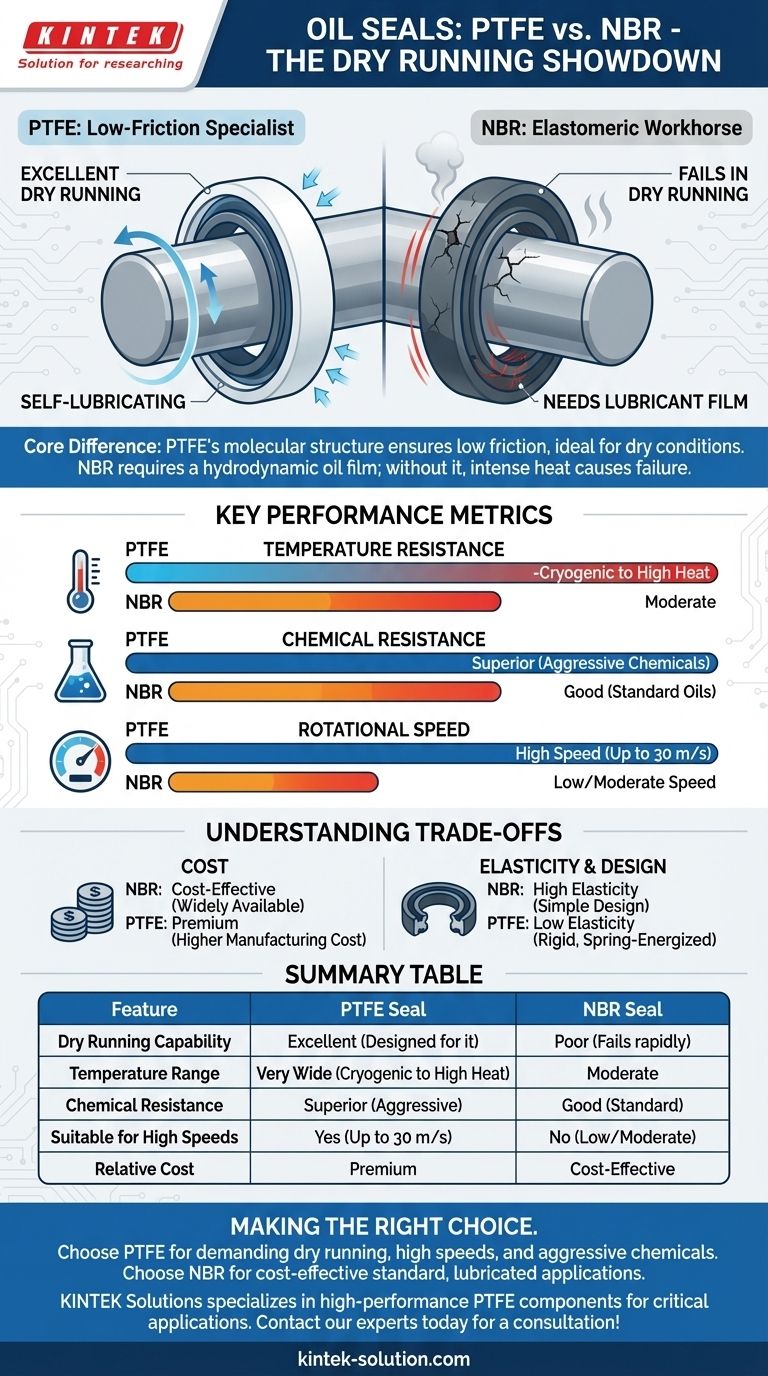
To be direct, PTFE (Polytetrafluoroethylene) oil seals are specifically designed for and excel in dry running conditions where lubrication is minimal or absent. In contrast, NBR (Nitrile Butadiene Rubber) oil seals are completely unsuitable for dry running and will fail rapidly without a consistent lubricant film.
The choice between PTFE and NBR is not about which material is universally better, but about matching the material's fundamental properties to the specific demands of the operating environment. PTFE is a high-performance specialist for extreme conditions, while NBR is the reliable standard for conventional, lubricated applications.

The Core Material Difference
The performance gap in dry running originates from the intrinsic nature of each material. Their molecular structures dictate how they handle friction and heat when lubrication is not present.
PTFE: The Low-Friction Specialist
PTFE is known for its exceptionally low coefficient of friction. This property makes it inherently "self-lubricating," allowing it to slide against a shaft with minimal heat generation even without external lubrication.
This characteristic is the primary reason PTFE seals are the definitive choice for dry running or applications with only trace amounts of fluid.
NBR: The Elastomeric Workhorse
NBR is an elastomer, a type of rubber that relies on a thin film of oil (a hydrodynamic film) between the seal lip and the shaft. This film both lubricates and cools the contact point.
Without this lubricant film, the friction between the NBR lip and a spinning shaft generates intense heat almost instantly, causing the material to harden, crack, and lose its sealing ability.
Comparing Key Performance Metrics
Beyond dry running, several other factors clearly differentiate these two materials, guiding the selection process for any application.
Temperature Resistance
PTFE seals operate effectively across an extremely wide temperature range, handling both cryogenic conditions and high heat.
NBR seals are limited to a more moderate temperature range. Exceeding their thermal limits will cause permanent material degradation.
Chemical Resistance
PTFE is almost completely inert, offering superior resistance to a vast array of aggressive chemicals, solvents, and oils.
NBR provides good resistance to standard petroleum-based oils, hydraulic fluids, and fuels but can be easily damaged by more aggressive chemical agents.
Rotational Speed
Due to their low friction and thermal stability, PTFE seals are engineered for high-speed applications, capable of handling surface speeds up to 30 m/s.
NBR seals perform reliably at lower and moderate speeds but are not suitable for the demands of very high-speed rotating equipment.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing the optimal seal requires an objective look at the limitations and costs associated with each option.
The Cost Factor
NBR seals are significantly more affordable and widely available, making them the default, cost-effective choice for a vast number of standard applications.
PTFE seals are a premium product. Their higher manufacturing cost is justified only when their unique performance capabilities are a strict requirement.
Material Elasticity and Design
NBR's natural elasticity allows it to conform easily to shaft surfaces, providing a reliable seal with a simple design.
PTFE is a much more rigid material with low elasticity. To compensate, PTFE seals are often engineered with a metallic spring energizer that ensures the seal lip maintains constant pressure against the shaft.
Thermal Conductivity
A key limitation of PTFE is its poor thermal conductivity, meaning it doesn't dissipate heat well. In high-friction scenarios, fillers like copper or graphene may be added to the PTFE compound to improve heat management.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your selection should be dictated entirely by the demands of your system.
- If your primary focus is dry running, high rotational speed, or resistance to aggressive chemicals: PTFE is the only suitable and reliable choice.
- If your primary focus is a standard, lubricated application with moderate temperatures and speeds: NBR offers excellent performance and is the most cost-effective solution.
- If your primary focus is balancing system cost and durability: Use NBR seals for standard-duty locations and reserve the more expensive PTFE seals for the critical, high-demand areas where they are essential.
Ultimately, selecting the correct seal material is a critical step in ensuring equipment reliability and longevity.
Summary Table:
| Feature | PTFE Seal | NBR Seal |
|---|---|---|
| Dry Running Capability | Excellent (Designed for it) | Poor (Fails rapidly) |
| Temperature Range | Very Wide (Cryogenic to High Heat) | Moderate |
| Chemical Resistance | Superior (Resists aggressive chemicals) | Good (Standard oils & fuels) |
| Suitable for High Speeds | Yes (Up to 30 m/s) | No (Best for low/moderate speeds) |
| Relative Cost | Premium | Cost-Effective |
Need a reliable seal for demanding conditions?
At KINTEK, we specialize in manufacturing high-performance PTFE components, including seals, liners, and labware, for industries where failure is not an option—such as semiconductor, medical, and specialized industrial applications. Our expertise in precision production and custom fabrication ensures you get a seal that matches your exact requirements, from prototypes to high-volume orders.
Let us help you enhance your equipment's reliability and longevity. Contact our experts today for a consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Customizable PTFE Rods for Advanced Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What are the main applications of PTFE type Teflon? Unlock Its Versatility for Your Industry
- What finishing techniques are effective for machined Teflon parts? Achieve Functional Performance and Dimensional Stability
- What industrial benefits do PTFE-machined parts offer? Achieve Peak Performance in Demanding Applications
- What fabrication services are available for PTFE? Shearing, Stamping, Laser Cutting, Molding & Machining
- What are the unique properties of PTFE? The 3 Pillars Driving Demand for High-Performance Parts



















