In short, adding fillers to PTFE enhances its physical properties, primarily by improving mechanical strength, wear resistance, and thermal conductivity. While pure PTFE is known for its low friction and chemical inertness, it is mechanically weak and prone to deforming under load; fillers are introduced to overcome these limitations and create a more robust engineering material.
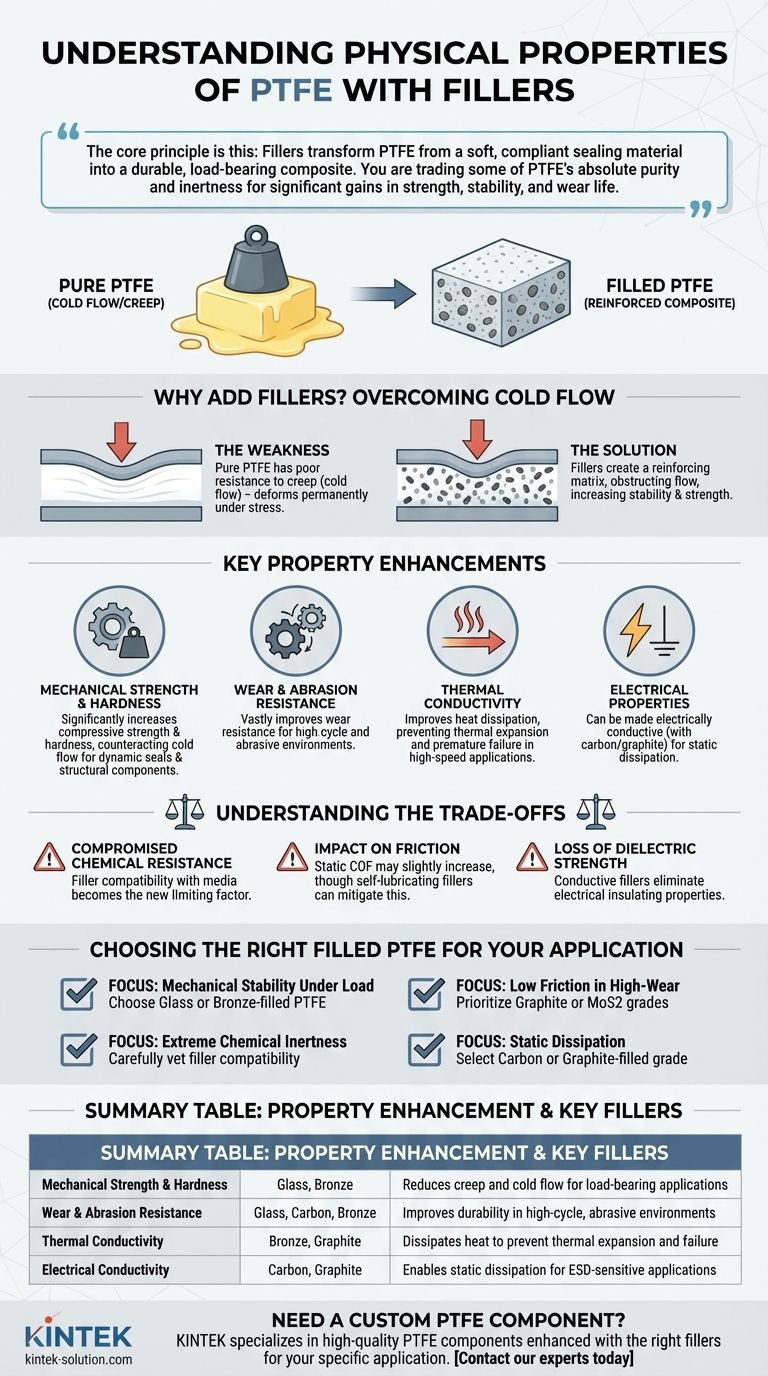
The core principle is this: Fillers transform PTFE from a soft, compliant sealing material into a durable, load-bearing composite. You are trading some of PTFE's absolute purity and inertness for significant gains in strength, stability, and wear life.

Why Add Fillers to PTFE?
To understand the properties of filled PTFE, you must first understand the limitations of pure, or "virgin," PTFE.
The Weakness of Pure PTFE: Cold Flow
Pure PTFE has poor resistance to creep, also known as cold flow. This is the tendency of a solid material to deform permanently under a persistent mechanical stress.
Imagine placing a heavy weight on a block of cold butter. Over time, the butter will slowly flatten and spread out. Pure PTFE behaves similarly, especially under compression in applications like gaskets or bearings.
This deformation limits its use in any structural or high-load application, as the material will not hold its shape or tolerances over time.
The Solution: A Reinforced Composite
Adding fillers like glass fiber, carbon, or bronze creates a composite material. These filler particles act as a reinforcing matrix within the soft PTFE.
This matrix physically obstructs the PTFE from flowing, dramatically increasing its dimensional stability, hardness, and overall strength.
Key Property Enhancements in Filled PTFE
Adding a filler fundamentally changes the material's profile. While it retains many of PTFE's base characteristics (like UV resistance and non-stick surfaces), the following properties are specifically targeted for improvement.
Mechanical Strength and Hardness
Fillers significantly increase the compressive strength and hardness of PTFE. This directly counteracts cold flow, allowing the material to be used in dynamic seals, bearings, and structural components where pure PTFE would fail.
Wear and Abrasion Resistance
This is one of the most significant improvements. Fillers like glass, carbon, and bronze can improve wear resistance by several orders of magnitude, making the material suitable for high-cycle and abrasive environments.
Thermal Conductivity
Pure PTFE is an excellent thermal insulator, which can be a problem in high-speed applications where friction generates heat.
Fillers like bronze, stainless steel, and graphite improve thermal conductivity, allowing the material to dissipate heat away from a wear surface, which prevents thermal expansion and premature failure.
Electrical Properties
By default, PTFE is an excellent electrical insulator with high dielectric strength.
However, adding conductive fillers like carbon, graphite, or stainless steel can make the material electrically conductive. This is highly desirable for applications requiring static dissipation to prevent electrical discharge.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Introducing a second material is never without compromises. It is critical to understand what you are giving up to achieve the desired property enhancements.
Compromised Chemical Resistance
While the PTFE itself remains highly inert, the filler may not be. For example, glass-filled PTFE can be attacked by strong alkalis, and bronze-filled PTFE is unsuitable for certain corrosive environments.
The chemical compatibility of the filler material becomes the new limiting factor for the entire composite.
Impact on Friction
Although filled PTFE has vastly superior wear performance, its static coefficient of friction (COF) may be slightly higher than that of virgin PTFE. However, self-lubricating fillers like graphite and molybdenum disulfide (MoS2) are used to keep friction very low.
Loss of Dielectric Strength
For applications requiring electrical insulation, adding conductive fillers is obviously a non-starter. You must choose a non-conductive filler like glass if you need to maintain insulating properties.
Choosing the Right Filled PTFE for Your Application
The specific properties depend entirely on the filler chosen. Your selection must be driven by the primary challenge you are trying to solve.
- If your primary focus is mechanical stability under load: Choose glass or bronze-filled PTFE for a dramatic reduction in creep and deformation.
- If your primary focus is low friction in a high-wear environment: Prioritize grades with graphite or molybdenum disulfide (MoS2) for their self-lubricating characteristics.
- If your primary focus is extreme chemical inertness: Carefully vet the filler's compatibility with your media, as this is the new potential point of failure.
- If your primary focus is static dissipation: Select a carbon or graphite-filled grade to provide the necessary electrical conductivity.
Ultimately, filled PTFE is a powerful tool for solving complex engineering challenges, provided you select the grade that aligns precisely with your application's demands.
Summary Table:
| Property Enhancement | Key Filler Types | Primary Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Mechanical Strength & Hardness | Glass, Bronze | Reduces creep and cold flow for load-bearing applications |
| Wear & Abrasion Resistance | Glass, Carbon, Bronze | Improves durability in high-cycle, abrasive environments |
| Thermal Conductivity | Bronze, Graphite | Dissipates heat to prevent thermal expansion and failure |
| Electrical Conductivity | Carbon, Graphite | Enables static dissipation for ESD-sensitive applications |
Need a custom PTFE component that balances performance with precision?
At KINTEK, we specialize in manufacturing high-quality PTFE components—including seals, liners, and labware—enhanced with the right fillers for your specific application. Whether you're in the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, or industrial sector, our expertise in custom fabrication from prototypes to high-volume orders ensures you get a solution that delivers superior mechanical strength, wear resistance, and thermal management.
Let us help you optimize your design with the perfect filled PTFE material. Contact our experts today for a consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Bottles for Diverse Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
People Also Ask
- What is the coefficient of friction for virgin PTFE? Achieve Superior Low-Friction Performance for Your Bushings
- What approvals does virgin PTFE have for use in food and pharmaceutical industries? FDA-Approved for Ultimate Purity & Safety
- What are the characteristics of PTFE coatings? Unlock Extreme Performance for Your Components
- How is MoS2 (Moly) typically combined in PTFE applications? Synergistic Fillers for Low Friction
- How does the built-in spring compensate for wear in PTFE shaft seals? Ensure Long-Term Sealing Reliability
- How does the sealing performance of PTFE gaskets benefit industrial applications? Ensure Leak-Free Reliability in Harsh Environments
- In what types of medical devices are PTFE liners particularly useful? Enhance Minimally Invasive Procedures with Superior Lubricity
- What are the common shapes of PTFE bushes? Cylindrical vs. Flanged for Load Management



















