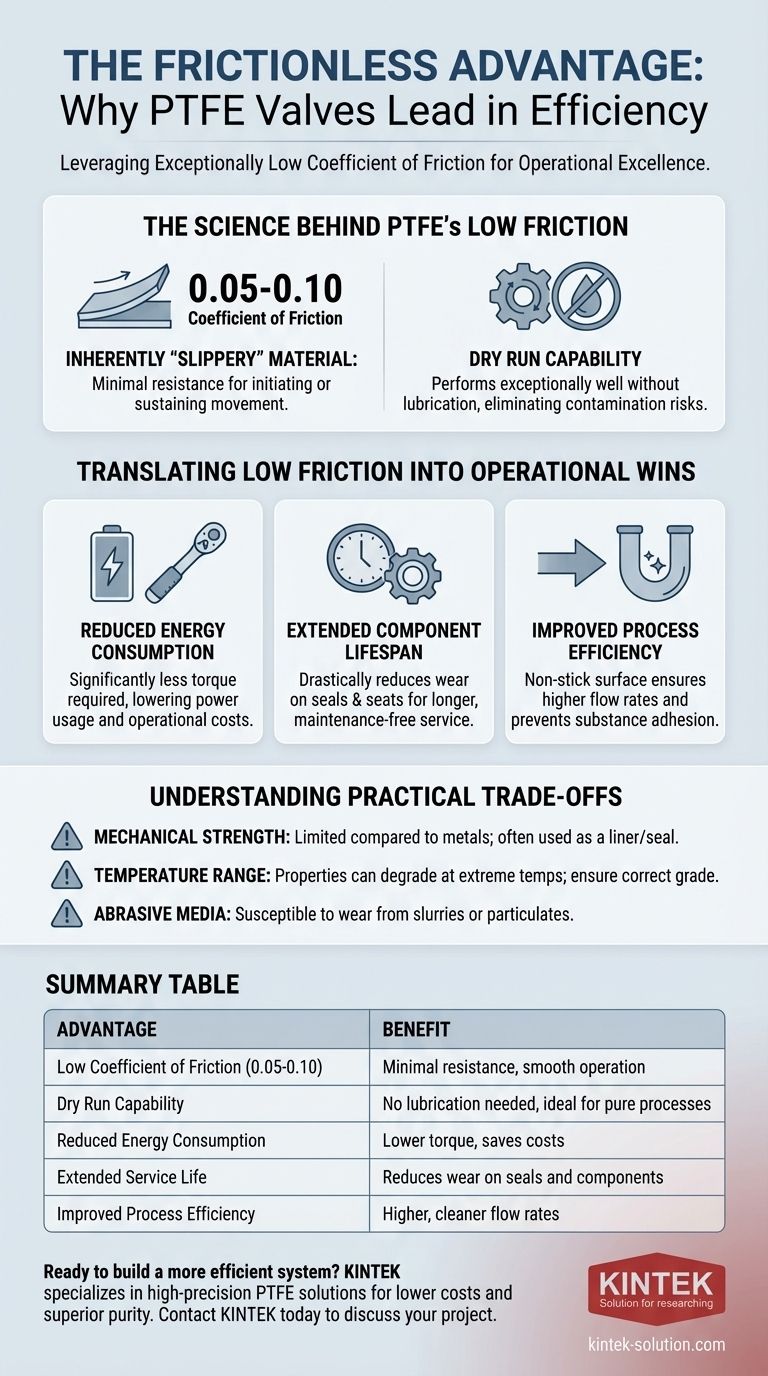
At its core, the primary advantage of Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) in valves is its exceptionally low coefficient of friction, which is among the lowest of any solid material known. This inherent slipperiness means PTFE components can operate with minimal resistance, significantly reducing the energy needed for actuation and dramatically cutting down on wear and tear. This allows for smoother operation, longer service life, and eliminates the need for external lubrication.
The true value of PTFE's low friction isn't just about being "non-stick." It's about how this single property creates a cascade of operational benefits, leading to lower energy costs, reduced maintenance, and improved system efficiency over the valve's entire lifespan.
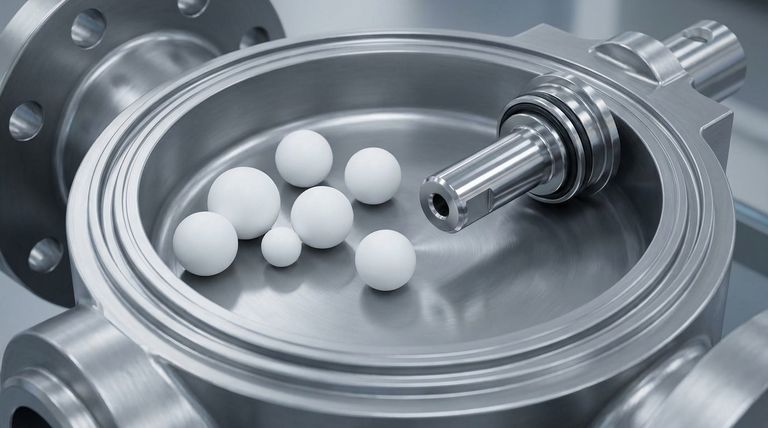

The Science Behind PTFE's Low Friction
Polytetrafluoroethylene, often known by the brand name Teflon, has a unique molecular structure that gives it remarkable properties. Understanding this foundation is key to appreciating its role in valve performance.
An Inherently "Slippery" Material
PTFE possesses one of the lowest coefficients of friction recorded for any solid. Its static coefficient is approximately 0.05 to 0.10, while its dynamic coefficient is even lower.
This means that very little energy is required to initiate or sustain movement between PTFE surfaces and other components. This property is intrinsic to the material itself.
The Ability to Run Dry
Unlike many materials, especially elastomers used in rubber seals, PTFE performs exceptionally well in dry, non-lubricated conditions.
This characteristic is critical in applications where lubricants could contaminate the process fluid or are impractical to apply, ensuring consistent performance without maintenance interventions.
Translating Low Friction into Operational Wins
The scientific properties of PTFE directly result in tangible, real-world advantages for industrial processes. These benefits compound over time, leading to significant cost savings and improved reliability.
Reduced Energy Consumption
Because PTFE surfaces slide past each other with minimal resistance, valves require significantly less torque to open and close.
This translates directly to lower energy consumption for automated valve actuators and less physical effort for manual ones, reducing operational costs and improving workplace ergonomics.
Extended Component Lifespan
Friction is a primary cause of wear in mechanical systems. By minimizing it, PTFE drastically reduces wear and tear on critical valve components like seals, O-rings, and valve seats.
This leads to a much longer, maintenance-free service life, decreasing downtime and the associated costs of replacement parts and labor.
Improved Process Efficiency
PTFE's smooth, non-stick surface not only reduces mechanical friction but also improves the flow of media through the valve.
This results in higher flow rates and prevents substances from adhering to the valve's internal surfaces. This self-cleaning characteristic is crucial for maintaining process purity and consistent throughput.
Understanding the Practical Trade-offs
While PTFE's low-friction properties are a significant advantage, they must be considered within the context of the entire application. Relying on this single benefit without understanding the material's other characteristics can lead to misapplication.
Mechanical Strength Limitations
PTFE is a polymer, not a metal. While durable, it does not possess the same rigidity or compressive strength as steel or other alloys.
In high-pressure or high-stress applications, the valve design must account for these mechanical properties. Often, PTFE is used as a liner or for sealing components within a robust metal body.
Temperature Range Considerations
PTFE has a wide operating temperature range, but it is not infinite. Its properties can degrade at extreme temperatures.
It is crucial to ensure the specific grade of PTFE and the valve's overall design are rated for the temperatures expected in your process to avoid component failure.
Susceptibility to Abrasive Media
The non-stick surface of PTFE excels with liquids and gases. However, in applications with highly abrasive slurries or particulates, the material can be subject to mechanical wear.
For these environments, a different valve material or a specialized design may be a more appropriate choice.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting a valve based on its friction characteristics requires aligning the properties of PTFE with your primary operational goal.
- If your primary focus is reducing long-term operating costs: PTFE is an excellent choice, as its ability to run without lubrication and its resistance to wear minimizes maintenance and energy expenses.
- If your primary focus is process purity and efficiency: The non-stick, chemically inert nature of PTFE ensures that the process media remains uncontaminated while maximizing flow rates.
- If your primary focus is system reliability and uptime: The extended, maintenance-free service life provided by PTFE's low-wear characteristics directly contributes to more consistent and reliable operations.
Ultimately, leveraging PTFE's low-friction properties allows you to design systems that are not just effective, but also remarkably efficient and durable.
Summary Table:
| Advantage | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Low Coefficient of Friction (0.05-0.10) | Minimal resistance for smooth, low-energy operation |
| Dry Run Capability | No lubrication needed, ideal for pure processes |
| Reduced Energy Consumption | Lower torque required for actuation saves costs |
| Extended Service Life | Drastically reduces wear on seals and components |
| Improved Process Efficiency | Non-stick surface ensures higher, cleaner flow rates |
Ready to build a more efficient and reliable system with PTFE components?
KINTEK specializes in manufacturing high-precision PTFE seals, liners, labware, and custom components for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Our expertise in custom fabrication—from prototypes to high-volume orders—ensures you get the exact PTFE solution to leverage low friction for lower energy costs, reduced maintenance, and superior process purity.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss your project and discover the long-term value we can bring to your operations.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
People Also Ask
- What properties can ceramics provide in PTFE-based laminates? Enhance Thermal, Mechanical & Electrical Performance
- What are the chemical resistance properties of expanded PTFE gaskets? A Guide to Universal Sealing Performance
- What are the different types of Teflon bearings available? Find the Right PTFE Bearing for Your Application
- What makes Metal-Polymer Bronze Backed PTFE Plain Bearings corrosion resistant? A Two-Layer Defense System Explained
- What materials are used to overcome the limitations of standard PTFE in ball valve seats? Upgrade to High-Performance Polymers
- What are the key benefits of using expanded PTFE gaskets? Achieve Superior Sealing in Demanding Environments
- What industries benefit from PTFE envelope gaskets? Seal Against Harsh Chemicals & High Purity Needs
- What cost advantages do expanded PTFE gaskets offer? Lower Your Total Cost of Ownership



















