-to-one replacement for virgin material in all cases.
Performance Differences
Recycled PTFE may exhibit slightly different mechanical and electrical properties compared to virgin PTFE. The grinding process can alter the polymer's structure, which may affect factors like tensile strength or dielectric properties. For this reason, it is often reserved for non-critical applications.
Purity is Paramount
The entire value of recycled PTFE hinges on its purity. Any contamination from other plastics, oils, or debris during collection or processing can drastically degrade the quality of the final powder and the products made from it.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Deciding how to leverage recycled PTFE depends entirely on your end goal, whether it's sustainability, cost reduction, or product enhancement.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective material for non-critical parts: Using recycled PTFE powder for in-house molding can be an excellent way to reduce raw material costs.
- If your primary focus is enhancing other products: The most widespread and valuable use is as a friction-reducing additive in lubricants, coatings, and inks.
- If your primary focus is sustainability: Reprocessing manufacturing scrap is a clear environmental win, significantly reducing landfill waste and maximizing the lifecycle of a valuable polymer.
By transforming manufacturing scrap into a valuable micropowder, you can reduce waste, lower costs, and enhance the performance of other materials.
Summary Table:
| Recycling Stage | Key Process | Output & Use |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Die cutting, stamping, punching scrap | Clean, uniform PTFE off-cuts |
| Processing | Mechanical grinding & milling | Fine, consistent PTFE micropowder |
| Application | Molding new parts or as an additive | Cost-effective components or enhanced lubricants/inks |
Optimize Your PTFE Manufacturing with KINTEK's Precision Solutions
Reduce waste and lower costs by transforming your PTFE scrap into valuable materials. KINTEK specializes in manufacturing high-precision PTFE components (seals, liners, labware) for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Our expertise in custom fabrication—from prototypes to high-volume orders—ensures you get the most out of your materials, whether using virgin or recycled PTFE.
Let us help you enhance sustainability and performance. Contact KINTEK today to discuss your specific needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- PTFE Chemical Solvent Sampling Spoon
- Custom PTFE Bottles for Diverse Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What are the different grades of PTFE and their uses? A Guide to Selecting the Right Material
- What is Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) commonly known as, and what are its properties? Discover the Power of Teflon
- What makes PTFE ideal for electrical insulation? Superior Performance in Extreme Conditions
- What are some industrial applications of expanded PTFE? Solve Critical Sealing, Filtration, and Insulation Challenges
- What impact has PTFE industrial coating had on daily life? Unlocking Modern Convenience & Performance
- What are the electrical properties of Teflon? Unmatched Insulation for High-Voltage & High-Frequency Use
- How are PTFE coatings applied? A Guide to Spray, Electrostatic, and Dip-Spin Methods
- What industries commonly use PTFE? Leverage Its Chemical Resistance, Low Friction & Electrical Insulation



















