In industrial settings, PTFE's exceptionally low friction is leveraged in critical mechanical components to enable smooth, efficient motion with minimal wear. It is most commonly found in applications like non-stick bearings, self-lubricating gears, and slide plates where reducing energy loss and extending component life are paramount.
The core value of PTFE's low friction is not just about making parts "slippery." It is about fundamentally re-engineering mechanical systems to operate with higher efficiency, greater longevity, and drastically lower maintenance by minimizing the destructive forces of friction.
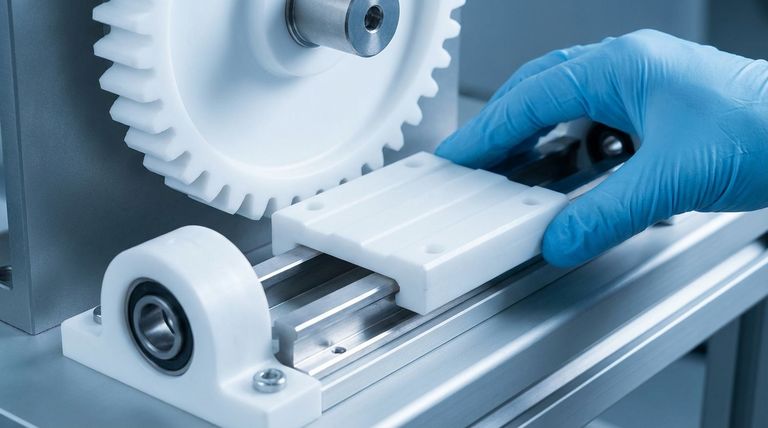

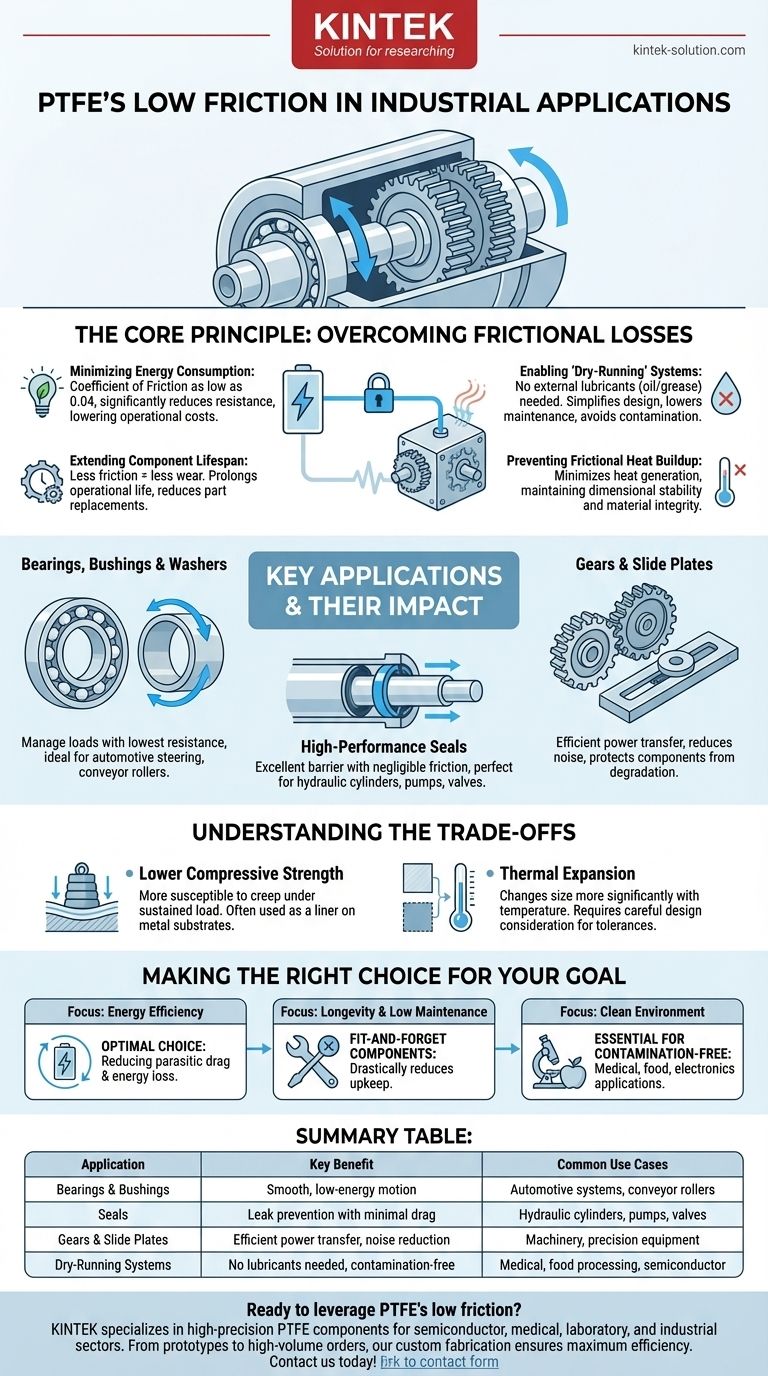
The Core Principle: Overcoming Frictional Losses
Friction is a primary source of inefficiency and failure in any mechanical system. It converts useful energy into wasted heat and physically wears down moving components over time.
Minimizing Energy Consumption
PTFE, with a coefficient of friction as low as 0.04, creates an incredibly smooth interface between moving parts.
This means less energy is wasted overcoming resistance, leading directly to more efficient machinery and lower operational costs, especially in continuous-motion applications.
Extending Component Lifespan
Less friction translates directly to less wear and tear on surfaces.
By using PTFE in components like bushings or washers, engineers can significantly prolong the operational life of a machine and reduce the frequency of costly part replacements.
Enabling 'Dry-Running' Systems
Unlike many materials, PTFE does not require external liquid lubricants like oil or grease to maintain its low-friction properties.
This "dry-running" capability is a major advantage. It simplifies mechanical design, lowers maintenance burdens, and eliminates the risk of contamination, which is critical in medical, food processing, and semiconductor industries.
Preventing Frictional Heat Buildup
High friction generates significant heat, which can cause parts to expand, warp, or degrade.
PTFE's low friction minimizes this thermal effect, helping to maintain dimensional stability and material integrity in dynamic, high-speed applications.
Key Applications and Their Impact
The principles of reducing friction and wear are applied across a wide range of industrial components.
Bearings, Bushings, and Washers
These components are designed to manage loads while allowing for rotational or linear movement.
Using PTFE ensures that this movement occurs with the lowest possible resistance. This is ideal for everything from automotive steering systems to conveyor rollers, where smooth, unlubricated motion is essential.
Gears and Slide Plates
Gears and slide plates transfer motion and force. Friction between these surfaces causes power loss and eventual failure.
Coating or manufacturing these parts with PTFE ensures a smooth, efficient transfer of energy, reduces operational noise, and protects the core components from degradation.
High-Performance Seals
Seals must prevent leakage, but they often make contact with a moving shaft or rod. A high-friction seal can cause significant drag and wear down the very part it is trying to protect.
PTFE seals provide an excellent barrier while adding negligible friction to the system, making them ideal for hydraulic cylinders, pumps, and valves.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While its low friction is a powerful asset, PTFE is not a universal solution. Its selection requires understanding its mechanical limitations.
Lower Compressive Strength
Compared to metals, PTFE has lower strength and is more susceptible to "creep," or deformation under a sustained load.
Because of this, it is often used as a liner or coating on a stronger metal substrate, combining the strength of the metal with the low-friction surface of the PTFE.
Thermal Expansion
PTFE has a relatively high coefficient of thermal expansion, meaning it changes size more significantly with temperature fluctuations than metals do.
Engineers must account for this in the design phase to ensure that tolerances are maintained across the expected operating temperature range of the application.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting PTFE is a strategic decision based on the primary engineering challenge you need to solve.
- If your primary focus is energy efficiency: PTFE is the optimal choice for reducing parasitic drag and energy loss in any system with moving parts.
- If your primary focus is longevity and low maintenance: The self-lubricating, "dry-running" nature of PTFE creates "fit-and-forget" components that drastically reduce upkeep.
- If your primary focus is operating in a clean environment: PTFE's ability to function without external lubricants makes it essential for medical, food, and electronics applications where contamination is not an option.
Ultimately, integrating PTFE allows engineers to design systems that are not just functional, but fundamentally more durable and efficient.
Summary Table:
| Application | Key Benefit | Common Use Cases |
|---|---|---|
| Bearings & Bushings | Smooth, low-energy motion | Automotive systems, conveyor rollers |
| Seals | Leak prevention with minimal drag | Hydraulic cylinders, pumps, valves |
| Gears & Slide Plates | Efficient power transfer, noise reduction | Machinery, precision equipment |
| Dry-Running Systems | No lubricants needed, contamination-free | Medical, food processing, semiconductor |
Ready to leverage PTFE's low friction in your components? KINTEK specializes in manufacturing high-precision PTFE seals, liners, bearings, and custom labware for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. From prototypes to high-volume orders, our custom fabrication ensures your systems achieve maximum efficiency, longevity, and cleanliness. Contact us today to discuss your project requirements!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Customizable PTFE Rods for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- How is Teflon coating utilized in security and detection? Enhancing Reliability in Demanding Environments
- What are the different types of PTFE rods available based on manufacturing technology? Choose the Right Type for Your Project
- What are PTFE bellows and what are they made of? Solve Tough Chemical & Thermal Challenges
- Why are PTFE gaskets considered safe for sensitive applications? Ensure Purity and Reliability
- What types of components can be made from PTFE? Discover High-Performance Seals, Bearings & More
- What are the advantages of PTFE lined dual plate check valves? Superior Corrosion Resistance & Flow Efficiency
- What are the medical applications of ePTFE? Discover its Life-Saving Uses in Implants
- What role does the stainless steel spring play in PTFE seals? The Engine for Reliable Sealing Performance



















