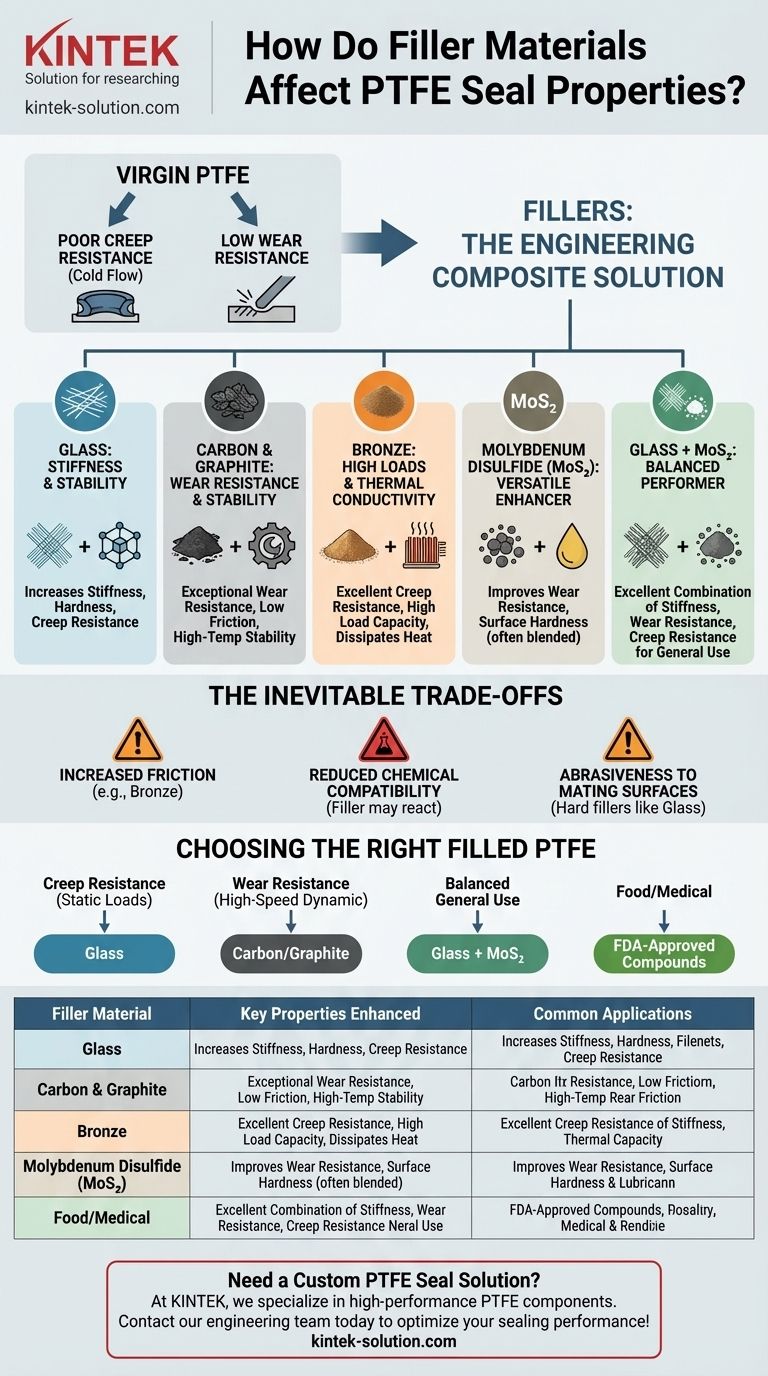
In short, filler materials are added to Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) to overcome its inherent mechanical weaknesses. While virgin PTFE offers exceptional chemical resistance and low friction, it suffers from poor creep resistance and low durability. Fillers dramatically enhance properties like wear resistance, stiffness, and dimensional stability, tailoring the seal's performance to specific operational demands.
The core principle is one of trade-offs. Adding fillers to PTFE transforms it from a soft, low-friction material into a robust engineering composite, but this enhancement in mechanical strength often comes at the cost of altering its friction coefficient or chemical compatibility.

Why Virgin PTFE Isn't Always Enough
Unfilled, or "virgin," PTFE is a remarkable polymer, but its utility as a dynamic seal is limited by two primary factors. Understanding these limitations clarifies exactly why fillers are necessary.
The Problem of Creep (Cold Flow)
Creep, also known as cold flow, is the tendency of a solid material to deform permanently under the influence of persistent mechanical stress.
Virgin PTFE has very low resistance to creep. Under pressure, it will slowly deform and lose its original shape, compromising its ability to maintain a reliable seal over time.
Low Wear Resistance
PTFE is a soft material. In dynamic applications involving friction and movement, it abrades quickly. This results in a short service life and potential contamination of the system.
A Breakdown of Common Fillers and Their Impact
Each filler material imparts a unique set of properties to the PTFE base. The choice of filler is a deliberate engineering decision based on the demands of the application.
Glass: For Stiffness and Stability
Adding glass fiber is one of the most common ways to enhance PTFE.
It significantly increases stiffness and hardness, which drastically improves the seal's resistance to creep and deformation under load. It also boosts general wear resistance.
Carbon and Graphite: For Wear Resistance and Stability
Carbon and graphite are excellent choices for enhancing dynamic properties.
These fillers provide exceptional wear resistance and improve dimensional stability, especially at higher temperatures. They also maintain a low coefficient of friction, making them ideal for high-speed applications.
Bronze: For High Loads and Thermal Conductivity
Bronze powder is added to PTFE for demanding, high-pressure applications.
It provides excellent creep resistance and wear properties. As a metal, it also increases the compound's thermal conductivity, helping to dissipate heat from the sealing surface.
Molybdenum Disulfide (MoS₂): A Versatile Enhancer
Molybdenum Disulfide (MoS₂) is a lubricity-enhancing filler often used in conjunction with other materials.
It improves wear resistance and surface hardness. MoS₂ is rarely used alone but acts as a synergistic additive in other filled compounds.
The Glass-Molybdenum Disulfide Combination
A blend of glass and MoS₂ is often considered the ideal general-purpose sealing compound.
This mixture provides the excellent stiffness and creep resistance from the glass, combined with the enhanced wear resistance and surface properties from the molybdenum disulfide, creating a well-balanced material for a wide range of uses.
The Inevitable Trade-offs
Enhancing PTFE with fillers is not without its compromises. These trade-offs are critical to consider during material selection to avoid unintended consequences.
Increased Friction
While carbon and graphite maintain low friction, other fillers can have the opposite effect. Bronze, for example, can increase the friction coefficient compared to virgin PTFE.
Reduced Chemical Compatibility
Virgin PTFE is famously inert to nearly all industrial chemicals. Adding a filler material can compromise this. The filler itself may not be as resistant to corrosive media as the PTFE matrix, reducing the seal's overall chemical compatibility.
Abrasiveness to Mating Surfaces
Hard fillers, particularly glass, can be abrasive to softer shaft or bore materials. Over time, a glass-filled seal can wear down the mating hardware if the surface hardness is not chosen correctly.
Choosing the Right Filled PTFE for Your Application
Your selection must be guided by the single most critical performance demand of your system.
- If your primary focus is creep resistance under high static loads: A glass-filled compound is the most effective choice.
- If your primary focus is wear resistance in a high-speed dynamic seal: A carbon or graphite-filled material offers superior durability and low friction.
- If your primary focus is a balanced, all-around performer for general use: A glass and MoS₂ blend provides an excellent combination of properties.
- If your primary focus is food, beverage, or medical applications: You must seek out specially formulated, FDA-approved PTFE compounds.
Ultimately, selecting the correct filled PTFE is about matching the material's enhanced properties directly to the challenges of its operating environment.
Summary Table:
| Filler Material | Key Properties Enhanced | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Glass | Stiffness, Creep Resistance, Dimensional Stability | High static load seals |
| Carbon/Graphite | Wear Resistance, Low Friction, Thermal Stability | High-speed dynamic seals |
| Bronze | High Load Capacity, Thermal Conductivity, Creep Resistance | High-pressure applications |
| Molybdenum Disulfide (MoS₂) | Wear Resistance, Surface Hardness (often used in blends) | General-purpose seals (with glass) |
| Glass + MoS₂ | Balanced Stiffness, Wear Resistance, Creep Resistance | Versatile, all-around sealing solutions |
Need a Custom PTFE Seal Solution for Your Specific Application?
At KINTEK, we specialize in manufacturing high-performance PTFE components, including custom seals, liners, and labware. Whether you're in the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, or industrial sector, our expertise in precision production and custom fabrication—from prototypes to high-volume orders—ensures you get a seal that perfectly balances wear resistance, chemical compatibility, and durability for your unique operational demands.
Let us help you optimize your sealing performance. Contact our engineering team today for a consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Customizable PTFE Seals Filter Holders for Versatile Applications
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
People Also Ask
- How do Teflon bellow mechanical seals enhance equipment efficiency in the pulp and paper industry? Boost Reliability and Cut Costs
- In what types of systems is PTFE packing commonly used? Essential Sealing for Extreme Chemical & Temperature Environments
- What are the advantages of graphite packing over PTFE packing? Superior Performance in High-Temp & High-Speed Applications
- What factors should be considered when selecting a PTFE expansion joint? Ensure System Integrity and Safety
- What are the general safety precautions when cleaning Teflon residue? Protect Your Team and Equipment
- What advantages do Teflon sheets have over metal sheets? Discover Unmatched Chemical & Non-Stick Properties
- What temperature limitations exist for PTFE lined butterfly valves? Ensure Safe, Leak-Free Operation
- What are the two main categories of polymers used for ball valve seats? PTFE vs. PEEK for Optimal Performance



















