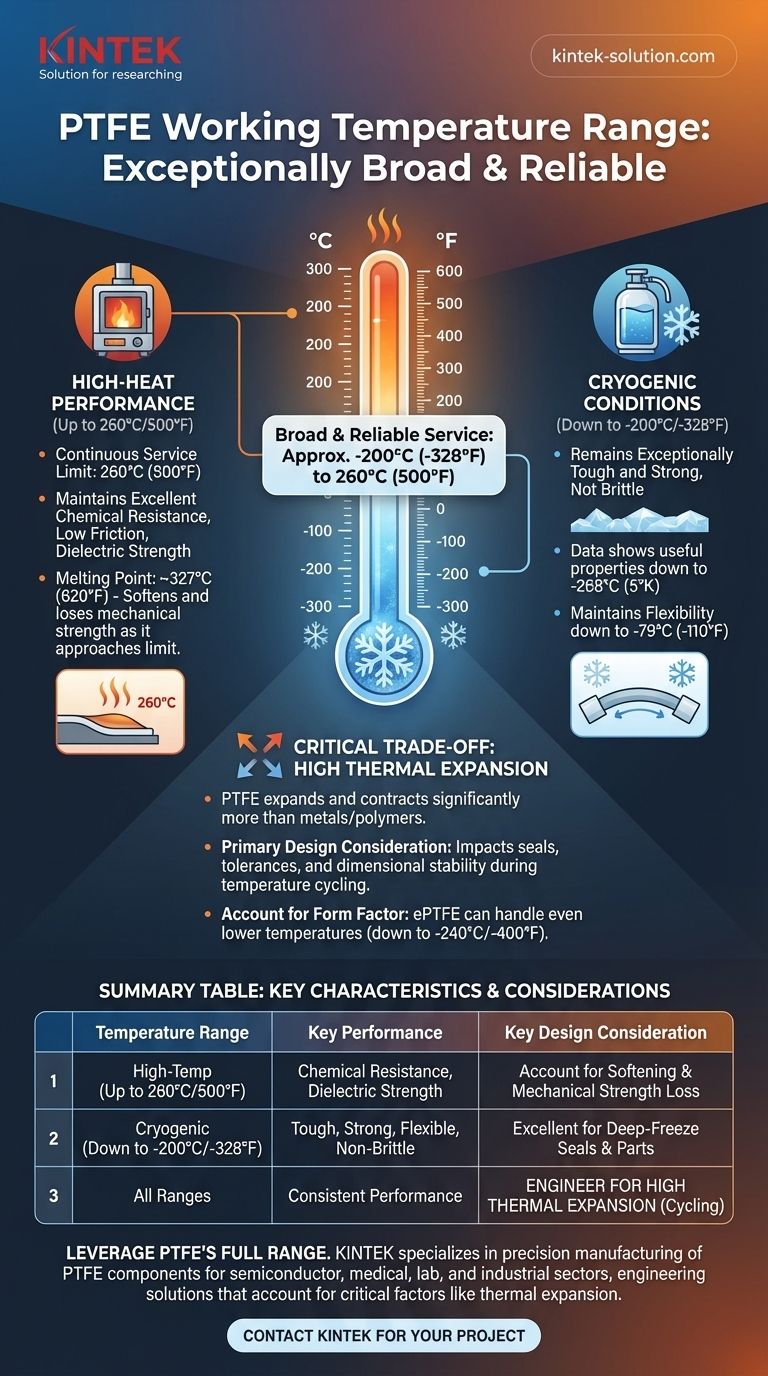
In short, the working temperature range of Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is exceptionally broad. It reliably performs in continuous service from approximately -200°C (-328°F) up to 260°C (500°F). This remarkable stability makes it one of the few materials suitable for both extreme cryogenic and high-heat industrial applications.
The key takeaway is not just the wide temperature range, but PTFE's consistent performance across it. While it excels at both temperature extremes, its high rate of thermal expansion is a critical design constraint that must be managed for any application involving significant temperature changes.

Understanding PTFE's High-Temperature Limit
The upper limit of PTFE's working range is defined by its ability to retain its unique physical properties under heat stress, not just by its melting point.
The Continuous Service Temperature
The most important figure for engineers is the maximum continuous service temperature of 260°C (500°F). Below this temperature, PTFE maintains its excellent chemical resistance, low-friction surface, and dielectric strength without significant degradation over time.
The Melting Point Distinction
PTFE's actual melting point is much higher, around 327°C (620°F). However, as the material approaches its service limit of 260°C, it begins to soften, and its mechanical properties (like tensile strength) will decrease. Operating above this recommended temperature will lead to accelerated wear and a loss of structural integrity well before it melts.
Performance in Cryogenic Conditions
PTFE's performance at low temperatures is just as impressive as its heat resistance. It does not become brittle in the same way many other polymers do.
Retaining Strength and Toughness
Even at extreme cryogenic temperatures, PTFE remains exceptionally tough and strong. Data shows it maintains useful properties and self-lubrication at temperatures as low as -268°C (5°K), making it a preferred material for cryogenic seals and components.
Maintaining Flexibility
While it becomes harder at lower temperatures, PTFE retains good flexibility down to -79°C (-110°F). This ensures that seals and moving parts continue to function effectively in deep-freeze environments.
The Critical Trade-off: Thermal Expansion
Understanding the temperature range is only half the story. The most significant challenge when designing with PTFE is its high coefficient of thermal expansion.
A High Rate of Expansion and Contraction
PTFE expands and contracts with temperature changes far more than metals or many other polymers. This means a precisely machined PTFE part at room temperature will have significantly different dimensions at its upper or lower service temperature.
Impact on Seals and Tolerances
This property is a primary design consideration. In a sealing application, a part that fits perfectly at 20°C may become too loose at -100°C or too tight at 200°C, compromising its function. This is why temperature swings should be carefully managed.
Accounting for Form Factor
The form of the material also matters. For example, expanded PTFE (ePTFE), a more porous version, can often handle even lower temperatures, with some grades rated down to -240°C (-400°F).
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting a material requires balancing its capabilities with the demands of the environment.
- If your primary focus is high-heat processes: PTFE is a reliable choice for continuous use up to 260°C (500°F), but you must account for its gradual softening as it approaches this limit.
- If your primary focus is cryogenic applications: PTFE is an excellent material, retaining its strength and integrity at temperatures where most plastics fail.
- If your design involves significant temperature cycling: You must engineer your design to accommodate PTFE's high thermal expansion to ensure seals remain effective and dimensional stability is maintained.
By understanding how PTFE behaves across its entire operational range, you can confidently leverage its unique properties for the most demanding applications.
Summary Table:
| Temperature Range | Key Performance Characteristics | Key Design Consideration |
|---|---|---|
| High-Temperature: Up to 260°C (500°F) | Maintains chemical resistance and dielectric strength. Softens near the limit. | Account for softening and potential loss of mechanical strength. |
| Cryogenic: Down to -200°C (-328°F) | Remains tough, strong, and flexible; does not become brittle. | Excellent for seals and parts in deep-freeze environments. |
| Critical Factor for All Ranges | Consistent performance across the entire spectrum. | High thermal expansion must be engineered into the design for temperature cycling. |
Leverage PTFE's Full Temperature Range for Your Critical Components
Understanding PTFE's behavior from -200°C to 260°C is crucial for applications in the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. At KINTEK, we specialize in precision manufacturing of PTFE components like seals, liners, and custom labware. We engineer solutions that not only withstand extreme temperatures but also account for critical factors like thermal expansion to ensure reliability and longevity.
Whether you need a prototype or a high-volume order, our expertise ensures your PTFE parts perform flawlessly.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss your specific requirements and get a quote for your project.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
- Customizable PTFE Rods for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What are the base characteristics of PTFE? Unlocking Extreme Performance in Friction, Temperature, and Chemical Resistance
- What are the primary applications of PTFE fasteners and custom parts? Critical Solutions for Extreme Environments
- Why is PTFE suitable for cryogenic or high-temperature applications? Unmatched Thermal Stability from -450°F to 500°F
- What are the unique properties of PTFE? Unlock Unmatched Performance in Demanding Applications
- What are the key benefits of PTFE in custom fabrication? Unlock Performance in Extreme Conditions



















