The short answer is that Teflon's superior chemical resistance stems from its unique molecular structure. The exceptionally strong chemical bond between its carbon and fluorine atoms, combined with a protective "sheath" of fluorine atoms shielding the carbon backbone, creates a highly stable, non-reactive surface that is impervious to nearly all common acids, bases, and solvents.
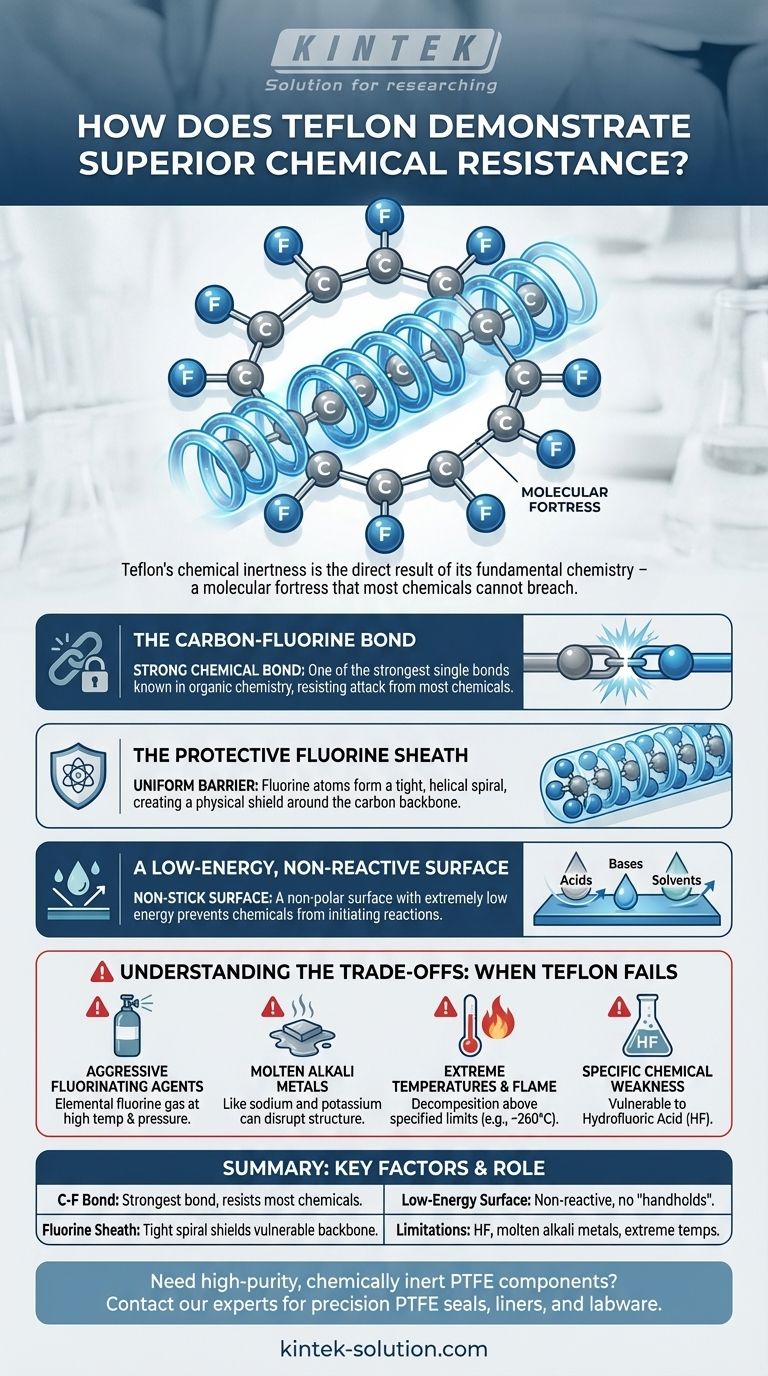
Teflon’s chemical inertness is not a feature added to the material, but the direct result of its fundamental chemistry. The strength of the carbon-fluorine bond creates a molecular fortress that most chemicals simply cannot breach.

The Molecular Basis of Teflon's Inertness
To truly understand Teflon's resilience, we must look at its structure at the atomic level. Its properties are not accidental; they are a direct consequence of its chemical makeup, specifically Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE).
The Carbon-Fluorine Bond
At the heart of Teflon's strength is the carbon-fluorine (C-F) bond. This is one of the strongest single bonds known in organic chemistry.
Breaking this bond requires a significant amount of energy. Most chemicals, including highly corrosive acids and bases, do not have enough reactive energy to sever it, so they simply fail to react with the Teflon molecule.
The Protective Fluorine Sheath
The fluorine atoms are larger than the carbon atoms they are bonded to. This causes them to arrange themselves in a tight, helical spiral around the carbon chain.
This formation creates a uniform, non-polar protective sheath. This physical barrier effectively armors the more vulnerable carbon backbone, preventing chemicals from ever getting close enough to attack it.
A Low-Energy, Non-Reactive Surface
The fluorine sheath also creates a surface with extremely low energy. This is why Teflon is famously non-stick; there's very little for other substances to adhere to.
This same principle applies to chemicals. Corrosive agents slide off the surface at a molecular level because there are no "handholds" to initiate a chemical reaction.
Understanding the Trade-offs: When Teflon Fails
While its resistance is vast, it is not absolute. Understanding Teflon's specific vulnerabilities is critical for its safe and effective use in demanding technical applications.
Aggressive Fluorinating Agents
Certain chemicals, such as elemental fluorine gas at high temperatures and pressures, are reactive enough to attack and break the carbon-fluorine bonds, causing the material to degrade.
Molten Alkali Metals
Highly reactive molten alkali metals, like sodium and potassium, are among the few substances that can disrupt Teflon's structure. They are able to strip fluorine atoms from the polymer chain.
Extreme Temperatures and Flame
Teflon has an upper service temperature limit (e.g., around 260°C or 500°F for PFA grade). Exposing it to direct flame or temperatures above this threshold will cause it to decompose.
Specific Chemical Weaknesses
Despite its broad resistance, Teflon is notably vulnerable to hydrofluoric acid (HF). This specific exception is a critical design consideration in industries that handle this particular chemical.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Ultimately, selecting the right material depends on a clear understanding of its strengths and, more importantly, its limitations.
- If your primary focus is general chemical processing: Teflon is an exceptionally reliable choice for handling the vast majority of common acids, bases, solvents, and industrial chemicals.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature stability: You must verify that your application's operating temperatures remain safely below Teflon's specified decomposition point.
- If your primary focus is handling exotic or highly reactive agents: You must confirm your process does not involve Teflon's specific weaknesses, such as hydrofluoric acid, molten alkali metals, or strong fluorinating agents.
Choosing the correct material for a demanding environment begins with understanding its fundamental chemistry.
Summary Table:
| Key Factor | Role in Chemical Resistance |
|---|---|
| Carbon-Fluorine Bond | One of the strongest bonds in organic chemistry, resisting attack from most chemicals. |
| Protective Fluorine Sheath | A tight spiral of fluorine atoms shields the vulnerable carbon backbone. |
| Low-Energy Surface | Creates a non-stick, non-reactive surface that offers no "handholds" for chemical reactions. |
| Limitations | Vulnerable to hydrofluoric acid, molten alkali metals, and extreme temperatures. |
Need high-purity, chemically inert PTFE components for your critical application?
At KINTEK, we specialize in manufacturing precision PTFE seals, liners, and labware for the semiconductor, medical, and laboratory industries. Our custom fabrication services, from prototypes to high-volume orders, ensure you get components that deliver the superior chemical resistance your processes demand.
Contact our experts today to discuss your specific requirements and leverage our material science expertise for your project.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Volumetric Flasks for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Use
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
People Also Ask
- What are the environmental properties of PTFE? Balancing Performance with Sustainability
- What does PTFE stand for and what are its primary characteristics? | The Ultimate High-Performance Polymer
- What are some alternative materials to Teflon and their properties? Find the Right High-Performance Polymer for Your Application
- Why is PTFE used in the chemical processing industry? Ensure Safety and Reliability in Harsh Environments
- What significant discovery about PTFE was made in the 1990s? Unlock Enhanced Performance with Radiation Cross-Linking
- What certifications does the manufacturer of PTFE products hold? The ISO 9001 Assurance for Quality
- What are the key properties of PTFE? A Guide to Its High-Performance Versatility
- How does Teflon's electrical insulation property benefit its applications? Achieve Unmatched Reliability in Extreme Conditions



















