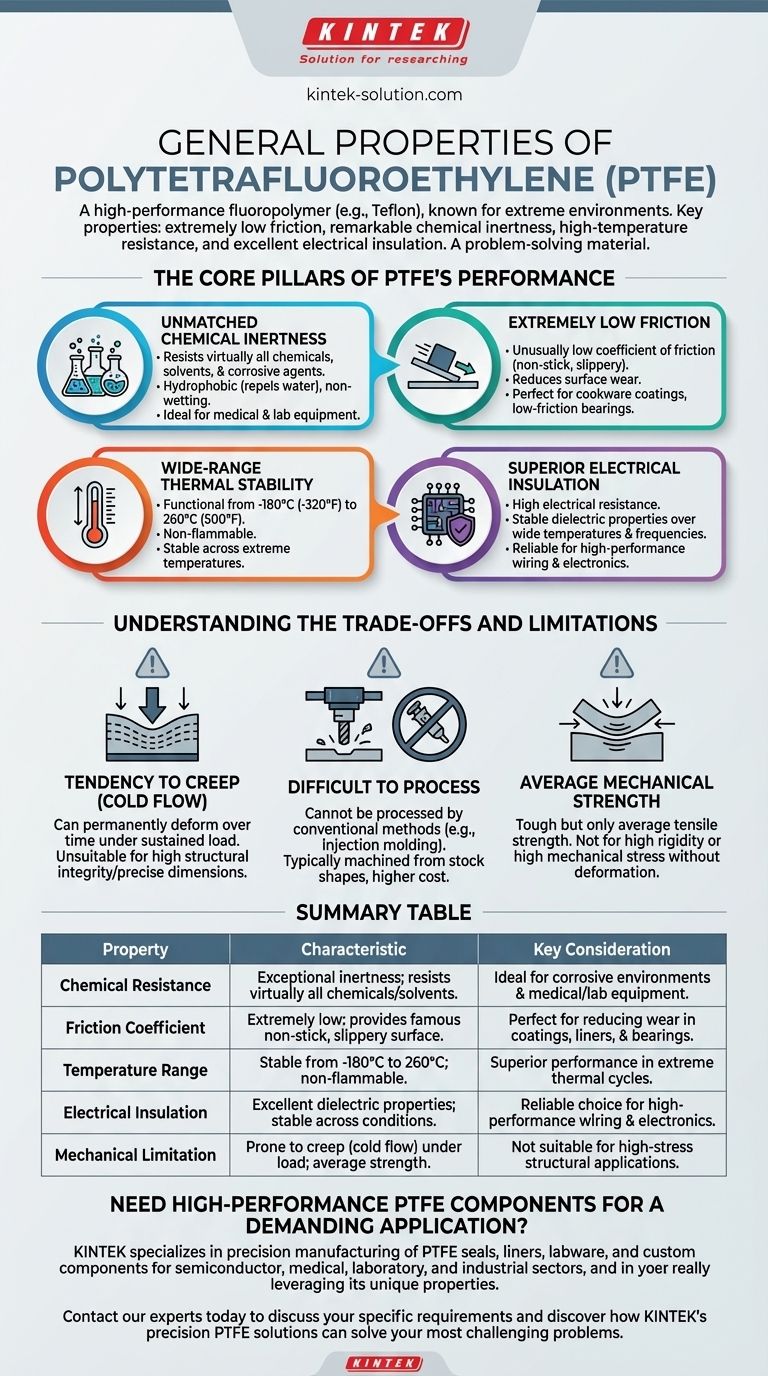
In short, Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is a high-performance fluoropolymer, widely known by the trade name Teflon. Its primary properties are an extremely low coefficient of friction, remarkable chemical inertness, high-temperature resistance, and excellent electrical insulation. This unique combination makes it an indispensable material for challenging industrial, medical, and commercial applications.
PTFE is best understood as a problem-solving material for extreme environments. Its value comes from its ability to simultaneously resist heat, chemicals, and surface adhesion where most other materials would fail, but this performance comes with trade-offs in mechanical strength and processing difficulty.

The Core Pillars of PTFE's Performance
PTFE's reputation is built on a few standout characteristics that make it unique among polymers. Understanding these is key to understanding its applications.
Unmatched Chemical Inertness
PTFE has exceptional resistance to virtually all chemicals, solvents, and corrosive agents. This high chemical stability means it does not react with the substances it contacts.
It is also hydrophobic, meaning it repels water and is non-wetting. This property, combined with its chemical inertness, makes it ideal for use in medical and laboratory equipment.
Extremely Low Friction
The material possesses an unusually low coefficient of friction, believed to be lower than any other solid. This gives it its famous non-stick and "slippery" quality.
This characteristic is crucial for applications where reducing surface wear is a priority, such as in non-stick coatings for cookware or as a component in low-friction bearings.
Wide-Range Thermal Stability
PTFE is an outstanding performer across an incredibly wide temperature range. It remains functional and stable from cryogenic conditions of -180°C (-320°F) up to high temperatures of 260°C (500°F).
Furthermore, the material is non-flammable, adding another layer of safety and stability in high-temperature applications.
Superior Electrical Insulation
PTFE is an excellent electrical insulator with high resistance to the passage of electric current.
Crucially, its insulating properties remain stable and effective over a wide spectrum of temperatures and frequencies, making it a reliable choice for high-performance wiring and electronics.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While its core properties are exceptional, PTFE is not a universal solution. Its mechanical characteristics and processing requirements present significant trade-offs.
Tendency to Creep (Cold Flow)
PTFE is a relatively soft, non-resilient material. A key limitation is its tendency to creep or "cold flow," meaning it can permanently deform over time when subjected to a sustained load.
This makes standard PTFE unsuitable for applications requiring high structural integrity or precise dimensional stability under compression.
Difficult to Process
Due to its high melt temperature and viscosity, PTFE cannot be processed using conventional methods like injection molding or extrusion.
It is typically machined from stock shapes (rods, sheets) into its final form. This process makes individual PTFE components significantly more expensive than mass-produced plastic parts.
Average Mechanical Strength
While considered tough and flexible, PTFE only possesses average tensile strength. It is not a material chosen for its rigidity or ability to withstand high mechanical stress without deformation.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting PTFE is about leveraging its unique strengths for specific, demanding scenarios where conventional materials are inadequate.
- If your primary focus is extreme chemical or thermal environments: PTFE is an elite choice due to its chemical inertness and vast operating temperature range.
- If your primary focus is reducing friction and wear: Its unparalleled low-friction, non-stick surface makes it ideal for coatings, linings, and self-lubricating parts.
- If your primary focus is high-frequency electrical insulation: Its stable dielectric properties across a wide temperature range make it a superior insulator.
- If your primary focus is structural integrity under load: You should proceed with caution and consider filled grades of PTFE or alternative materials due to its tendency to creep.
Ultimately, PTFE should be chosen for its unique combination of resistances when performance in a challenging environment is the most critical factor.
Summary Table:
| Property | Characteristic | Key Consideration |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Resistance | Exceptional inertness; resists virtually all chemicals and solvents. | Ideal for corrosive environments and medical/lab equipment. |
| Friction Coefficient | Extremely low; provides famous non-stick, slippery surface. | Perfect for reducing wear in coatings, liners, and bearings. |
| Temperature Range | Stable from -180°C to 260°C; non-flammable. | Superior performance in extreme thermal cycles. |
| Electrical Insulation | Excellent dielectric properties stable across temperatures/frequencies. | Reliable choice for high-performance wiring and electronics. |
| Mechanical Limitation | Prone to creep (cold flow) under sustained load; average tensile strength. | Not suitable for high-stress structural applications without modification. |
Need High-Performance PTFE Components for a Demanding Application?
At KINTEK, we specialize in precision manufacturing of PTFE seals, liners, labware, and custom components. We understand how to leverage PTFE's unique properties—like its chemical inertness and thermal stability—while expertly managing its limitations for applications in the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors.
Whether you require prototypes or high-volume orders, our custom fabrication expertise ensures you get the right part for your extreme environment.
Contact our experts today to discuss your specific requirements and discover how KINTEK's precision PTFE solutions can solve your most challenging problems.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Customizable PTFE Rods for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Volumetric Flasks for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Use
People Also Ask
- How does PTFE compare to Polyethylene (PE) in terms of chemical and temperature resistance? Choose the Right Polymer for Extreme Conditions
- What are the challenges in processing PTFE? Overcoming High Melt Viscosity and Machining Difficulties
- What is PTFE and what is its commercial name? A Guide to Teflon and ePTFE
- What significant discovery about PTFE was made in the 1990s? Unlock Enhanced Performance with Radiation Cross-Linking
- What are the key features of PTFE laminated fabric? Unmatched Protection & Breathability
- Is PTFE the same as Teflon? Understanding the Brand vs. Material Distinction
- How does Teflon demonstrate superior chemical resistance? Unlocking Its Molecular Fortress
- How is PTFE synthesized? From TFE Gas to High-Performance Polymer



















