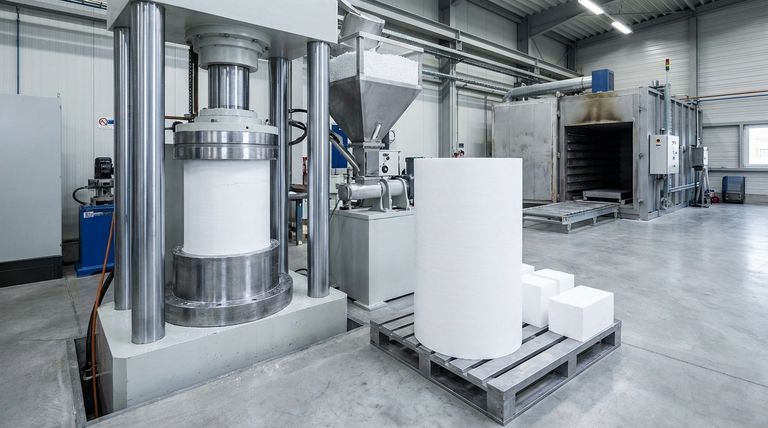
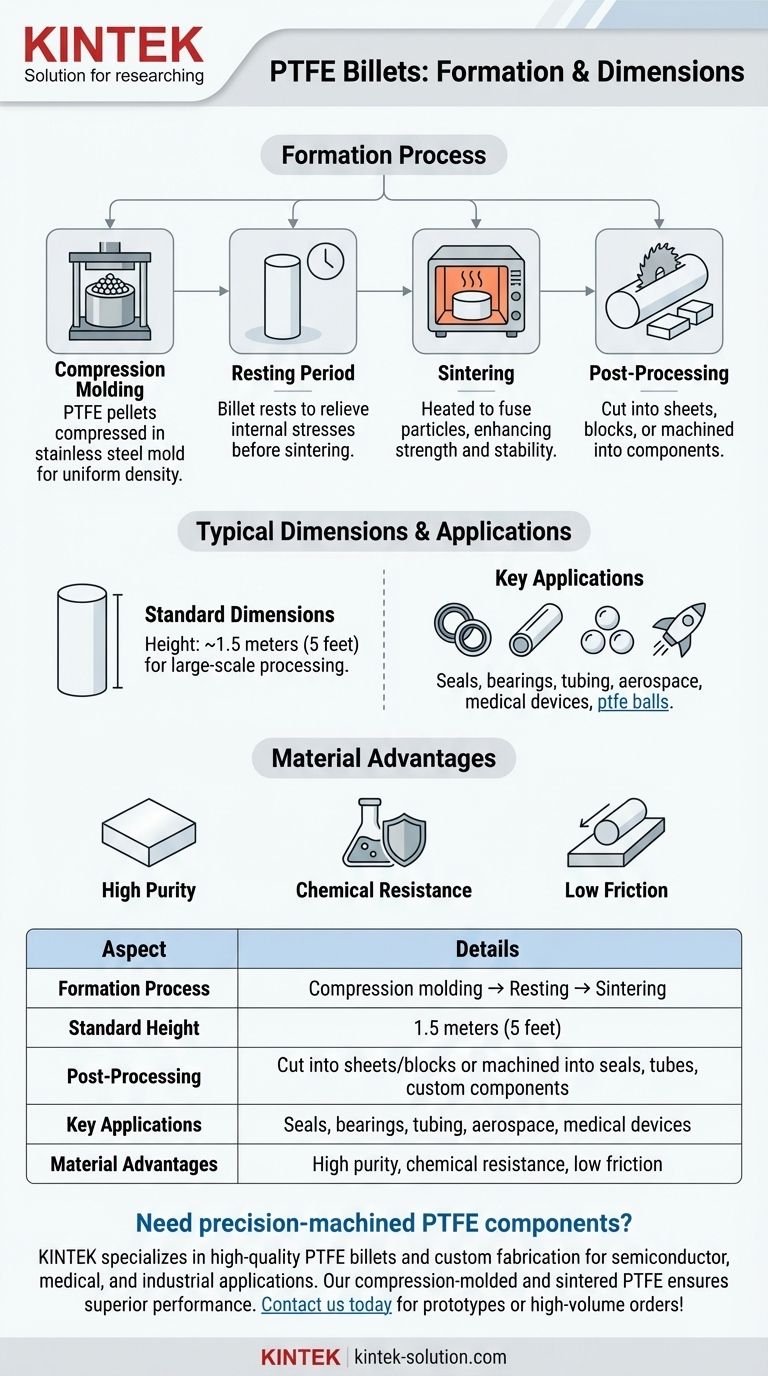
PTFE billets are formed through a process involving compression molding and sintering, starting with PTFE pellets poured into cylindrical molds and compressed under hydraulic pressure. After removal from the mold, the material rests before sintering, resulting in large billets typically 1.5 meters tall. These billets are then cut into sheets or smaller blocks for further machining or processing into products like ptfe balls, seals, or tubes.

Key Points Explained:
-
Formation Process of PTFE Billets
- Compression Molding: PTFE pellets are poured into a cylindrical stainless steel mold and compressed using a hydraulic press with a weighted ram. This step ensures uniform density and eliminates voids.
- Resting Period: After compression, the mold is removed, and the PTFE billet is allowed to rest. This helps relieve internal stresses before sintering.
- Sintering: The billet is heated in an oven to fuse the PTFE particles, enhancing mechanical strength and thermal stability.
-
Typical Dimensions of PTFE Billets
- Standard Height: Billets are commonly 5 feet (1.5 meters) tall, making them suitable for large-scale industrial processing.
- Post-Processing: These billets can be cut into sheets, blocks, or machined into specialized components like seals, tubes, or ptfe balls.
-
Applications & Further Processing
- Machining: Billets are often CNC-machined into seals with tight tolerances, available in standard and custom sizes (diameters from 1/32 to 150 inches).
- Extrusion: For tubing, PTFE is processed via paste or ram extrusion, yielding thin-walled (under 2mm) or thick-walled (2–5mm) tubes for electrical insulation.
-
Material Considerations
- PTFE’s low friction and chemical resistance make it ideal for seals, bearings, and ptfe balls.
- The billet-forming process ensures high purity and structural integrity, critical for demanding applications like aerospace or medical devices.
By understanding these steps and dimensions, purchasers can better assess billet suitability for their specific machining or fabrication needs.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Formation Process | Compression molding → Resting → Sintering |
| Standard Height | 1.5 meters (5 feet) |
| Post-Processing | Cut into sheets/blocks or machined into seals, tubes, or custom components |
| Key Applications | Seals, bearings, tubing, aerospace, medical devices |
| Material Advantages | High purity, chemical resistance, low friction |
Need precision-machined PTFE components? KINTEK specializes in high-quality PTFE billets and custom fabrication for industries like semiconductor, medical, and industrial applications. Our compression-molded and sintered PTFE ensures superior performance in seals, liners, and labware. Contact us today for prototypes or high-volume orders!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Customizable PTFE Rods for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Bottles for Diverse Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What are the special features of PTFE that make it suitable for medical applications? Unlock Superior Biocompatibility & Performance
- How are PTFE seals used in medical device and life sciences applications? Essential for Sterility & Precision
- What are PTFE envelope gaskets? The Ultimate Sealing Solution for Corrosive Environments
- Why are PTFE washers considered cost-effective despite their higher initial cost? Maximize ROI with Long-Term Savings
- What are the typical structural designs of PTFE oil seals? A Guide to Spring-Energized, Filled, and Multi-Lip Seals
- In what medical applications are PTFE Liners commonly used? Enhancing Device Performance & Patient Safety
- What are the key properties of PTFE industrial coating? Discover Unmatched Performance for Demanding Industries
- What makes PTFE gaskets ideal for marine applications? Superior Sealing for Harsh Saltwater Environments



















