In chemical applications, Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is predominantly used for three key functions: sealing, fluid transport, and critical component manufacturing. Its unique properties make it essential for creating gaskets and seals, lining pipes and vessels, and fabricating parts like valves and bearings that must withstand highly corrosive environments.
PTFE's value stems from its near-total chemical inertness combined with a wide operational temperature range. This makes it the default engineering material for applications involving aggressive chemicals where other plastics, elastomers, and even metals would quickly degrade or fail.

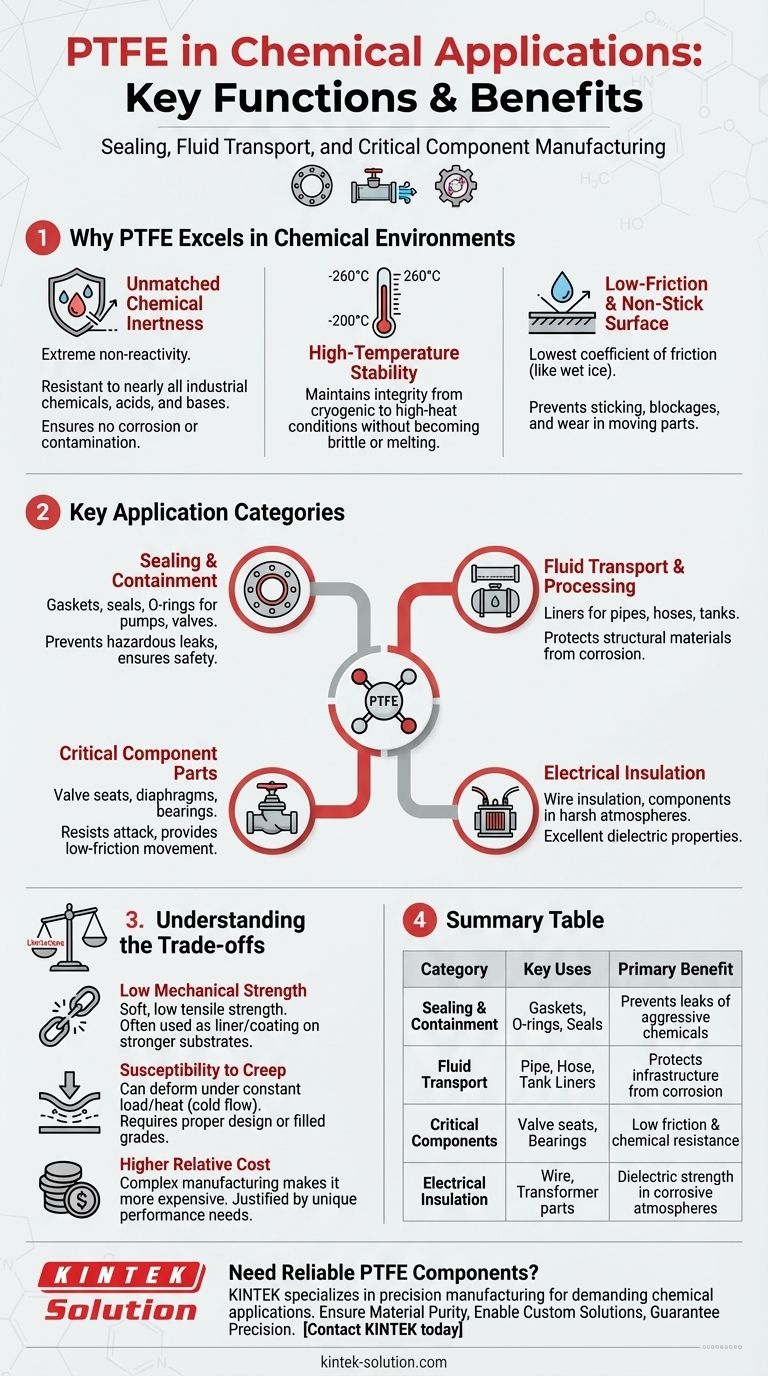
Why PTFE Excels in Chemical Environments
To understand its applications, we must first understand its core properties. PTFE is not chosen for its strength, but for its extraordinary resilience and stability in the face of chemical attack.
Unmatched Chemical Inertness
PTFE is famous for its extreme non-reactivity. It is resistant to nearly all industrial chemicals, solvents, acids, and bases.
This property ensures that the material does not corrode, degrade, or leach contaminants into the process fluid, which is critical for both safety and product purity.
High-Temperature Stability
The material maintains its integrity across a vast temperature spectrum, from cryogenic conditions (-200°C) up to high-heat applications (260°C / 500°F).
This allows it to be used reliably in chemical processes that involve significant temperature fluctuations without becoming brittle or melting.
Low-Friction and Non-Stick Surface
PTFE has one of the lowest coefficients of friction of any solid material, often compared to wet ice on wet ice.
This low-friction surface prevents other materials from sticking to it, which is vital for preventing blockages in transport lines and ensuring the smooth operation of moving parts like valve seats and bearings.
Key Application Categories in the Chemical Industry
PTFE’s properties translate directly into specific, high-value uses across chemical processing, transport, and engineering.
Sealing and Containment
This is arguably the most common chemical application. PTFE is fabricated into gaskets, seals, and O-rings for use in pumps, valves, and flanged pipe connections.
Its ability to create a tight, durable seal prevents the leakage of hazardous or corrosive chemicals, ensuring operational safety and environmental protection.
Fluid Transport and Processing
PTFE is frequently used as a liner for industrial pipelines, hose assemblies, and storage tanks.
A thin layer of PTFE protects the structural material (typically steel or another metal) from the corrosive contents within. This is a cost-effective way to build large, corrosion-resistant systems.
Critical Component Parts
Many internal components of chemical processing equipment are made from PTFE. These include valve seats, pump diaphragms, bearings, and bushings.
In these roles, PTFE must both resist chemical attack and provide a low-friction surface for moving parts to operate smoothly without seizing or excessive wear.
Electrical Insulation
In chemical plants, electrical components are often exposed to corrosive fumes or splashes.
PTFE's excellent dielectric properties combined with its chemical resistance make it an ideal material for wire insulation and insulating components within transformers in these harsh atmospheres.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While incredibly useful, PTFE is not a universal solution. An objective assessment requires understanding its limitations.
Low Mechanical Strength
PTFE is a relatively soft material with low tensile strength and abrasion resistance compared to metals or engineering plastics. It is not suitable for purely structural applications.
This is why it is often used as a liner or coating, relying on a stronger substrate material for structural support.
Susceptibility to Creep
Under a constant load, especially at elevated temperatures, PTFE can slowly deform. This phenomenon, known as creep or cold flow, can be a concern in high-pressure sealing applications.
Designers must account for this by using proper gasket designs or by using filled grades of PTFE, which incorporate materials like glass or carbon to improve creep resistance.
Higher Relative Cost
Due to the complexities of its manufacturing process, PTFE is more expensive than many common polymers. Its use is therefore justified in applications where its unique performance is a strict requirement, not just a preference.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct material is about matching its properties to your primary goal. PTFE should be considered when chemical resilience is the top priority.
- If your primary focus is preventing leaks of aggressive chemicals: Use PTFE for gaskets, seals, and O-rings to ensure long-term, reliable containment.
- If your primary focus is safely transporting corrosive or high-purity fluids: Specify PTFE-lined pipes, hoses, and tanks to protect your infrastructure and prevent contamination.
- If your primary focus is designing moving parts for a chemical environment: Choose PTFE for bearings, bushings, and valve components to minimize friction and prevent seizure from chemical attack.
Ultimately, PTFE is the material you turn to when chemical resistance and operational reliability are non-negotiable.
Summary Table:
| Application Category | Key PTFE Uses | Primary Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Sealing & Containment | Gaskets, O-rings, Seals | Prevents leaks of aggressive chemicals |
| Fluid Transport | Pipe liners, Hose liners, Tank liners | Protects infrastructure from corrosion |
| Critical Components | Valve seats, Bearings, Pump diaphragms | Low friction & chemical resistance for moving parts |
| Electrical Insulation | Wire insulation, Transformer components | Dielectric strength in corrosive atmospheres |
Need Reliable PTFE Components for Your Chemical Application?
KINTEK specializes in the precision manufacturing of high-performance PTFE components—from custom seals and liners to complex labware and industrial parts. We serve the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and specialized industrial sectors where material integrity is critical.
We deliver value by:
- Ensuring Material Purity: Our PTFE components offer unmatched chemical inertness, protecting your processes from contamination.
- Enabling Custom Solutions: We provide custom fabrication from prototypes to high-volume orders, designed to meet your exact specifications.
- Guaranteeing Precision: Our focus on precision production ensures consistent performance and reliability in the most demanding environments.
Let us help you solve your toughest chemical resistance challenges. Contact KINTEK today to discuss your project requirements.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What are the three main steps in the manufacturing process of PTFE? From Monomer to High-Performance Polymer
- How was Teflon (PTFE) discovered? The Accidental Invention That Revolutionized Industry
- What are the advantages of RPTFE over standard PTFE? Superior Strength and Durability for Demanding Applications
- How was PTFE discovered? The Accidental Invention of a Super-Material
- What are the key properties of bronze bushings? Achieve High-Load, Low-Maintenance Performance
- What are common uses of PTFE? Unlock Versatility for Your Industry
- How does the grade and type of resin affect the electrical properties of PTFE? Optimize Your Component's Performance
- What makes PTFE an ideal material for corrosion-resistant applications? Unmatched Chemical Inertness for Harsh Environments



















