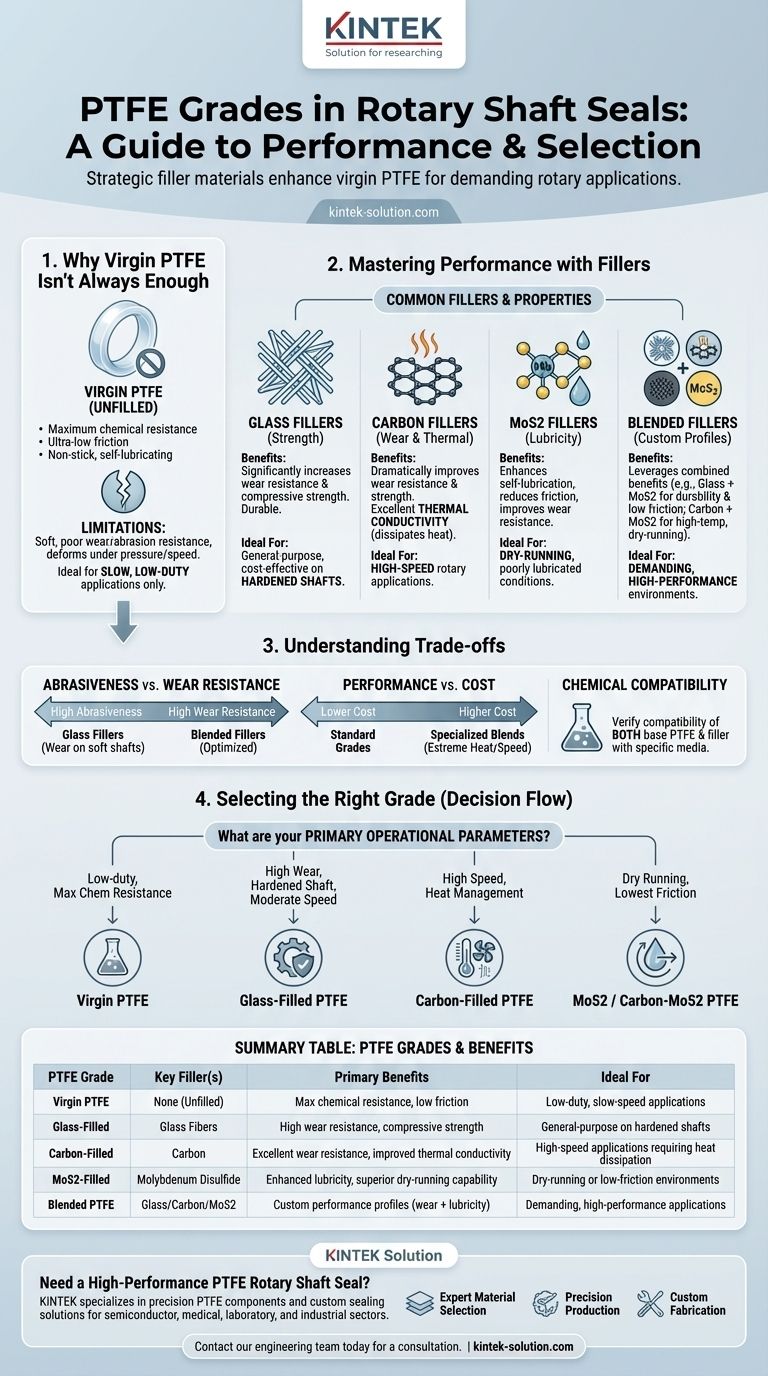
The primary grades of PTFE used in rotary shaft seals are distinguished by the filler materials blended with the base polymer to enhance specific properties. The most common grades include virgin (unfilled) PTFE, glass-filled, carbon-filled, Molybdenum Disulfide (MoS2)-filled, and various combinations of these fillers, each engineered to solve a different operational challenge.
The choice of PTFE grade is a critical engineering decision. While pure, virgin PTFE offers unmatched chemical resistance and low friction, it is the strategic addition of fillers like glass, carbon, and MoS2 that unlocks the high-performance capabilities—such as wear resistance, thermal conductivity, and dry-running ability—required for demanding rotary applications.

Why Pure PTFE Isn't Always Enough
Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is a remarkable polymer, but its base form has inherent limitations. Understanding these is key to appreciating the role of fillers.
The Strengths of Virgin PTFE
Virgin PTFE is an excellent choice for applications where its core properties are paramount. It boasts exceptional chemical inertness across a vast range of media and possesses one of the lowest coefficients of friction of any solid material.
Its non-stick, self-lubricating nature makes it inherently suitable for sealing.
The Limitations of Virgin PTFE
However, virgin PTFE is relatively soft and has poor resistance to wear and abrasion. Under significant pressure or at high rotational speeds, it can deform and wear out quickly.
This limits its use to slow, low-duty applications where mechanical stress is minimal.
A Guide to Common PTFE Fillers and Their Properties
Fillers are added to the PTFE matrix to enhance its mechanical properties, transforming it into a robust material capable of handling extreme conditions.
Glass Fillers: For Enhanced Strength
Adding glass fibers is one of the most common methods to improve the mechanical properties of PTFE.
This filler significantly increases wear resistance and compressive strength, making the seal more durable. It is a cost-effective way to boost performance in many general-purpose applications.
Carbon Fillers: For Wear and Thermal Conductivity
Carbon is another popular filler that dramatically improves wear resistance and strength, often without increasing friction as much as other fillers might.
Crucially, carbon also improves thermal conductivity. This allows the seal to dissipate frictional heat more effectively, making it ideal for high-speed rotary applications.
Molybdenum Disulfide (MoS2): The Lubricity Enhancer
Molybdenum Disulfide (MoS2) is a dry-film lubricant that enhances the self-lubricating properties of PTFE.
It reduces friction and improves wear resistance, especially in dry-running or poorly lubricated conditions. MoS2 is often used for higher-duty applications where minimizing friction is critical.
Blended Fillers: Achieving Specific Performance Profiles
For the most demanding environments, fillers are often combined to leverage the benefits of each.
A glass and MoS2 blend combines the high wear resistance of glass with the low friction of MoS2. This creates a durable seal that is less abrasive to the shaft than a purely glass-filled compound.
A carbon and MoS2 blend is a high-performance option that offers excellent wear resistance, high-temperature capability, and superior dry-running performance.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Selecting a PTFE grade is an exercise in balancing competing properties. No single formula is perfect for every situation.
Abrasiveness vs. Wear Resistance
While glass fillers provide excellent wear resistance for the seal itself, they can be abrasive to softer shaft materials. To prevent premature shaft wear, glass-filled seals should be run on a hardened shaft.
Performance vs. Cost
Highly specialized compounds, such as those with polyimide or blended carbon and MoS2, offer superior performance in extreme heat or high-speed conditions. However, this performance comes at a higher unit cost compared to more common glass or carbon-filled grades.
Chemical Compatibility
Although base PTFE is almost universally inert, some fillers can have slightly reduced chemical resistance in certain aggressive media. It is essential to verify the compatibility of both the base polymer and the filler with the application's specific chemical environment.
Selecting the Right Grade for Your Application
The optimal grade is determined entirely by your specific operational parameters, including speed, pressure, temperature, and media.
- If your primary focus is low-duty sealing with maximum chemical resistance: Virgin PTFE is the most suitable and cost-effective choice.
- If you need high wear resistance for a hardened shaft at moderate speeds: Glass-filled PTFE provides an excellent balance of durability and cost.
- If you are dealing with high speeds and need to manage heat: Carbon-filled PTFE excels at dissipating heat while providing great wear resistance.
- If your application involves dry running or requires the lowest possible friction: An MoS2-filled or Carbon/MoS2-filled grade is the ideal solution.
By matching the filler material to your specific operational challenges, you ensure the reliability and longevity of your rotary shaft seal.
Summary Table:
| PTFE Grade | Key Filler(s) | Primary Benefits | Ideal For |
|---|---|---|---|
| Virgin PTFE | None (Unfilled) | Maximum chemical resistance, low friction | Low-duty, slow-speed applications |
| Glass-Filled PTFE | Glass Fibers | High wear resistance, compressive strength | General-purpose use on hardened shafts |
| Carbon-Filled PTFE | Carbon | Excellent wear resistance, improved thermal conductivity | High-speed applications requiring heat dissipation |
| MoS2-Filled PTFE | Molybdenum Disulfide | Enhanced lubricity, superior dry-running capability | Dry-running or low-friction environments |
| Blended PTFE | Glass/Carbon/MoS2 Combos | Custom performance profiles (e.g., wear + lubricity) | Demanding, high-performance applications |
Need a High-Performance PTFE Rotary Shaft Seal?
Selecting the right PTFE grade is critical for the reliability and longevity of your equipment. The wrong material can lead to premature failure and costly downtime.
KINTEK specializes in manufacturing precision PTFE components, including custom rotary shaft seals. We help engineers in the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors solve their toughest sealing challenges.
We provide:
- Expert Material Selection: Our team will help you choose the optimal PTFE grade (virgin, glass-filled, carbon-filled, MoS2, or a custom blend) based on your specific speed, pressure, temperature, and media.
- Precision Production: We manufacture seals to exacting tolerances for consistent, reliable performance.
- Custom Fabrication: From prototype development to high-volume production runs, we deliver solutions tailored to your application.
Ensure your equipment operates at peak performance. Contact our engineering team today for a consultation on your custom PTFE seal requirements.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
- Customizable PTFE Rods for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
People Also Ask
- Why is PTFE rod suitable for automotive applications? Boost Vehicle Performance & Durability
- What are the main advantages of using PTFE parts in industrial applications? Unlock Unmatched Chemical Resistance and Reliability
- What tips can improve Teflon machining results? Master Sharp Tools, Heat Control, and Rigid Support
- How does PTFE contribute to low friction and wear resistance? Achieve Superior Performance with Advanced Materials
- What industries use PTFE machined parts and for what applications? Critical Components for Demanding Environments



















