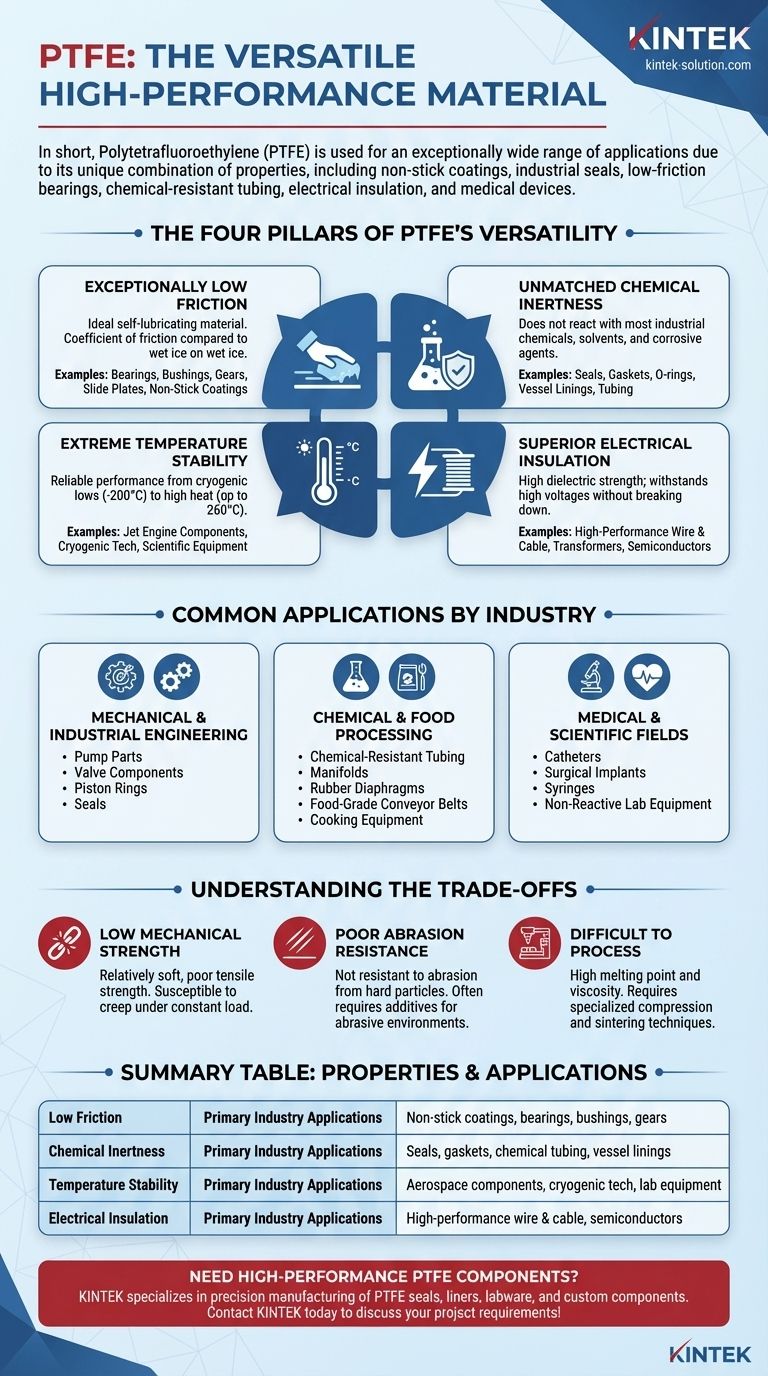
In short, Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is used in an exceptionally wide range of applications due to its unique properties. The most common uses include non-stick coatings, industrial seals and gaskets, low-friction bearings and bushings, chemical-resistant tubing and linings, high-performance electrical wire insulation, and medical devices.
The true value of PTFE lies not in any single feature, but in its rare combination of four key properties: extreme chemical inertness, a vast operating temperature range, excellent electrical insulation, and one of the lowest coefficients of friction of any solid material.
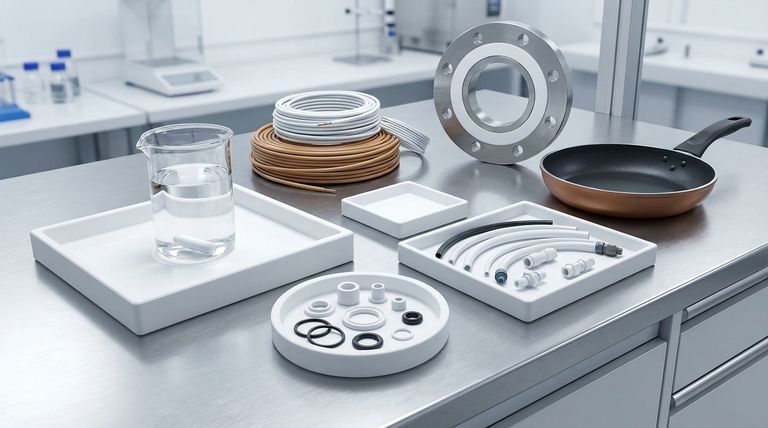

The Four Pillars of PTFE's Versatility
To understand why PTFE is so ubiquitous, you must look beyond the list of applications and focus on the fundamental material properties that drive its selection. These core characteristics solve critical engineering challenges across dozens of industries.
Pillar 1: Exceptionally Low Friction
PTFE has an incredibly low coefficient of friction, often compared to wet ice on wet ice. This makes it an ideal self-lubricating material.
This property is the reason it is the go-to material for bearings, bushings, gears, and slide plates where smooth, low-effort movement is required without external lubricants. It is also the principle behind its most famous consumer use: non-stick coatings on cookware.
Pillar 2: Unmatched Chemical Inertness
PTFE is almost completely inert, meaning it does not react with the vast majority of industrial chemicals, solvents, and corrosive agents.
This makes it indispensable in the chemical processing industry for seals, gaskets, O-rings, and vessel linings. It ensures the integrity of systems handling aggressive substances, preventing leaks and contamination.
Pillar 3: Extreme Temperature Stability
PTFE performs reliably across a massive temperature spectrum, from cryogenic lows (-200°C) to high-heat applications (up to 260°C).
Its ability to withstand high temperatures makes it suitable for components in jet engines and scientific equipment, while its performance in extreme cold is critical for cryogenic technology.
Pillar 4: Superior Electrical Insulation
PTFE is an excellent electrical insulator with a very high dielectric strength, meaning it can withstand high voltages without breaking down.
This property is essential for producing high-performance wire and cable insulation, especially in aerospace and computing where signal integrity is critical. It is also used in transformers and semiconductor manufacturing.
Common Applications by Industry
While the properties explain the "why," seeing the applications grouped by industry provides a practical context for where PTFE is most often found.
Mechanical and Industrial Engineering
In this sector, the focus is on durability and performance under mechanical stress. PTFE is used for pump parts, valve components, piston rings, and seals to reduce wear and ensure reliable operation.
Chemical and Food Processing
Here, chemical resistance and safety are paramount. PTFE is used for chemical-resistant tubing, manifolds, and rubber diaphragms. Its non-toxic and non-stick nature also makes it perfect for food-grade conveyor belts and cooking equipment.
Medical and Scientific Fields
Biocompatibility and purity are the key drivers in this arena. PTFE is frequently used for catheters, surgical implants, and syringes. Its inertness also makes it ideal for non-reactive scientific and laboratory equipment.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No material is perfect, and PTFE is no exception. While its primary characteristics are outstanding, its limitations dictate where it cannot be used.
Low Mechanical Strength
Compared to other engineering plastics, PTFE is relatively soft and has poor tensile strength. It is susceptible to creep, meaning it can slowly deform over time when under a constant load.
Poor Abrasion Resistance
While it has low friction, PTFE is not highly resistant to abrasion from hard particles. In abrasive environments, "bearing grade" PTFE filled with additives like glass or carbon is often required.
Difficult to Process
PTFE has a very high melting point and viscosity, making it difficult to process using conventional methods like injection molding. It typically requires specialized compression and sintering techniques, which can increase manufacturing costs.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting a material depends entirely on the primary problem you need to solve.
- If your primary focus is reducing friction and wear: PTFE is an elite choice for self-lubricating bearings, slide plates, and non-stick surfaces.
- If your primary focus is chemical resistance: It is the industry standard for seals, gaskets, and linings in aggressive chemical environments.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature electrical performance: PTFE is the material of choice for high-frequency, high-temperature wire insulation and connectors.
- If your primary focus is biocompatibility or food safety: Its inert and non-toxic nature makes it a proven material for medical devices and food processing equipment.
Ultimately, PTFE's success stems from its ability to solve multiple engineering challenges simultaneously.
Summary Table:
| Key Property | Primary Industry Applications |
|---|---|
| Low Friction | Non-stick coatings, bearings, bushings, gears |
| Chemical Inertness | Seals, gaskets, chemical tubing, vessel linings |
| Temperature Stability | Aerospace components, cryogenic tech, lab equipment |
| Electrical Insulation | High-performance wire & cable, semiconductors |
Need High-Performance PTFE Components?
KINTEK specializes in the precision manufacturing of PTFE seals, liners, labware, and custom components for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Whether you require prototypes or high-volume production, our expertise ensures you get parts that leverage PTFE's full potential for your specific application.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss your project requirements and get a quote!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Customizable PTFE Rods for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Volumetric Flasks for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Use
People Also Ask
- What industrial advantages does PTFE offer? Achieve Unmatched Reliability in Harsh Environments
- When did the industrial production of PTFE begin? From Military Secret to Industrial Revolution
- What factors should be considered when choosing PTFE for a specific application? A Guide to Virgin vs. Filled Grades
- What is the role of valves in industrial piping systems? Ensure Safety, Control, and Efficiency
- What are the disadvantages of bronze bushings? Understanding the Trade-Offs for Heavy-Duty Applications
- What are the key physical properties of PTFE? Unlock Its Extreme Performance for Demanding Applications
- What chemicals can degrade Teflon? A Guide to PTFE's Chemical Limits
- What is the relationship between PTFE and Teflon? A Guide to the Material vs. the Brand Name



















