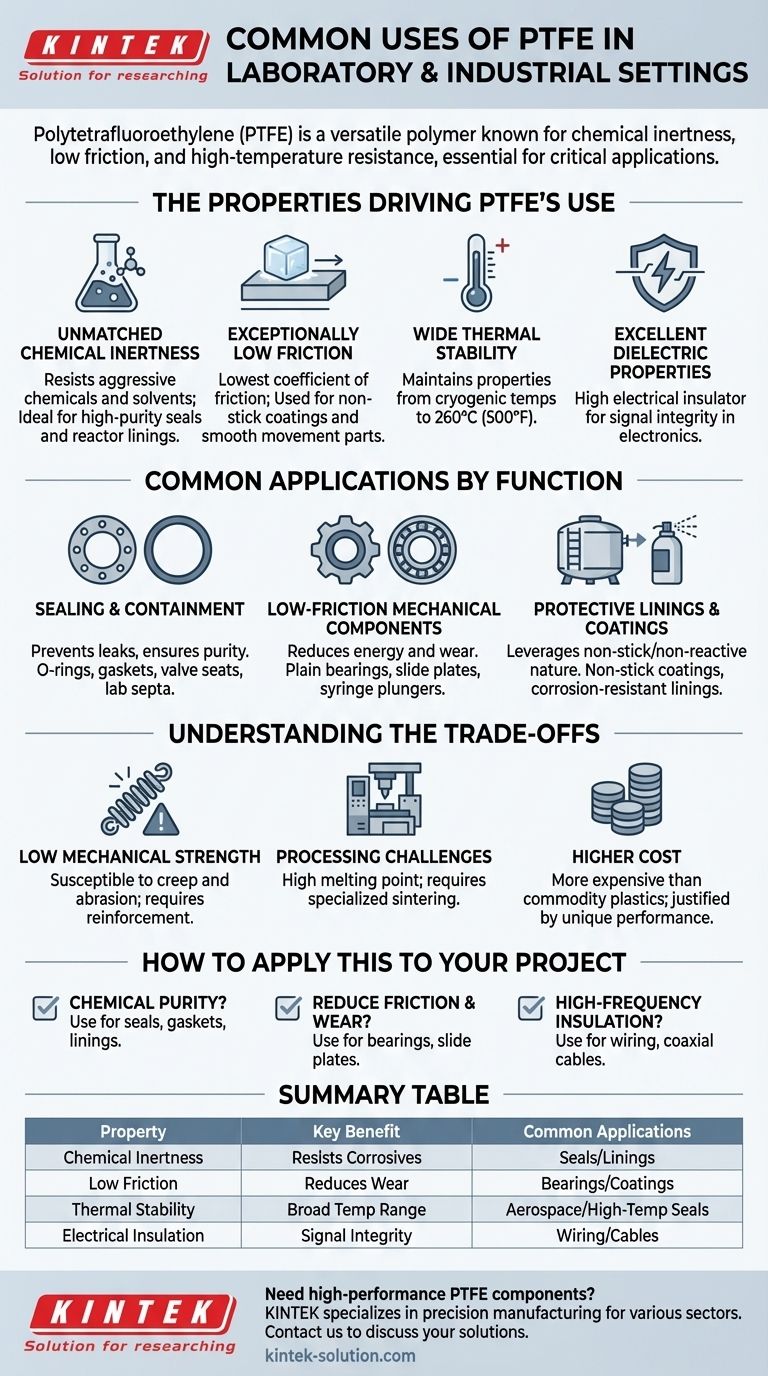
In both laboratory and industrial settings, Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is a uniquely versatile polymer primarily used for its extreme chemical inertness, low-friction surface, and high-temperature resistance. Its most common applications include high-purity seals and gaskets, non-stick coatings, linings for chemical reactors and pipes, and low-friction mechanical parts like bearings and slide plates.
PTFE is not just a single-use material; it is a fundamental problem-solver. Its value comes from a rare combination of properties that allow it to perform reliably in environments where most other materials would fail, whether due to chemical attack, extreme temperatures, or mechanical friction.

The Properties Driving PTFE's Use
To understand where PTFE is used, you must first understand why it is chosen. A few core characteristics make it an indispensable material in demanding technical applications.
Unmatched Chemical Inertness
PTFE is virtually inert and does not react with the vast majority of industrial chemicals, solvents, and corrosive agents. This makes it a default choice for handling aggressive or high-purity substances.
This property is critical in pharmaceutical research for sealing vials containing Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients (APIs) and in chemical synthesis for gaskets and linings that come into contact with reactive materials.
Exceptionally Low Friction
PTFE has one of the lowest coefficients of friction of any known solid material, often compared to wet ice on wet ice. This "slipperiness" is inherent to the material and does not require external lubricants.
This is why it is used for non-stick coatings on cookware and industrial equipment, as well as for mechanical components like gears, bearings, and slide plates that require smooth, effortless movement.
Wide Thermal Stability
PTFE maintains its properties over a very wide temperature range. It can be used in continuous service at temperatures up to 260°C (500°F) while also retaining its properties at cryogenic temperatures.
This stability makes it suitable for equipment in petrochemical plants, aerospace applications, and laboratory instruments that undergo significant temperature cycling.
Excellent Dielectric Properties
PTFE is an outstanding electrical insulator, maintaining high dielectric strength and low signal loss even at high frequencies.
Because of this, it is a key material in electronics and communications, used for insulating high-frequency coaxial cables and hookup wires where signal integrity is paramount.
Common Applications by Function
These core properties translate directly into specific, practical uses across multiple industries, from life sciences to heavy manufacturing.
Sealing and Containment
The most common use of PTFE is to prevent leaks and protect purity. Its ability to form a tight seal while resisting chemical degradation is invaluable.
Common components include O-rings, gaskets, washers, valve seats, and seals for pumps and reactors. In labs, PTFE septa are used to seal chromatography vials, ensuring sample integrity.
Low-Friction Mechanical Components
Where parts must move against each other with minimal resistance and wear, PTFE is a top choice. It reduces energy consumption and eliminates the need for liquid lubricants that could cause contamination.
Applications include plain bearings, slide plates, gears, and syringe plungers, which must provide hygienic and frictionless movement in medical instruments.
Protective Linings and Coatings
Applying PTFE to a surface leverages its non-stick and non-reactive nature to protect either the underlying material or the substance being processed.
This includes non-stick coatings in the food industry and corrosion-resistant linings for chemical transport pipes, storage tanks, and glass-lined reactors.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No material is perfect, and PTFE is no exception. Acknowledging its limitations is key to using it effectively.
Low Mechanical Strength
PTFE is a relatively soft material. It is susceptible to "creep," meaning it can slowly deform under a constant load, and has poor abrasion resistance compared to harder plastics. For this reason, it is often reinforced with fillers like glass, carbon, or bronze for structural applications.
Processing Challenges
PTFE has an extremely high melting point and melt viscosity, which means it cannot be processed using conventional thermoplastic methods like injection molding or extrusion. It requires specialized techniques like sintering, which can increase manufacturing complexity and cost.
Higher Cost
Compared to commodity plastics like polyethylene or polypropylene, PTFE is significantly more expensive. Its use is therefore justified only when its unique performance characteristics are a strict requirement for the application.
How to Apply This to Your Project
Your choice to use PTFE should be driven by a specific performance need that other materials cannot meet.
- If your primary focus is chemical purity and containment: PTFE is the industry standard for seals, gaskets, and linings in pharmaceutical, semiconductor, and chemical processing.
- If your primary focus is reducing mechanical friction and wear: Use PTFE for bearings, slide plates, or as a coating where smooth motion is critical and external lubricants are undesirable.
- If your primary focus is high-frequency electrical insulation: PTFE is the correct choice for critical wiring and coaxial cables where maintaining signal integrity is essential.
Ultimately, PTFE is selected when performance and reliability in an extreme environment are more important than initial material cost.
Summary Table:
| Property | Key Benefit | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Inertness | Resists corrosive substances | Seals, gaskets, reactor linings |
| Low Friction | Reduces wear, no lubricants needed | Bearings, slide plates, non-stick coatings |
| Thermal Stability | Performs from cryogenic to 260°C (500°F) | High-temp seals, aerospace components |
| Electrical Insulation | Maintains signal integrity | Coaxial cables, high-frequency wiring |
Need high-performance PTFE components for your application?
KINTEK specializes in the precision manufacturing of PTFE seals, liners, labware, and custom components for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. We deliver reliable solutions that withstand aggressive chemicals, extreme temperatures, and demanding mechanical conditions.
Whether you require prototypes or high-volume orders, our custom fabrication expertise ensures your specifications are met with unmatched accuracy and quality.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss how our PTFE solutions can solve your most challenging material problems.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What is PTFE and what are its unique properties? Unlock the Power of a High-Performance Polymer
- When did Teflon become a registered trademark, and what was an early use of the material? Discover Its Industrial Origins
- What are some common household applications of PTFE? Discover Its Hidden Uses Beyond Non-Stick Pans
- What factors should be considered when choosing PTFE for a specific application? A Guide to Virgin vs. Filled Grades
- What are the key applications enabled by PTFE's properties? Solve Extreme Mechanical, Chemical & Electrical Challenges
- What are some consumer product applications of PTFE? Discover its Versatility Beyond Non-Stick Pans
- How is PTFE synthesized? From TFE Gas to High-Performance Polymer
- Is Teflon hard or soft compared to other engineering plastics? A Guide to Its Unique Properties



















