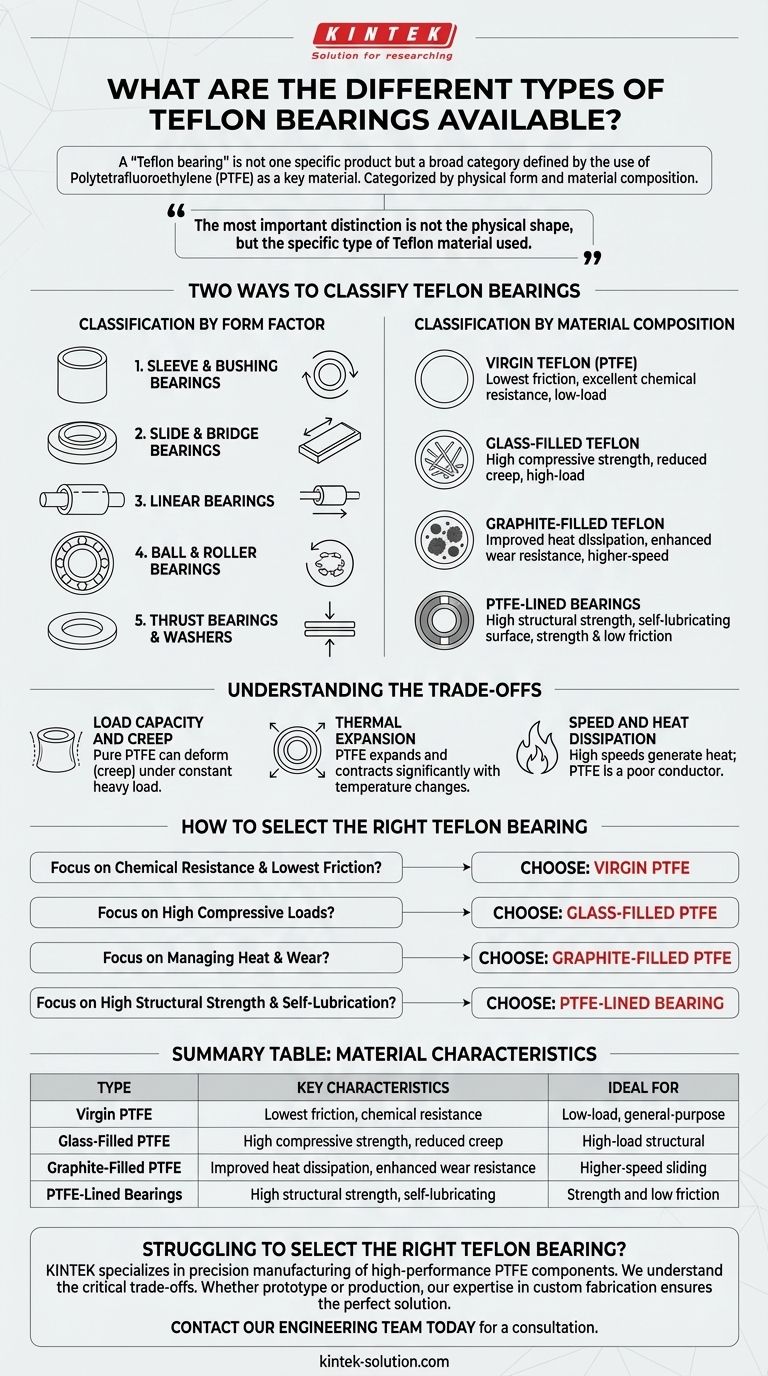
At its core, a "Teflon bearing" is not one specific product but a broad category defined by the use of Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) as a key material. These bearings are primarily categorized in two ways: by their physical form (such as sleeve, ball, or slide bearings) and, more critically, by their specific PTFE material composition (such as virgin, glass-filled, or graphite-filled Teflon). Each combination is engineered to solve a distinct set of operational challenges.
The most important distinction is not the physical shape of the bearing, but the specific type of Teflon material used. Matching the right PTFE compound to your application's load, temperature, and wear requirements is the key to successful implementation.
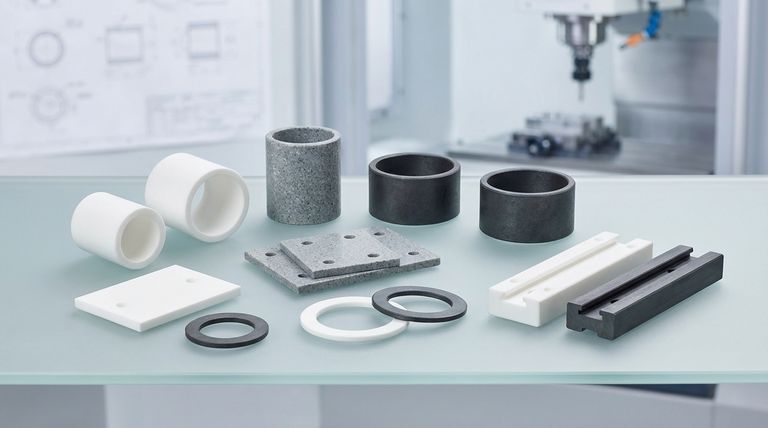

Two Ways to Classify Teflon Bearings
To select the correct bearing, you must first understand that its "type" is defined by both its mechanical design and its material science.
Classification by Form Factor
The physical shape of a bearing dictates how it handles motion and load.
Sleeve & Bushing Bearings These are simple cylindrical bearings designed for sliding, rotating, or oscillating motion. They are among the most common forms due to their simplicity and effectiveness.
Slide & Bridge Bearings These are typically flat pads or plates designed to accommodate linear movement and thermal expansion, often seen in large-scale structural applications like bridges and buildings.
Linear Bearings These are designed to provide low-friction movement in one direction along a linear axis.
Ball & Roller Bearings While less common for the core rolling elements to be solid PTFE, Teflon is frequently used for the cages or as a low-friction lining in these types of anti-friction bearings.
Thrust Bearings & Washers These are designed specifically to handle axial loads (pushing forces) along a shaft. PTFE washers are a simple and effective form of thrust bearing.
Classification by Material Composition
This is the most critical factor for performance. The properties of pure PTFE can be dramatically enhanced by adding fillers.
Virgin Teflon (PTFE) This is the pure, unfilled material. It offers the lowest coefficient of friction and excellent chemical resistance, making it ideal for general-purpose, low-load applications.
Glass-Filled Teflon Adding glass fibers significantly increases compressive strength and dimensional stability. This makes it suitable for higher loads and reduces deformation under pressure.
Graphite-Filled Teflon Adding graphite improves thermal conductivity (dissipating heat) and enhances wear resistance. This compound is often chosen for higher-speed applications where friction-induced heat is a concern.
PTFE-Lined Bearings These bearings combine the best of both worlds: a strong metal backing (like steel or bronze) for high load capacity and structural integrity, with a thin layer of PTFE on the contact surface for low friction and self-lubrication.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While Teflon bearings offer significant advantages, they are not universally superior. Understanding their limitations is key to avoiding misapplication.
Load Capacity and Creep
Pure, virgin PTFE is a relatively soft material. Under a constant heavy load, it can slowly deform over time in a process known as "creep" or cold flow. This is why glass-filled variants are essential for high-load structural applications.
Thermal Expansion
PTFE has a significantly higher coefficient of thermal expansion than metals. This means it expands and contracts more with temperature changes, a critical design consideration for maintaining precise clearances in machinery.
Speed and Heat Dissipation
Although PTFE has very low friction, high-speed applications can still generate heat. Because PTFE is a poor thermal conductor, this heat can build up and accelerate wear or cause dimensional instability. Graphite-filled compounds are specifically designed to help mitigate this issue.
How to Select the Right Teflon Bearing
Your selection should be driven entirely by the demands of your specific application.
- If your primary focus is chemical resistance and the lowest possible friction in a low-load environment: Choose a bearing made from virgin PTFE.
- If your primary focus is supporting high compressive loads with minimal deformation: Choose a glass-filled PTFE bearing.
- If your primary focus is managing heat and wear in a higher-speed sliding application: A graphite-filled PTFE compound is the superior choice.
- If your primary focus is combining high structural strength with a maintenance-free, self-lubricating surface: The ideal solution is a metal-backed, PTFE-lined bearing.
Ultimately, choosing the right Teflon bearing is an exercise in matching the material's properties to the physical demands of the job.
Summary Table:
| Type of Teflon Bearing | Key Characteristics | Ideal For |
|---|---|---|
| Virgin PTFE | Lowest friction, excellent chemical resistance | Low-load, general-purpose applications |
| Glass-Filled PTFE | High compressive strength, reduced creep | High-load structural applications |
| Graphite-Filled PTFE | Improved heat dissipation, enhanced wear resistance | Higher-speed sliding applications |
| PTFE-Lined Bearings | High structural strength, self-lubricating surface | Applications requiring both strength and low friction |
Struggling to select the right Teflon bearing for your specific load, speed, and environmental conditions?
KINTEK specializes in the precision manufacturing of high-performance PTFE components, including custom bearings, seals, and liners. We understand the critical trade-offs between material properties like creep resistance, thermal stability, and wear.
Whether you need a prototype for testing or a high-volume order for production, our expertise in custom fabrication ensures you get a bearing solution that is perfectly matched to your application's demands in the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, or industrial sectors.
Contact our engineering team today for a consultation and let us help you solve your most challenging motion control problems.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
People Also Ask
- What are some common industrial applications of PTFE Lip Seals? Critical Uses in High-Speed, Chemical & Extreme Environments
- What makes PTFE seals suitable for extreme temperature applications? Unmatched Stability from -200°C to +260°C
- What factors should be considered when determining if PTFE bellows are the best material? Select the Right Material for Your System
- How is PTFE used in sports rehabilitation and medical devices? Unlock Superior Biocompatibility and Performance
- How does PTFE contribute to sustainable solutions in manufacturing? Enhance Durability & Efficiency
- What role does PTFE play in the printing and packaging industry? Enhancing Efficiency and Quality
- What are the benefits of PTFE sealed ball bearings? Achieve Peak Performance with Low Friction & Zero Maintenance
- What are the key properties of PTFE that make it useful in sports equipment? Boost Speed and Durability



















