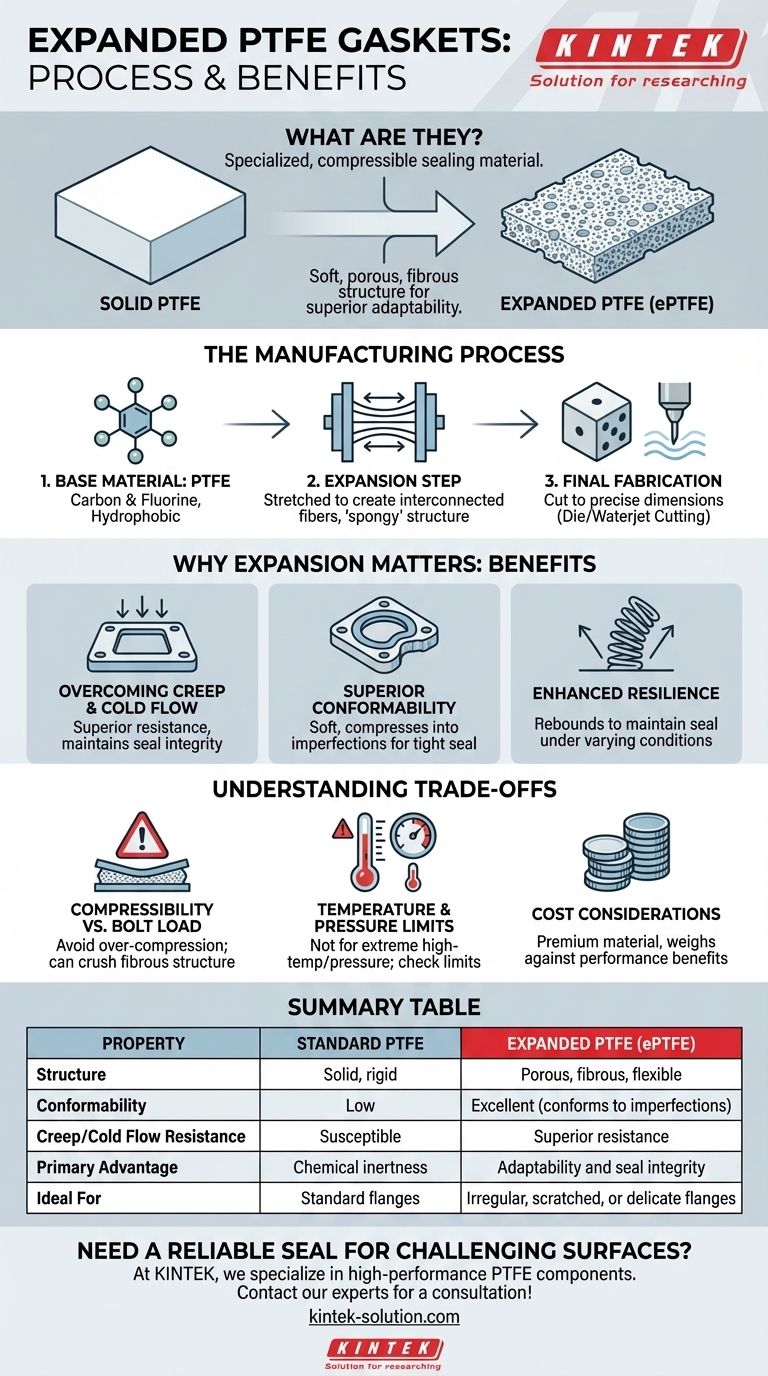
Expanded PTFE gaskets are a specialized form of Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) that has been physically altered to create a soft, porous, and highly compressible sealing material. Unlike standard, solid PTFE, they are manufactured through a unique expansion process that transforms the raw material into a strong, multi-directional fibrous structure, which provides superior adaptability and sealing performance.
The critical takeaway is that the manufacturing process of expanding PTFE is what gives the material its most valuable properties. This process changes it from a rigid plastic into a soft, conformable gasket that excels at sealing imperfect surfaces where standard gaskets would fail.
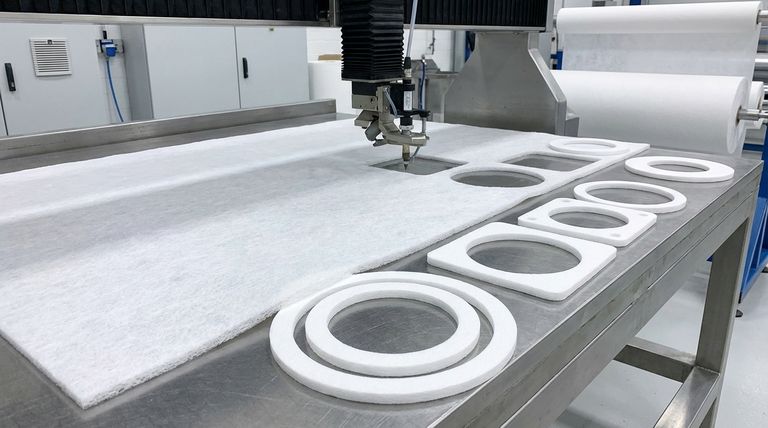

From Solid to Spongy: The ePTFE Manufacturing Process
The unique characteristics of expanded PTFE (ePTFE) gaskets are a direct result of their specialized manufacturing method, which transforms a common industrial polymer into a high-performance sealing solution.
The Base Material: Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE)
The process begins with PTFE, a synthetic fluoropolymer made entirely of carbon and fluorine atoms. This molecular structure is the source of PTFE's renowned chemical inertness and makes it inherently hydrophobic, meaning it repels water.
The Key Step: Expansion
The defining manufacturing step is the expansion process. Solid PTFE material is subjected to a special treatment that stretches it, transforming its solid construction into a porous, flexible matrix. This creates a distinctive internal structure of interconnected, multi-directional fibers.
It is this fibrous, "spongy" structure—not a change in chemical composition—that differentiates ePTFE from its rigid, solid counterpart.
Final Gasket Fabrication
Once the PTFE has been expanded into large sheets, the final gaskets are cut to precise dimensions. This is typically accomplished using methods like die cutting for high-volume, exact shapes or waterjet cutting, which allows for intricate designs and the cutting of very thick materials.
Why Expansion Matters: ePTFE vs. Standard PTFE
The decision to use ePTFE over standard PTFE almost always comes down to the need for superior adaptability and long-term seal integrity, benefits derived directly from the expansion process.
Overcoming Rigidity and Creep
Standard PTFE gaskets, which are either molded or cut from solid sheets, can suffer from uneven density and poor flexibility. More importantly, they are susceptible to creep and cold flow—a tendency to deform permanently under pressure, which can lead to seal failure over time.
The fibrous internal structure of ePTFE provides vastly superior resistance to creep and cold flow, ensuring the gasket maintains its shape and sealing force.
Superior Conformability
The most significant advantage of ePTFE is its softness and compressibility. This allows it to conform perfectly to irregular, scratched, or uneven flange surfaces.
Where a rigid gasket might leave microscopic gaps, an ePTFE gasket compresses into these imperfections to create an exceptionally tight and reliable seal.
Enhanced Resilience and Flexibility
Expanded PTFE possesses excellent compression resilience. It can be compressed to fit a joint and will rebound to maintain a seal even as operating conditions fluctuate. This makes it easier to install and helps extend the service life of the flanges themselves.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While ePTFE is a high-performance material, its unique properties create specific limitations that must be considered for any application.
Compressibility vs. Bolt Load
The very softness that makes ePTFE an excellent sealant for delicate or uneven flanges can be a disadvantage under extremely high bolt loads. Over-compressing the gasket can crush the fibrous structure, potentially reducing its effectiveness or leading to extrusion from the flange.
Temperature and Pressure Limits
While ePTFE has an impressive operational temperature range (from cryogenic up to +260°C / 500°F), it is not a solution for extreme high-temperature applications where metallic or semi-metallic gaskets would be required. Its pressure limits are also dictated by its compressible nature.
Cost Considerations
The specialized manufacturing process makes ePTFE a premium material. It is generally more expensive than standard PTFE and many other common gasketing materials. This cost must be weighed against the performance benefits and the potential cost of a seal failure.
Making the Right Choice for Your Sealing Application
Selecting the correct gasket requires matching the material's properties to the specific demands of the equipment and process.
- If your primary focus is sealing old, damaged, or lightweight flanges: ePTFE is the ideal choice due to its outstanding compressibility and ability to conform to surface imperfections.
- If your primary focus is preventing product contamination in food or pharma: The chemical inertness and non-contaminating properties of ePTFE make it a safe and reliable option.
- If your primary focus is managing extreme pressures or temperatures: You must carefully verify that your application's requirements fall within ePTFE's specified limits and consider more robust materials if they do not.
Ultimately, understanding that ePTFE's value comes from its manufactured fibrous structure is the key to deploying it effectively for demanding sealing challenges.
Summary Table:
| Property | Standard PTFE | Expanded PTFE (ePTFE) |
|---|---|---|
| Structure | Solid, rigid | Porous, fibrous, flexible |
| Conformability | Low | Excellent (conforms to imperfections) |
| Creep/Cold Flow Resistance | Susceptible | Superior resistance |
| Primary Advantage | Chemical inertness | Adaptability and seal integrity |
| Ideal For | Standard flanges | Irregular, scratched, or delicate flanges |
Need a reliable seal for challenging surfaces?
At KINTEK, we specialize in manufacturing high-performance PTFE components, including precision-cut expanded PTFE gaskets. Our custom fabrication process, from prototypes to high-volume orders, ensures you get the exact sealing solution for your application in the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, or industrial sectors.
Let us help you solve your toughest sealing challenges. Contact our experts today for a consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Customizable PTFE Seals Filter Holders for Versatile Applications
People Also Ask
- How does a PTFE lined wafer check valve function? A Guide to Reliable Backflow Prevention
- How does the built-in spring compensate for wear in PTFE shaft seals? Ensure Long-Term Sealing Reliability
- What are some examples of electrical insulation products that can be made from PTFE? High-Performance Solutions for Demanding Applications
- How does a PTFE Lined Ball Valve function? Achieve Reliable Flow Control in Corrosive Environments
- Why is material selection critical for valve seat performance? Ensure Long-Term Reliability and Prevent Leaks
- What are the specifications of a high-pressure, low-speed PTFE seal profile? Handle 3,000 psi with Confidence
- What is the function of PTFE lined check valves? Ensure Unidirectional Flow and Corrosion Resistance
- How do PTFE O-Rings perform under high heat conditions? Achieve Extreme Temperature Sealing



















