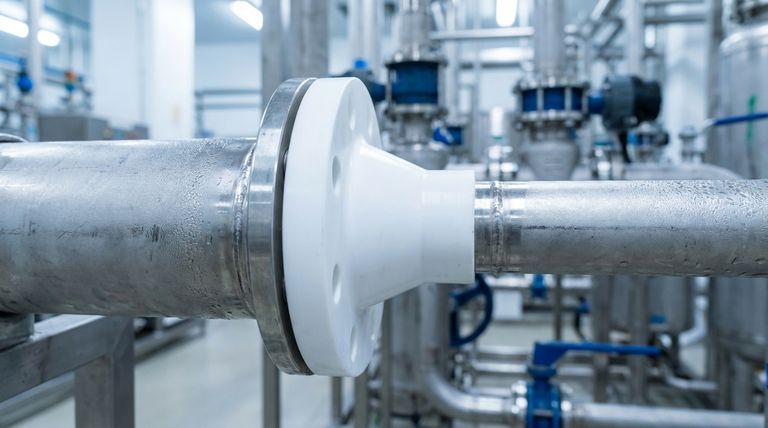
In industrial piping, a PTFE reducing flange is a specialized fitting used to connect pipes of two different diameters. Its key features are derived directly from its material, Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), and include exceptional chemical resistance, wide temperature tolerance, a non-stick low-friction surface, and straightforward installation. These properties make it a critical component for ensuring system integrity and efficiency in demanding environments.
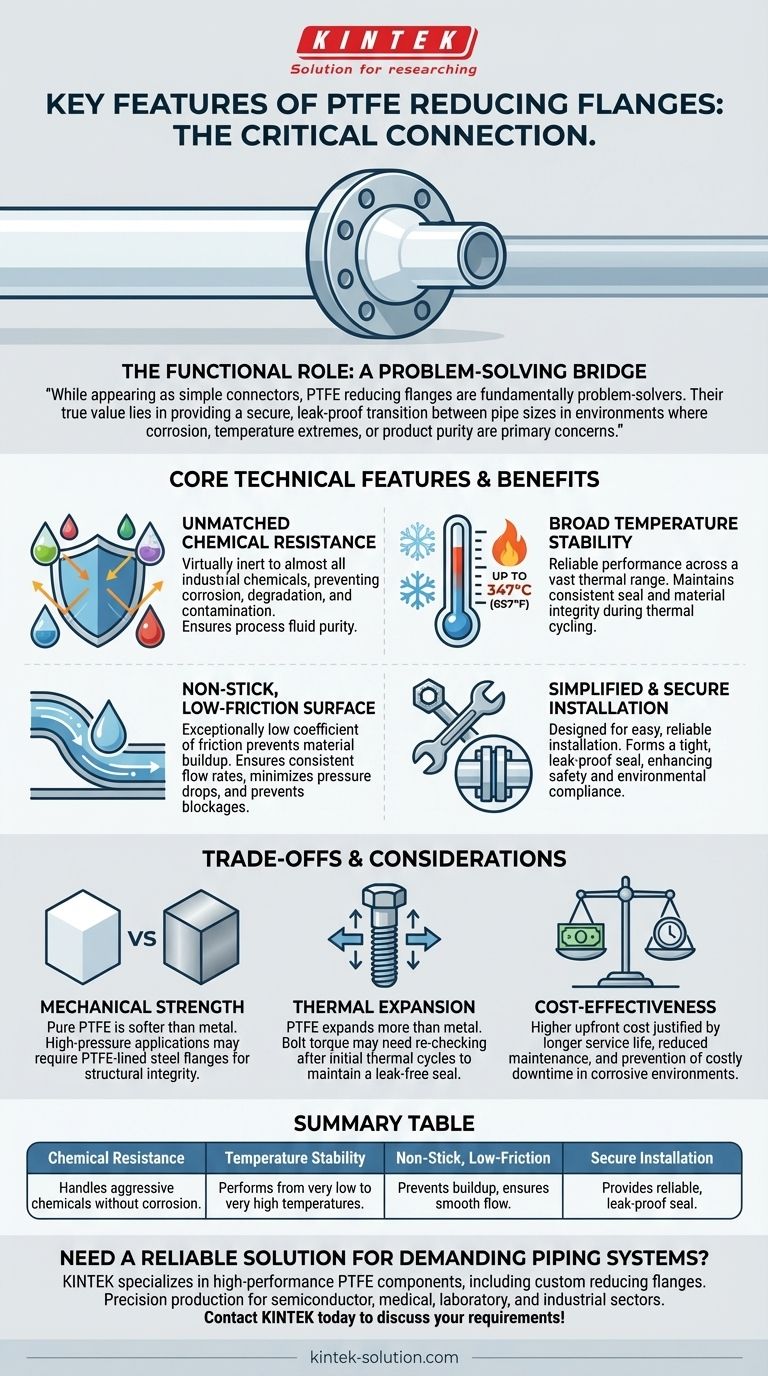
While appearing as simple connectors, PTFE reducing flanges are fundamentally problem-solvers. Their true value lies in providing a secure, leak-proof transition between pipe sizes in environments where corrosion, temperature extremes, or product purity are primary concerns.

The Functional Role of a PTFE Reducing Flange
A reducing flange serves a simple but critical purpose: to create a secure joint between a larger pipe and a smaller one. The use of PTFE as the construction material elevates this function significantly.
A Bridge Between Different Pipe Sizes
The primary function is to reduce the line size of a piping system. This is common when connecting a main process line to smaller equipment, instrumentation, or branch lines without needing additional complex fittings.
The Significance of PTFE Construction
PTFE is a high-performance fluoropolymer, often known by the brand name Teflon. Using it for a reducing flange means the component inherits all of PTFE's remarkable material properties, making it far more than a simple mechanical connector.
Core Technical Features and Their Impact
Each feature of a PTFE reducing flange directly translates to a tangible benefit in safety, performance, and operational longevity.
Unmatched Chemical Resistance
PTFE is virtually inert to almost all industrial chemicals, including aggressive acids, bases, and solvents. This prevents the flange from corroding, degrading, or leaching contaminants into the process fluid, which is essential for both safety and product purity.
Broad Temperature Stability
With a high melting point around 347°C (657°F) and flexibility at very low temperatures, these flanges perform reliably across a vast thermal range. This stability ensures a consistent seal and material integrity during thermal cycling.
The Non-Stick, Low-Friction Surface
The exceptionally low coefficient of friction gives PTFE its non-stick quality. This smooth surface prevents materials from adhering to the flange, which is critical for maintaining consistent flow rates, minimizing pressure drops, and preventing blockages, especially in systems handling slurries or viscous fluids.
Simplified and Secure Installation
PTFE reducing flanges are designed for easy and reliable installation. Their ability to form a tight seal helps prevent leaks of hazardous materials, directly enhancing plant safety and environmental compliance.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Considerations
While highly effective, PTFE components are not a universal solution. Understanding their limitations is key to proper application.
Mechanical Strength vs. Chemical Inertness
Pure PTFE is a relatively soft material compared to metals like steel. In very high-pressure applications, a solid PTFE flange may not provide sufficient mechanical strength. In these cases, a PTFE-lined steel flange is often used to combine the strength of metal with the chemical resistance of PTFE.
Thermal Expansion
PTFE has a higher coefficient of thermal expansion than metal. In systems with significant temperature fluctuations, bolt torque may need to be re-checked after the initial thermal cycle to compensate for this expansion and maintain a leak-free seal.
Cost-Effectiveness
Upfront, PTFE flanges are typically more expensive than standard carbon or stainless steel alternatives. However, their cost is justified by a longer service life, reduced maintenance, and the prevention of costly failures and downtime in corrosive environments.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting a PTFE reducing flange depends entirely on the specific demands of your piping system.
- If your primary focus is handling aggressive chemicals: PTFE's near-universal inertness makes it the superior and often necessary choice for ensuring system longevity and safety.
- If your primary focus is process efficiency and purity: The non-stick surface is invaluable for preventing contamination and ensuring smooth, uninterrupted flow.
- If your primary focus is operating in a high-pressure environment: You must evaluate whether a solid PTFE flange is sufficient or if a PTFE-lined metal flange is required to meet mechanical demands.
By understanding these features and their underlying impact, you can confidently specify the right component to ensure your system's long-term safety and efficiency.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Key Benefit |
|---|---|
| Chemical Resistance | Handles aggressive acids, bases, and solvents without corrosion. |
| Temperature Stability | Performs reliably from very low temperatures up to 347°C (657°F). |
| Non-Stick, Low-Friction | Prevents material buildup, ensuring consistent flow and minimizing blockages. |
| Secure Installation | Provides a reliable, leak-proof seal for enhanced safety and compliance. |
Need a reliable solution for demanding piping systems?
KINTEK specializes in manufacturing high-performance PTFE components, including custom reducing flanges. We ensure precision production and material integrity for critical applications in the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors.
Whether you require prototypes or high-volume orders, our custom fabrication expertise delivers components that enhance your system's safety, efficiency, and longevity.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss your specific requirements and get a quote!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
- Customizable PTFE Seals Filter Holders for Versatile Applications
People Also Ask
- What are some common configurations of Teflon back-up rings? Achieve Superior O-Ring Support and Extrusion Resistance
- How are PTFE billets formed, and what are their typical dimensions?
- What industries commonly use Teflon encapsulated O-rings for chemical resistance? Protect Critical Processes from Corrosion
- What are expanded PTFE gaskets and how are they made? A Guide to Superior Sealing Performance
- What are the different grades of PTFE used in rotary shaft seals? Choose the Right Filler for Peak Performance
- How do PTFE gaskets perform in extreme temperatures? From -200°C to +260°C
- How do PTFE and NBR oil seals compare in terms of dry running capability? The Ultimate Guide for Reliability
- What temperature range can PTFE sheets withstand? From -200°C to +260°C for Extreme Applications



















