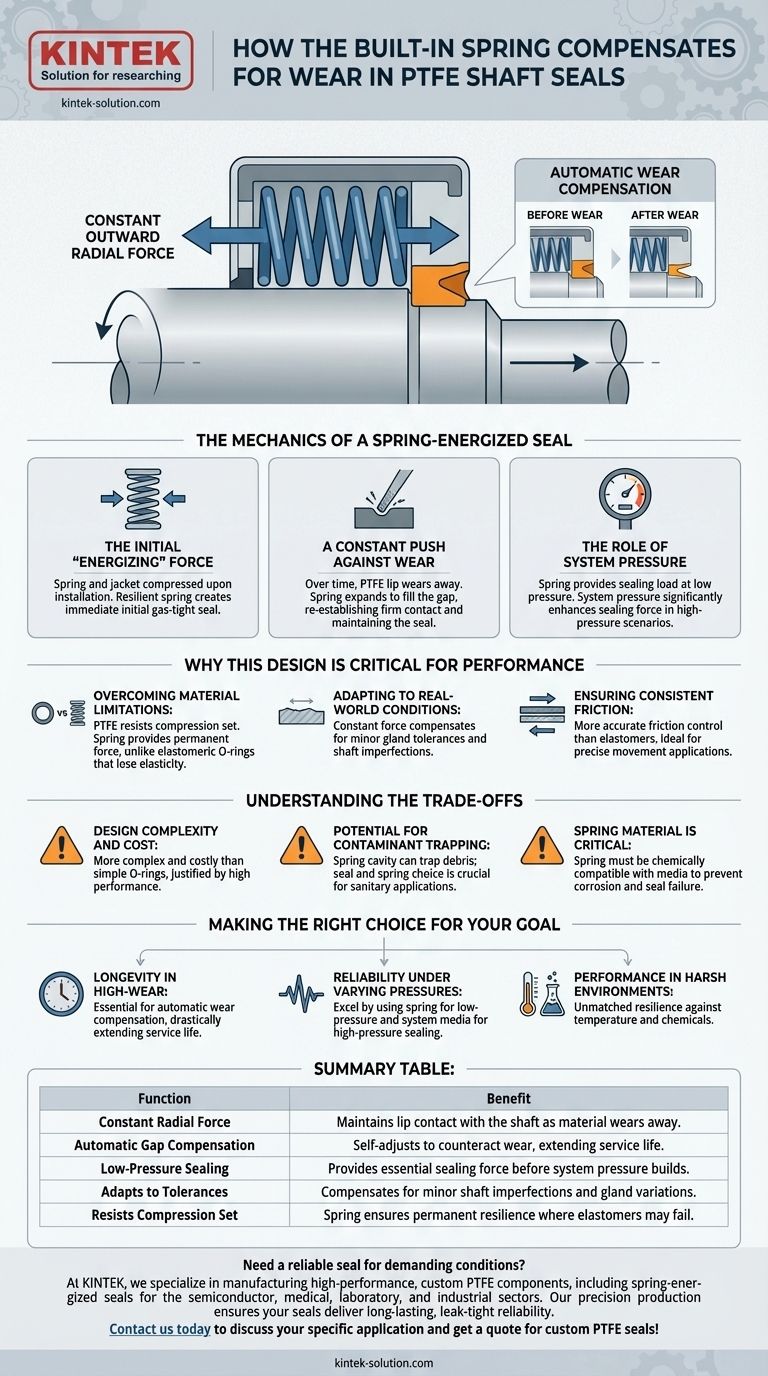
In a PTFE shaft seal, the built-in spring compensates for wear by exerting a continuous, outward radial force on the seal lip. This constant mechanical pressure ensures the lip remains in tight contact with the shaft, automatically closing the microscopic gap created as material wears away from either surface. This mechanism guarantees a consistent sealing force throughout the component's operational life.
The spring in a PTFE seal is not just a component; it's an energizer that creates a dynamic sealing system. It provides a constant baseline force to handle wear and low-pressure situations, while working in tandem with system pressure to ensure a reliable seal across a wide range of operating conditions.

The Mechanics of a Spring-Energized Seal
To understand how the spring compensates for wear, we must first look at how the seal functions from the moment of installation. It's a system of complementary forces.
The Initial "Energizing" Force
When the seal is installed into its housing (the gland), the flexible PTFE jacket and the internal spring are slightly compressed.
The resilient spring immediately responds with a constant outward force. This force pushes the sealing lips firmly against the shaft and the gland wall, creating the initial, gas-tight seal before any system pressure is even applied.
A Constant Push Against Wear
Over millions of cycles, microscopic amounts of the PTFE lip material will abrade away. Without a spring, this material loss would create a leak path.
The spring energizer, however, stores potential energy. As wear creates a tiny gap, the spring expands slightly, pushing the seal lip forward to re-establish firm contact and maintain the seal. This self-adjusting capability is the key to the seal's long and reliable lifespan.
The Role of System Pressure
The spring's primary role is to provide the necessary sealing load when media pressure is low or non-existent.
As system pressure increases, that pressure acts on the seal profile, significantly enhancing the sealing force. The spring ensures the seal is properly positioned to take advantage of this pressure, but the system pressure itself does most of the work in high-pressure scenarios.
Why This Design is Critical for Performance
The spring-energized design isn't just about wear. It solves several fundamental challenges that simpler seals, like elastomeric O-rings, cannot address effectively in demanding environments.
Overcoming Material Limitations
Standard elastomeric seals can suffer from compression set. Over time, they lose their elasticity and ability to rebound, creating a permanent leak path.
PTFE is highly resistant to compression set, and the metal spring provides a permanent, resilient force. This combination ensures the seal will not degrade under harsh temperatures or chemical exposure.
Adapting to Real-World Conditions
The spring's constant force allows the seal to compensate for minor gland tolerance variations or slight imperfections on the shaft surface. It ensures continuous contact where a less forgiving seal might fail.
Ensuring Consistent Friction
Because the spring provides a more constant and predictable load than the material memory of an elastomer, it allows for more accurate control over friction. This is critical in applications where precise movement and low drag are required.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While highly effective, this design is not a universal solution. Understanding its limitations is key to proper application.
Design Complexity and Cost
A multi-component, spring-energized seal is inherently more complex and costly to manufacture than a simple O-ring. Its use is justified by performance requirements that exceed the capabilities of simpler seals.
Potential for Contaminant Trapping
The cavity that houses the spring can potentially trap debris or viscous media. In sanitary or particulate-heavy applications, the seal profile and spring type must be chosen carefully to mitigate this risk.
Spring Material is Critical
The spring itself, typically made of stainless steel or other alloys, must be chemically compatible with the system media. A corroded spring will fail, leading to a complete loss of sealing force at low pressures.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting a spring-energized seal is a decision based on performance demands.
- If your primary focus is longevity in a high-wear application: The spring-energized design is essential for its automatic wear compensation, drastically extending service life.
- If your primary focus is reliability under varying pressures: This design excels by using the spring for low-pressure sealing and leveraging system media for high-pressure sealing.
- If your primary focus is performance in harsh chemical or temperature environments: The combination of an inert PTFE jacket and a corrosion-resistant spring offers unmatched resilience where elastomers would quickly degrade.
Ultimately, the spring transforms the seal from a passive blocker into an active, responsive system engineered for reliability.
Summary Table:
| Function | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Constant Radial Force | Maintains lip contact with the shaft as material wears away. |
| Automatic Gap Compensation | Self-adjusts to counteract wear, extending service life. |
| Low-Pressure Sealing | Provides essential sealing force before system pressure builds. |
| Adapts to Tolerances | Compensates for minor shaft imperfections and gland variations. |
| Resists Compression Set | Spring ensures permanent resilience where elastomers may fail. |
Need a reliable seal for demanding conditions?
At KINTEK, we specialize in manufacturing high-performance, custom PTFE components, including spring-energized seals for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Our precision production ensures your seals deliver long-lasting, leak-tight reliability.
Contact us today to discuss your specific application and get a quote for custom PTFE seals!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What are the material advantages of machining Teflon? Unlock Unmatched Chemical & Thermal Resistance
- What are the key benefits of PTFE in custom fabrication? Unlock Performance in Extreme Conditions
- What are some common applications of machined PTFE? Leverage its Unique Properties for Demanding Applications
- What is the working temperature range of PTFE? Master Extreme Heat and Cryogenic Applications
- What is PTFE commonly known as and what are its unique properties? Unlock Unmatched Chemical & Thermal Resistance



















