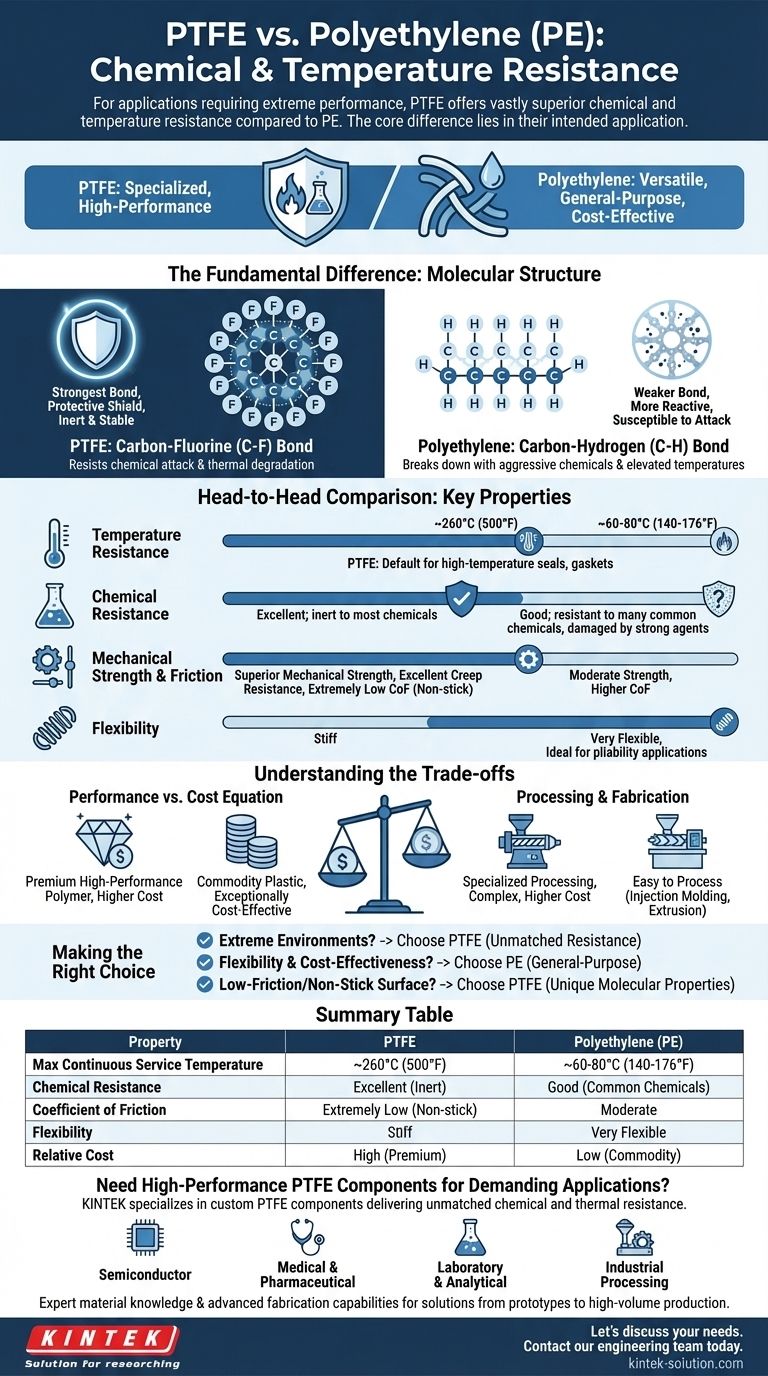
For applications requiring extreme performance, Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) offers vastly superior chemical and temperature resistance compared to Polyethylene (PE). PTFE's unique molecular structure makes it nearly inert and stable across a wide temperature range where PE would quickly degrade. PE, however, is a more flexible and cost-effective material suitable for less demanding environments.
The core difference lies in their intended application: PTFE is a specialized, high-performance polymer for extreme chemical and thermal environments, while Polyethylene is a versatile, general-purpose plastic valued for its flexibility and cost-efficiency.
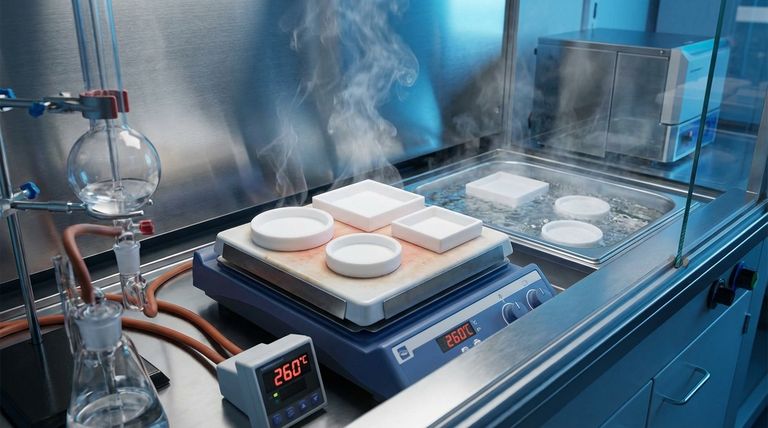

The Fundamental Difference: Molecular Structure
The dramatic gap in performance between PTFE and PE originates from their core chemistry. Understanding this is key to selecting the right material.
PTFE's Carbon-Fluorine Bond
PTFE consists of a carbon chain completely surrounded by fluorine atoms. The carbon-fluorine (C-F) bond is one of the strongest known in organic chemistry.
This incredibly stable bond acts as a protective shield, preventing chemicals from reacting with the carbon backbone and resisting degradation from thermal energy.
Polyethylene's Carbon-Hydrogen Bond
Polyethylene is made of a simple carbon chain bonded with hydrogen atoms. The carbon-hydrogen (C-H) bond is significantly weaker and more reactive than the C-F bond.
This makes the polymer more susceptible to attack from aggressive chemicals and breakdown at elevated temperatures.
Head-to-Head Comparison: Key Properties
While both are common plastics, their operational capabilities are worlds apart.
Temperature Resistance
PTFE has a much higher melting point and continuous service temperature than PE. It can operate in environments where PE would melt or lose all structural integrity.
This makes PTFE the default choice for high-temperature seals, gaskets, and linings.
Chemical Resistance
PTFE is renowned for being one of the most chemically inert substances known. It resists nearly all industrial chemicals, acids, and bases.
Polyethylene offers good resistance to many common chemicals but can be damaged by strong oxidizing agents and certain organic solvents.
Mechanical Strength and Friction
PTFE has superior mechanical strength and excellent creep resistance, meaning it resists deforming under a sustained load.
It also possesses an extremely low coefficient of friction, giving it the famous non-stick quality used in cookware and low-friction bearings.
Flexibility
Polyethylene is significantly more flexible and less dense than PTFE. This makes it ideal for applications requiring pliability, such as squeeze bottles, plastic bags, and tubing.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a material is never just about performance; it's about balancing performance with practicality and cost.
The Performance vs. Cost Equation
There is a significant cost difference between the two materials. PTFE is a premium, high-performance polymer, and its price reflects its advanced capabilities.
Polyethylene is a commodity plastic produced in massive volumes, making it exceptionally cost-effective for a wide range of everyday applications.
Processing and Fabrication
Polyethylene is relatively easy to process using common methods like injection molding and extrusion.
PTFE, due to its high melting point and viscosity, requires specialized processing techniques, which can add to the complexity and cost of manufacturing parts.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your final decision must be guided by the specific demands of your project.
- If your primary focus is extreme environments: Choose PTFE for its unmatched resistance to high temperatures and aggressive chemicals.
- If your primary focus is flexibility and cost-effectiveness: Choose Polyethylene for general-purpose applications where conditions are not demanding.
- If your primary focus is a low-friction or non-stick surface: Choose PTFE, as its unique molecular properties are essential for these applications.
Ultimately, selecting the correct polymer requires aligning the material's inherent capabilities with the precise challenges of its intended environment.
Summary Table:
| Property | PTFE | Polyethylene (PE) |
|---|---|---|
| Max Continuous Service Temperature | ~260°C (500°F) | ~60-80°C (140-176°F) |
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent; inert to most chemicals | Good; resistant to many common chemicals |
| Coefficient of Friction | Extremely Low (Non-stick) | Moderate |
| Flexibility | Stiff | Very Flexible |
| Relative Cost | High (Premium Polymer) | Low (Commodity Plastic) |
Need High-Performance PTFE Components for Demanding Applications?
Choosing the right material is critical for the success and safety of your project. At KINTEK, we specialize in the precision manufacturing of custom PTFE components—including seals, liners, and labware—that deliver unmatched chemical and thermal resistance.
We serve a wide range of specialized industries, including:
- Semiconductor
- Medical & Pharmaceutical
- Laboratory & Analytical
- Industrial Processing
Our value to you: We combine expert material knowledge with advanced fabrication capabilities to provide solutions from prototypes to high-volume production runs, ensuring your components meet the most stringent performance requirements.
Let's discuss your specific needs. Contact our engineering team today for a consultation and quote.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
People Also Ask
- What is PTFE commonly known as and what are its unique properties? Unlock Unmatched Chemical & Thermal Resistance
- What are some common applications of machined PTFE? Leverage its Unique Properties for Demanding Applications
- What are the unique properties of PTFE? Unlock Unmatched Performance in Demanding Applications
- What is the working temperature range of PTFE? Master Extreme Heat and Cryogenic Applications
- What are the best practices for achieving tight tolerances in Teflon (PTFE) machining? Master Precision for Demanding Applications



















