At its core, expanded PTFE (ePTFE) is the go-to gasket material for sealing critical process equipment across a vast range of industries. It is commonly used in pipelines, valves, pumps, pressure vessels, heat exchangers, condensers, and air compressors, especially where chemical resistance and adaptability to imperfect surfaces are paramount.
The widespread use of ePTFE gaskets stems from a unique combination of properties: it is almost completely chemically inert while also being exceptionally soft and conformable, allowing it to create a reliable seal on fragile or irregular equipment where other materials would fail.
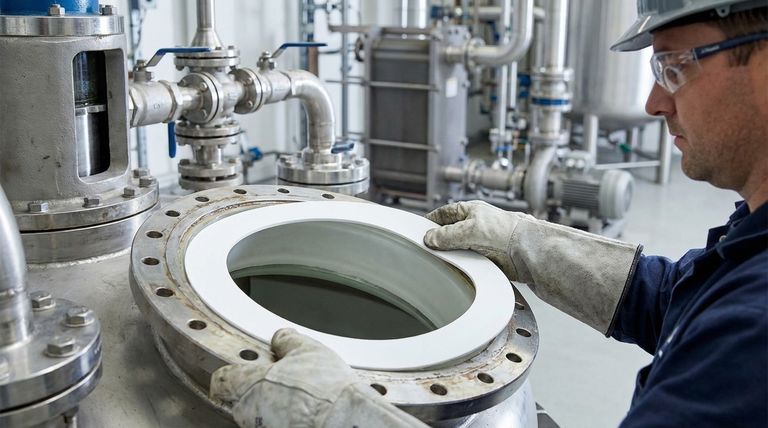

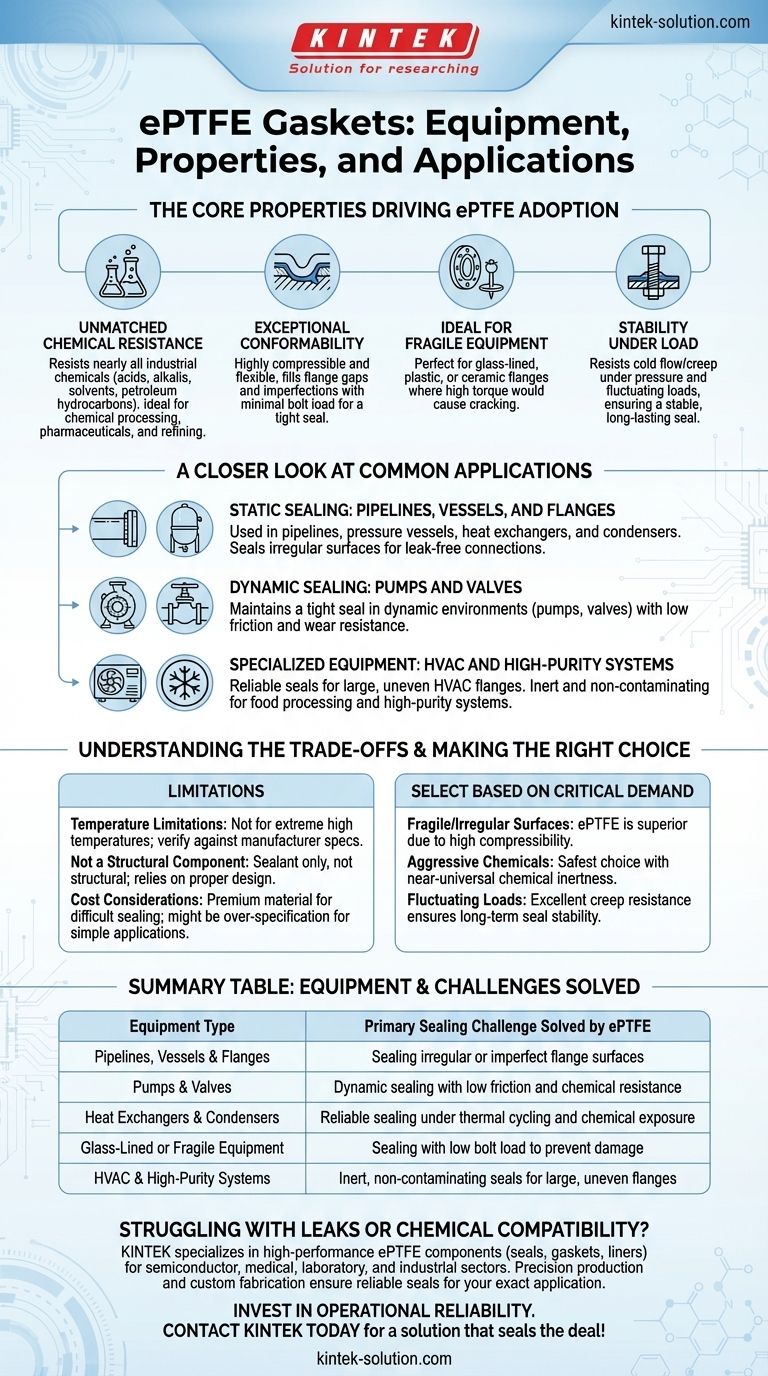
The Core Properties Driving ePTFE Adoption
To understand where ePTFE is used, we must first understand its fundamental characteristics. These properties solve specific, persistent challenges in industrial sealing.
Unmatched Chemical Resistance
ePTFE is resistant to nearly all industrial chemicals, including aggressive acids, alkalis, solvents, and petroleum hydrocarbons. This makes it a default choice in demanding industries like chemical processing, pharmaceuticals, and refining.
Exceptional Conformability
Unlike rigid gaskets, ePTFE is highly compressible and flexible. It can easily fill in wide flange gaps, scratches, and other surface imperfections to create an exceptionally tight seal with minimal bolt load.
Ideal for Fragile Equipment
This high conformability makes it perfect for equipment that could be damaged by the high bolt torque required for other gasket types. It is frequently used on glass-lined, plastic, or ceramic flanges where excessive pressure would cause cracking.
Stability Under Load
Standard PTFE is known for "cold flow," or creep, where the material deforms permanently under pressure. The expansion process gives ePTFE a fibrous structure that dramatically resists this tendency, ensuring a stable, long-lasting seal even under changing loads and high pressures.
A Closer Look at Common Applications
These properties directly translate into its use in specific types of equipment, solving distinct sealing problems in each.
Static Sealing: Pipelines, Vessels, and Flanges
This is the most common application. ePTFE sheets are cut to seal flanges in pipelines and on pressure vessels, heat exchangers, and condensers. Its ability to seal irregular surfaces ensures a leak-free connection in real-world conditions.
Dynamic Sealing: Pumps and Valves
In applications with movement, such as in pump housings or on valve stems, ePTFE's properties help maintain a tight seal while allowing for smooth operation. Its low friction and resistance to wear are critical in these dynamic environments.
Specialized Equipment: HVAC and High-Purity Systems
In HVAC and ventilation systems, ePTFE provides a reliable seal for large, potentially uneven flange surfaces. In food processing or high-purity manufacturing, its chemical inertness and the fact that it is harmless on contact with food make it an essential material.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While incredibly versatile, ePTFE is not a universal solution. Understanding its limitations is key to using it effectively.
Temperature Limitations
ePTFE has a broad operating temperature range, but it is not suitable for extreme high-temperature applications where metallic or graphite-based gaskets would be required. Always verify the manufacturer's specifications against your process temperature.
Not a Structural Component
ePTFE is a sealant, not a structural material. It is designed to conform and fill gaps. It does not add rigidity to a flange connection and relies on proper bolt load and flange design to function correctly.
Cost Considerations
For simple, non-critical applications involving water or air at ambient temperatures with perfectly flat, rigid flanges, a less expensive rubber or fiber gasket may be sufficient. ePTFE is a premium material designed to solve more difficult sealing challenges.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Select your gasket material based on the most critical demand of your application.
- If your primary focus is sealing fragile or irregular surfaces: ePTFE is the superior choice due to its high compressibility and ability to seal with low bolt force.
- If your primary focus is containing aggressive chemicals: ePTFE's near-universal chemical inertness makes it one of the safest and most reliable options available.
- If your primary focus is maintaining a seal under fluctuating loads: Its excellent resistance to creep and cold flow ensures a durable, long-term seal where other materials might fail.
Ultimately, choosing ePTFE is an investment in operational reliability for your most demanding sealing environments.
Summary Table:
| Equipment Type | Primary Sealing Challenge Solved by ePTFE |
|---|---|
| Pipelines, Vessels & Flanges | Sealing irregular or imperfect flange surfaces |
| Pumps & Valves | Dynamic sealing with low friction and chemical resistance |
| Heat Exchangers & Condensers | Reliable sealing under thermal cycling and chemical exposure |
| Glass-Lined or Fragile Equipment | Sealing with low bolt load to prevent damage |
| HVAC & High-Purity Systems | Inert, non-contaminating seals for large, uneven flanges |
Struggling with leaks or chemical compatibility in your equipment?
KINTEK specializes in manufacturing high-performance ePTFE components, including seals, gaskets, and liners, for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Our precision production and custom fabrication services—from prototypes to high-volume orders—ensure you get a reliable, long-lasting seal tailored to your exact application.
Invest in operational reliability. Contact KINTEK today for a solution that seals the deal!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
- Custom PTFE Volumetric Flasks for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Use
People Also Ask
- What are the key properties of PTFE that make it suitable for lined bearings? Discover the Ultimate Low-Friction Solution
- What are the reasons for intentionally designing a wide contact area in PTFE sealing elements? Boost Reliability & Lifespan
- How is expanded PTFE (ePTFE) produced? A Guide to the Controlled Stretching Process
- What is the temperature range for PTFE O-rings? Withstand Extremes from -200°C to 260°C
- How are PTFE bridge bearing pads installed on supporting pads? A Guide to Direct Bonding vs. Embedded Plates
- What makes PTFE lined valves suitable for handling aggressive media? Superior Chemical Resistance for Harsh Fluids
- What factors influence a PTFE seal's temperature capabilities? Maximize Performance in High-Heat Applications
- What are the installation benefits of PTFE compensators compared to metal alternatives? Achieve Faster, Safer, and More Cost-Effective Installation



















