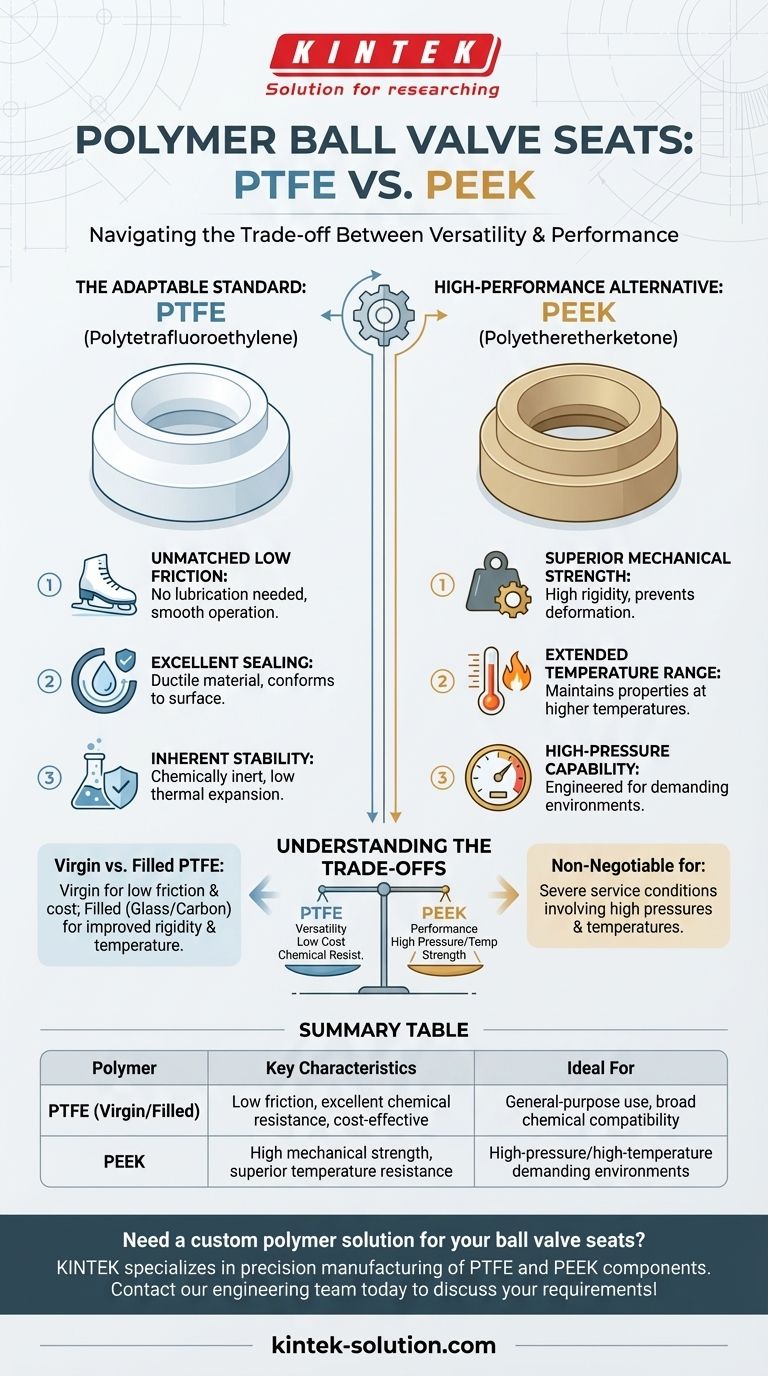
The two primary categories of polymers used for ball valve seats are Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), in both virgin and filled forms, and Polyetheretherketone (PEEK). These two material families cover the vast majority of industrial applications, from general-purpose use to demanding high-performance environments.
The core decision between these materials is a trade-off between versatility and performance. PTFE is the adaptable, low-friction standard, while PEEK is specified for applications demanding superior strength at high pressures and temperatures.

The Foundation: Understanding PTFE
Polytetrafluoroethylene, or PTFE, is often the default choice for ball valve seats due to its unique combination of properties. It establishes the baseline for performance in many industries.
Unmatched Low Friction
PTFE has the lowest coefficient of friction of any solid material. This allows it to operate smoothly without lubricants and prevents the "stick-slip" phenomenon, where the valve can jerk upon opening.
Excellent Sealing Properties
The material exhibits sufficient ductility, allowing the seat to conform to the ball's surface and create a tight, reliable seal under pressure.
Inherent Stability
PTFE is chemically inert in most situations, hydrophobic (repels water), and non-wetting. It also has low thermal expansion, ensuring a consistent seal across a moderate temperature range.
The High-Performance Alternative: PEEK
When application demands exceed the mechanical or thermal limits of PTFE, Polyetheretherketone (PEEK) becomes the material of choice. It is engineered for environments where PTFE would fail.
Superior Mechanical Strength
PEEK has significantly higher rigidity and strength compared to PTFE. This prevents the seat from deforming or "cold flowing" under high pressure, a known limitation of softer PTFE.
Extended Temperature Range
PEEK maintains its mechanical properties at much higher temperatures than any form of PTFE. This makes it essential for high-temperature service where polymer seats are still viable.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing the right seat material requires a clear understanding of the operational environment. The limitations of one material are often the strengths of another.
When to Use Standard PTFE
Virgin PTFE is ideal for applications where low friction, excellent chemical resistance, and cost-effectiveness are the primary drivers. It is the workhorse for a wide range of standard industrial services.
When to Upgrade to Filled PTFE
To overcome the softness of virgin PTFE, fillers like glass or carbon are added. Filled PTFE provides a bridge between virgin PTFE and PEEK, offering improved rigidity and a higher maximum service temperature at a moderate cost increase.
When PEEK is Non-Negotiable
PEEK is specified for severe service conditions involving high pressures, high temperatures, or both. Its mechanical robustness ensures seat integrity where any grade of PTFE would deform and fail.
The Ultimate Limitation
It is critical to recognize that even high-performance polymers have their limits. For service temperatures consistently exceeding 280°C (536°F), a metal-seated ball valve is required.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your final selection depends entirely on the specific demands of your system.
- If your primary focus is broad chemical compatibility and low friction: Virgin or filled PTFE is almost always the correct and most cost-effective choice.
- If your primary focus is performance at high pressure and temperature: PEEK provides the essential mechanical strength and thermal stability that PTFE lacks.
- If you need to balance cost with improved performance over the standard: Filled PTFE offers a significant upgrade in rigidity and temperature resistance without the full investment in PEEK.
Understanding these material capabilities empowers you to select a valve seat that ensures both safety and reliability.
Summary Table:
| Polymer | Key Characteristics | Ideal For |
|---|---|---|
| PTFE (Virgin/Filled) | Low friction, excellent chemical resistance, cost-effective | General-purpose use, broad chemical compatibility |
| PEEK | High mechanical strength, superior temperature resistance | High-pressure/high-temperature demanding environments |
Need a custom polymer solution for your ball valve seats? KINTEK specializes in precision manufacturing of PTFE and PEEK components for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Whether you require prototypes or high-volume orders, our expertise ensures a seat that delivers reliability and performance in your specific application. Contact our engineering team today to discuss your requirements!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE and Nitrile Diaphragm Pump Components for Demanding Applications
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
People Also Ask
- What industries use PTFE machined parts and for what applications? Critical Components for Demanding Environments
- What are the best practices for achieving tight tolerances in Teflon (PTFE) machining? Master Precision for Demanding Applications
- What are the main advantages of using PTFE parts in industrial applications? Unlock Unmatched Chemical Resistance and Reliability
- Why is PTFE rod suitable for automotive applications? Boost Vehicle Performance & Durability
- What are the key advantages of PTFE? Unmatched Performance for Extreme Environments



















