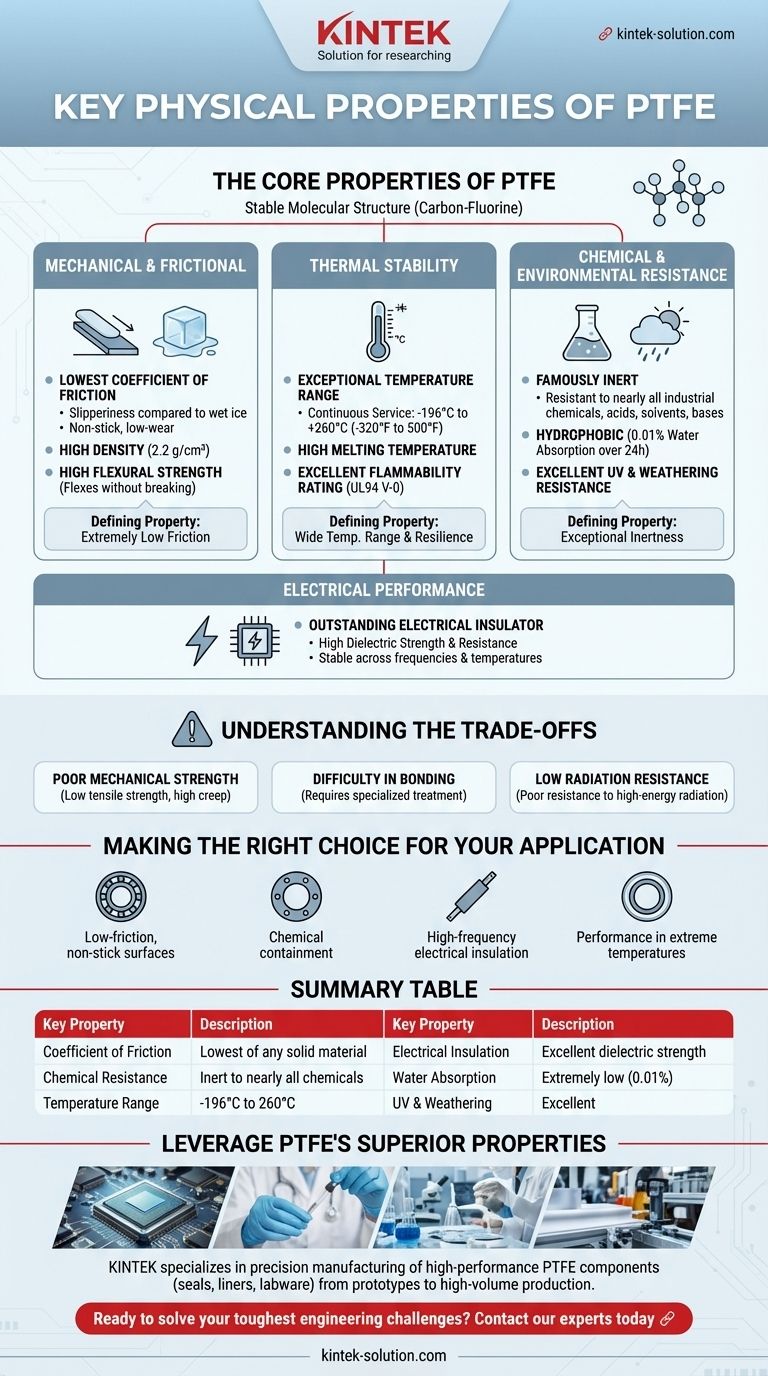
The defining physical properties of Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) are its extremely low coefficient of friction, exceptional chemical inertness, and stability across a wide temperature range. It is also a superb electrical insulator and is highly resistant to water and UV degradation, making it one of the most versatile and specialized polymers in modern engineering.
PTFE is not a single-purpose material; it is a unique combination of high-performance characteristics. Its value comes from the rare intersection of properties that allow it to function in extreme chemical, thermal, and electrical environments where other materials would quickly fail.
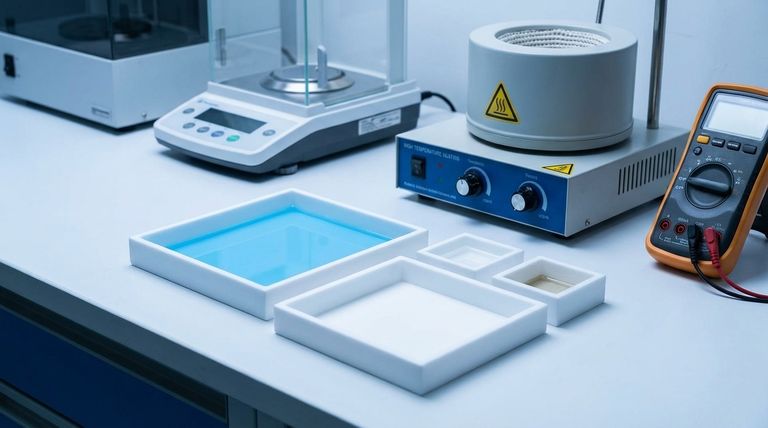

The Core Properties of PTFE
PTFE's physical characteristics are a direct result of its molecular structure: a long chain of carbon atoms completely sheathed by highly electronegative fluorine atoms. This stable and protected structure is the source of its remarkable properties.
Mechanical and Frictional Properties
PTFE is best known for its slipperiness. It possesses the lowest coefficient of friction of any known solid material, often compared to wet ice on wet ice.
This non-stick, low-wear characteristic makes it invaluable for applications where smooth, repeatable motion is critical.
Its density is also notably high for a plastic, typically around 2.2 g/cm³. This density contributes to its robust feel and durability in certain applications.
While not a high-strength structural plastic, it maintains high flexural strength, meaning it can bend and flex without breaking, even at cryogenic temperatures.
Thermal Stability
PTFE operates across an exceptionally wide temperature range. It remains functional and stable from cryogenic conditions of -196°C (-320°F) up to a continuous service temperature of 260°C (500°F).
This thermal resilience allows it to be used in demanding aerospace, automotive, and industrial processes involving extreme heat or cold.
It has a high melting temperature compared to other polymers and an excellent flammability rating (UL94 V-0), meaning it resists ignition and does not promote the spread of flames.
Chemical and Environmental Resistance
The material is famously inert. PTFE is resistant to nearly all industrial chemicals, acids, solvents, and bases, making it the default choice for seals, gaskets, and linings in corrosive environments.
It is hydrophobic, meaning it repels water and absorbs almost none (0.01% absorption over 24 hours). This property prevents swelling or degradation due to moisture.
Furthermore, it has excellent resistance to ultraviolet (UV) light and weathering, ensuring it does not degrade or become brittle with long-term outdoor exposure.
Electrical Performance
PTFE is an outstanding electrical insulator. It has very high dielectric strength and electrical resistance, preventing the flow of electric current.
Its excellent dielectric properties are stable across a wide range of frequencies and temperatures, making it a critical material for high-performance wires, cables, and circuit boards, especially in high-frequency applications.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No material is perfect, and PTFE's unique strengths come with specific limitations that are crucial to understand for proper application.
Poor Mechanical Strength
While it has good flexural strength, PTFE is a relatively soft material with low tensile strength and high creep (a tendency to deform slowly under mechanical stress). It is not suitable for load-bearing structural components.
Difficulty in Bonding
The same low-friction, non-stick surface that makes PTFE so useful also makes it extremely difficult to bond or glue to other materials. Specialized surface treatments, such as chemical etching, are required to create a bondable surface.
Low Radiation Resistance
PTFE has poor resistance to high-energy radiation, such as gamma rays. Radiation can break down the polymer's molecular chains, causing the material to become brittle and lose its desirable properties.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting PTFE is about leveraging its unique combination of properties for a specific, demanding goal.
- If your primary focus is low-friction, non-stick surfaces: PTFE's exceptionally low coefficient of friction makes it the definitive choice for bearings, non-stick coatings, and low-wear seals.
- If your primary focus is chemical containment: Its near-total chemical inertness is essential for gaskets, vessel linings, and tubing that handle corrosive substances.
- If your primary focus is high-frequency electrical insulation: Its stable and high dielectric strength is critical for insulating coaxial cables and high-performance printed circuit boards.
- If your primary focus is performance in extreme temperatures: Its stability from cryogenic lows to high heat makes it ideal for seals and components in aerospace and specialized industrial equipment.
Ultimately, understanding these core properties empowers you to deploy PTFE precisely where its unparalleled performance characteristics can solve the most challenging engineering problems.
Summary Table:
| Key Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Coefficient of Friction | Lowest of any solid material |
| Chemical Resistance | Inert to nearly all chemicals and solvents |
| Temperature Range | Stable from -196°C to 260°C (-320°F to 500°F) |
| Electrical Insulation | Excellent dielectric strength, stable across frequencies |
| Water Absorption | Extremely low (0.01% over 24 hours) |
| UV & Weathering Resistance | Excellent, does not degrade outdoors |
Leverage PTFE's Superior Properties for Your Most Demanding Applications
PTFE's unique combination of extreme chemical resistance, thermal stability, and low friction makes it the ideal material for challenging environments in the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors.
KINTEK specializes in the precision manufacturing of high-performance PTFE components—including custom seals, liners, and labware—from prototypes to high-volume production. We ensure your components meet the exact specifications required to perform reliably under extreme conditions.
Ready to solve your toughest engineering challenges with PTFE? Contact our experts today to discuss your custom fabrication needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
People Also Ask
- How does PTFE's molecular structure contribute to its non-stick properties? The Science Behind Its Slick Surface
- How does PTFE react to common solvents? Discover Its Near-Total Chemical Immunity
- What is the molecular structure of PTFE? The Key to Its Unmatched Chemical & Thermal Resistance
- What is Teflon and what is its chemical name? Unpacking the Science of PTFE
- What is PTFE commonly known as and what type of material is it? A Guide to High-Performance PTFE Properties



















