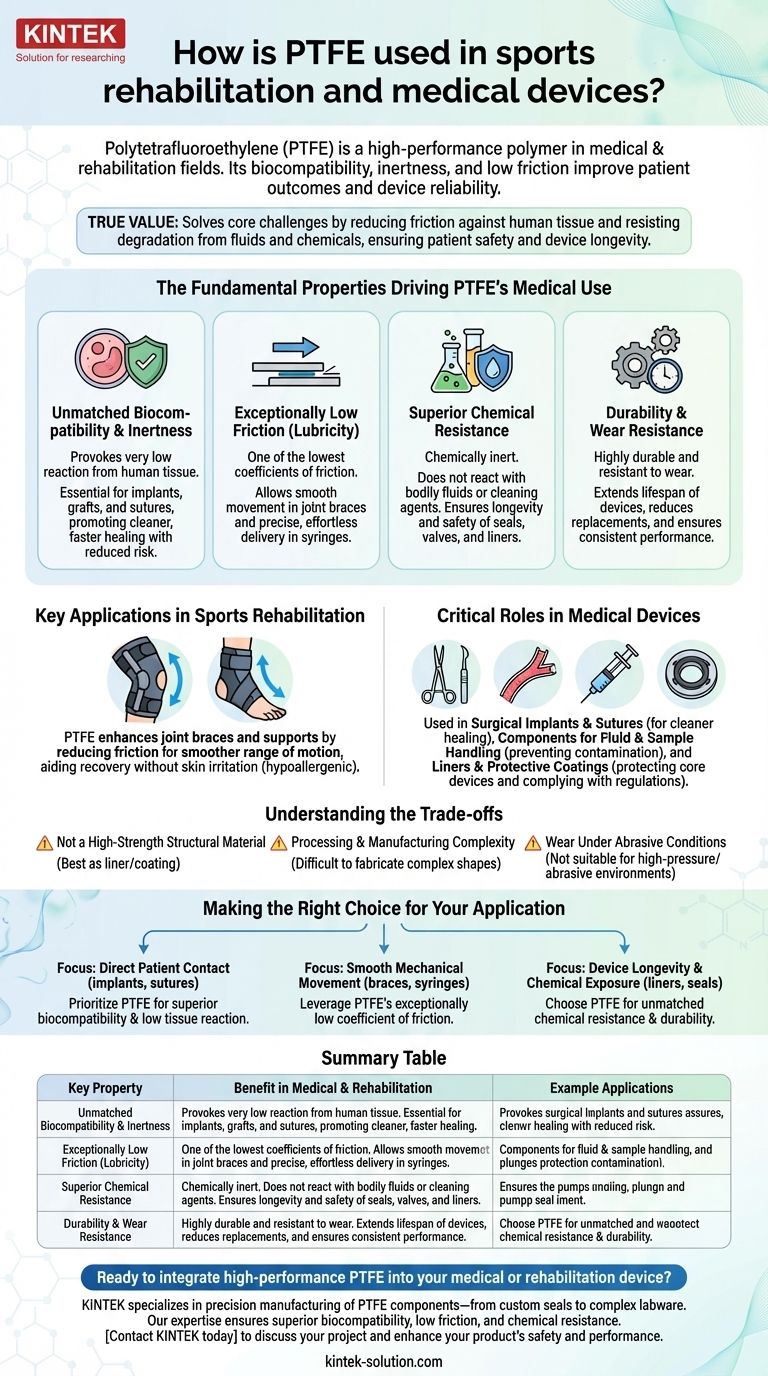
In the medical field, Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is a high-performance polymer used in applications ranging from joint braces and surgical sutures to critical components in medical devices like grafts and syringe plungers. Its widespread adoption is due to a unique combination of properties: it is biocompatible, chemically inert, and has an extremely low coefficient of friction, all of which contribute to improved patient outcomes and device reliability.
The true value of PTFE in medicine and rehabilitation isn't just its versatility, but its ability to solve two core challenges: reducing friction against human tissue and resisting degradation from bodily fluids and sterilizing chemicals. This dual-action performance makes it a uniquely reliable material for improving patient safety and device longevity.

The Fundamental Properties Driving PTFE's Medical Use
To understand PTFE's role, you must first understand the core material properties that make it so valuable in sensitive medical and rehabilitation environments.
Unmatched Biocompatibility and Inertness
PTFE is highly biocompatible, meaning it provokes a very low reaction from human tissue. The body does not recognize it as a foreign invader, which is critical for anything placed inside the body.
This property is essential for implants, surgical grafts, and sutures, as it promotes cleaner, faster healing with a reduced risk of inflammation or rejection.
Exceptionally Low Friction (Lubricity)
PTFE has one of the lowest coefficients of friction of any known solid. This "non-stick" quality allows components to move against each other—or against human tissue—with minimal resistance.
This is the key property behind its use in joint braces, where it allows for smoother, more natural movement during recovery, and in syringe plungers, where it ensures precise, effortless delivery of medication.
Superior Chemical Resistance
PTFE is almost entirely chemically inert. It does not react with bodily fluids, aggressive cleaning agents, or the vast majority of industrial chemicals.
This resistance ensures the material will not degrade over time, which is critical for the longevity and safety of device components like seals, valves, and liners used in testing and fluid handling equipment.
Durability and Wear Resistance
Despite being a relatively soft material, PTFE is highly durable and resistant to wear in its intended applications. As a liner or component, it extends the lifespan of medical devices by resisting friction and chemical degradation.
This durability reduces the need for frequent replacements, leading to greater cost efficiency and more consistent performance in clinical settings.
Key Applications in Sports Rehabilitation
In sports medicine, recovery often depends on facilitating proper movement while minimizing irritation. PTFE excels in this area.
Enhancing Joint Braces and Supports
PTFE is integrated into modern joint braces and supports to reduce friction between the brace components and the user's body.
This allows for a smoother, less restrictive range of motion, which helps aid recovery without causing skin irritation. Its hypoallergenic nature further ensures it is safe for prolonged skin contact.
Critical Roles in Medical Devices
From single-use instruments to permanent implants, PTFE is a trusted material for enhancing performance and safety.
Surgical Implants and Sutures
Because the body tolerates it so well, PTFE is a go-to material for vascular grafts, tissue patches, and other implants.
It is also used for specialized surgical sutures. Its smooth, non-reactive surface allows it to pass through delicate tissue with minimal trauma and supports a clean healing process.
Components for Fluid and Sample Handling
PTFE is frequently used for components like syringe plungers, pump seals, check valves, and sample transport mechanisms.
Its inert, non-stick surface is crucial for hygiene, preventing cross-contamination and ensuring that delicate samples or precise doses of medication are not altered by a chemical reaction with the device itself.
Liners and Protective Coatings
Many medical instruments and pieces of testing equipment are lined with PTFE. This liner acts as a durable, chemical-proof barrier.
It protects the core device from degradation, ensures consistent performance, and complies with strict FDA regulations for materials in medical-grade equipment.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While highly effective, PTFE is not a universal solution. Understanding its limitations is key to applying it correctly.
Not a High-Strength Structural Material
PTFE is a relatively soft polymer and is not suitable for high-load-bearing structural applications on its own. It is most effective as a liner, coating, or component where its surface properties are paramount.
Processing and Manufacturing Complexity
Fabricating complex shapes from PTFE can be more difficult and costly than with more common plastics. This is a factor that engineers must consider during the device design phase.
Wear Under Abrasive Conditions
Although durable, PTFE can wear down under high-pressure, abrasive conditions. It excels in low-load, sliding applications but may not be suitable for environments with sharp or abrasive particles.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
When considering PTFE, your decision should be guided by the primary performance requirement of the device or application.
- If your primary focus is direct patient contact (implants, sutures): Prioritize PTFE for its superior biocompatibility and low tissue reaction to ensure optimal healing.
- If your primary focus is smooth mechanical movement (braces, syringes): Leverage PTFE's exceptionally low coefficient of friction for frictionless and precise operation.
- If your primary focus is device longevity and chemical exposure (liners, seals): Choose PTFE for its unmatched chemical resistance and durability, which prevents degradation and reduces maintenance.
By understanding its core strengths, you can strategically apply PTFE to create safer, more effective, and more reliable medical and rehabilitative solutions.
Summary Table:
| Key Property | Benefit in Medical & Rehabilitation | Example Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Biocompatibility & Inertness | Minimizes tissue reaction, promotes healing | Surgical grafts, implants, sutures |
| Low Coefficient of Friction | Enables smooth, effortless movement | Joint braces, syringe plungers |
| Superior Chemical Resistance | Resists bodily fluids & sterilants, ensures longevity | Seals, valves, fluid handling liners |
| Durability & Wear Resistance | Reduces maintenance and extends device life | Protective coatings, instrument liners |
Ready to integrate high-performance PTFE into your medical or rehabilitation device?
KINTEK specializes in the precision manufacturing of PTFE components—from custom seals and liners to complex labware—for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Whether you need prototypes or high-volume production, our expertise ensures your devices benefit from PTFE's superior biocompatibility, low friction, and chemical resistance.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss your project and discover how our custom PTFE solutions can enhance your product's safety, reliability, and performance.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What are PTFE envelope gaskets? The Ultimate Sealing Solution for Corrosive Environments
- What microstructure does expanded PTFE sheet have? Unlock Superior Sealing & Insulation
- How are PTFE Teflon washers used in the automotive industry? Essential for High-Temp, Corrosive Seals
- How does the cost of PTFE PCBs compare to FR4 PCBs? A Guide to High-Frequency Material Selection
- How can PTFE lip seals be enhanced for extreme temperature performance? Optimize with Fillers & Design
- What are the key advantages of using PTFE envelope gaskets? Superior Sealing for Aggressive Chemical & High-Pressure Applications
- What are the key properties of PTFE spacer rings? Unlock Superior Performance in Demanding Environments
- What is a PTFE lined butterfly valve? A Guide to Corrosion-Resistant Flow Control



















