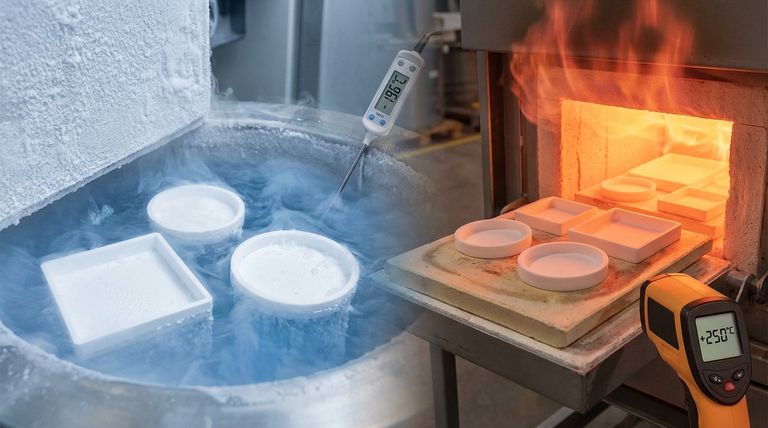
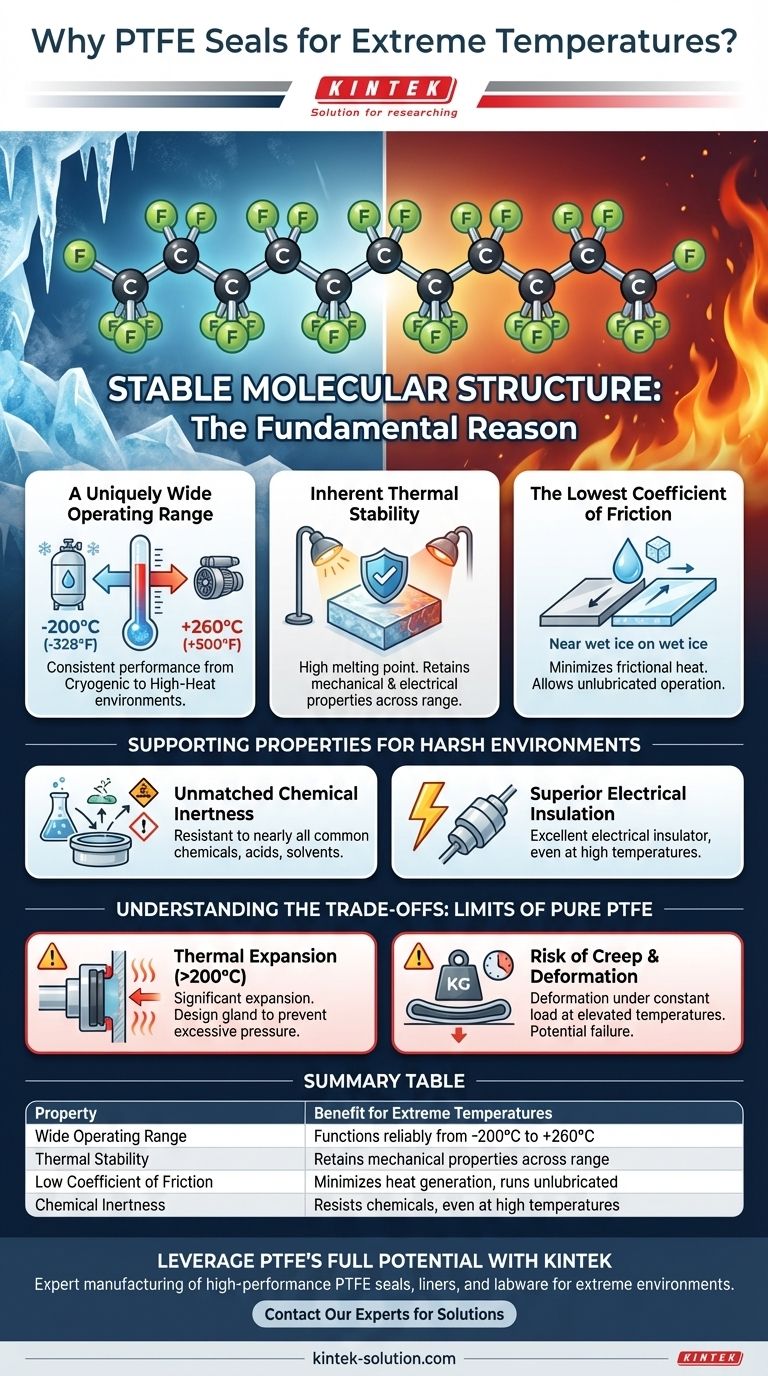
The fundamental reason PTFE seals are suitable for extreme temperatures is their incredibly stable molecular structure. This stability gives Polytetrafluoroethylene the widest operating temperature range of any plastic, allowing it to maintain its core properties in both cryogenic deep-freeze and high-heat industrial environments where other materials would fail.
The true value of PTFE in extreme environments is not just its heat resistance, but a unique combination of three core properties: a vast temperature tolerance, near-universal chemical inertness, and the lowest coefficient of friction of any solid.

The Foundation: Why PTFE Excels in Extreme Temperatures
To understand PTFE's performance, we must look at its specific material characteristics. These properties work in concert to create a uniquely resilient sealing material.
A Uniquely Wide Operating Range
PTFE can operate consistently in temperatures ranging from -200°C to +260°C (-328°F to +500°F).
This makes it one of the few materials suitable for both cryogenic applications, like liquid nitrogen systems, and high-temperature processes found in aerospace and chemical manufacturing.
Inherent Thermal Stability
The strong carbon-fluorine bonds in PTFE's structure give it a very high melting point.
This molecular stability means the material retains most of its mechanical and electrical properties across its entire operating temperature range, ensuring predictable and reliable performance.
The Lowest Coefficient of Friction
PTFE has one of the lowest friction coefficients of any known solid, comparable to wet ice on wet ice.
This is critical in dynamic sealing applications because it minimizes frictional heat generation, preventing premature failure. It also allows systems to run without lubrication, which is vital in temperatures where lubricants would either freeze or burn off.
Key Supporting Properties for Harsh Environments
Beyond its temperature tolerance, PTFE has other characteristics that make it an ideal choice for the demanding conditions often associated with extreme temperatures.
Unmatched Chemical Inertness
PTFE is resistant to nearly all common chemicals, acids, and solvents.
This is crucial in applications like chemical processing or aerospace, where a seal may be exposed to both high temperatures and corrosive substances simultaneously.
Superior Electrical Insulation
PTFE is an excellent electrical insulator and retains this property even at high temperatures.
It can withstand high voltages, making it a reliable choice for sealing components in demanding electronic and aerospace applications.
Understanding the Trade-offs: The Limits of Pure PTFE
While exceptionally capable, PTFE is not without limitations. Understanding these trade-offs is critical for successful engineering and application. An improperly specified PTFE seal can fail despite the material's potential.
The Challenge of Thermal Expansion
At the upper end of its temperature range (above 200°C / 392°F), PTFE experiences significant thermal expansion.
Its rate of expansion can be ten times that of stainless steel, a factor that must be accounted for in the design of the seal gland to prevent excessive pressure and extrusion.
The Risk of Creep and Deformation
Creep is the tendency of a material to deform permanently under a constant load, a process that accelerates with temperature.
At elevated temperatures, pure PTFE is susceptible to creep, which can lead to a loss of sealing force over time and eventual failure. This is especially true in high-pressure applications.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the right material requires matching its properties to your specific operational goals.
- If your primary focus is cryogenic performance (below -150°C): PTFE is an exceptional choice, as it remains flexible and effective while many other polymers become brittle and fail.
- If your primary focus is moderate to high heat (up to 200°C): Pure PTFE offers a reliable balance of thermal stability, low friction, and chemical resistance for a vast range of industrial uses.
- If your primary focus is extreme heat (above 200°C): You must carefully engineer for thermal expansion and consider using filled grades of PTFE, which add materials like carbon or glass to improve creep resistance and dimensional stability.
Ultimately, leveraging PTFE's remarkable capabilities depends on a clear understanding of both its strengths and its physical limits.
Summary Table:
| Property | Benefit for Extreme Temperatures |
|---|---|
| Wide Operating Range | Functions reliably from -200°C to +260°C (-328°F to +500°F) |
| Thermal Stability | Retains mechanical properties across the entire temperature range |
| Low Coefficient of Friction | Minimizes heat generation in dynamic applications, can run unlubricated |
| Chemical Inertness | Resists nearly all chemicals, even at high temperatures |
Leverage PTFE's full potential for your most demanding applications.
At KINTEK, we specialize in manufacturing high-performance PTFE components, including seals, liners, and labware. Our expertise ensures that your PTFE seals are precision-engineered to handle extreme temperatures, chemical exposure, and specific operational pressures, whether you need prototypes or high-volume orders for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, or industrial sectors.
Let's engineer a solution for your extreme environment. Contact our experts today to discuss your requirements.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Customizable PTFE Seals Filter Holders for Versatile Applications
People Also Ask
- What are the benefits of PTFE Industrial and Heavy Wall tubing? Maximize Reliability in Harsh Environments
- How are Teflon rods utilized in the chemical processing industry? For Seals, Liners & Valves That Resist Corrosion
- What are some exceptional properties of PTFE? Unlock Unmatched Performance in Extreme Environments
- Which type of PTFE gasket is better for high-pressure and high-temperature applications? Discover the Best Solution for Demanding Seals
- What are the two major subcomponents of PTFE pneumatic valve assemblies? Achieve Reliable Corrosive Fluid Control
- What role does thermal history play in the processing of PTFE? Master Heat Control for Superior Components
- What are the optimal cutting speeds and feed rates for machining PTFE? Master the Art of Precision Machining
- What is FEP and how does it differ from PTFE? Key Differences in Performance & Manufacturing



















