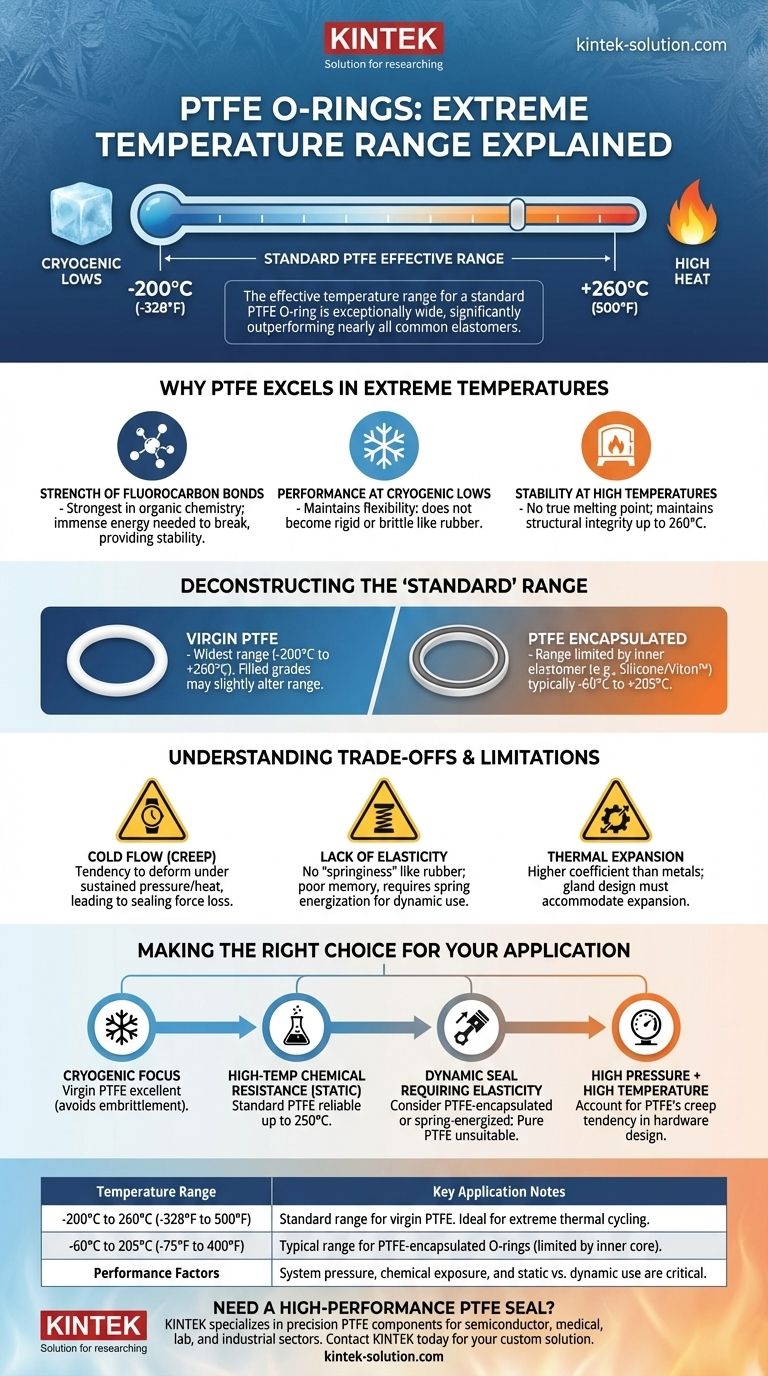
The effective temperature range for a standard PTFE O-ring is exceptionally wide, significantly outperforming nearly all common elastomers. Generally, you can expect reliable performance from a cryogenic low of -200°C (-328°F) up to a high of 250°C (482°F), with some grades capable of handling temperatures up to 260°C (500°F).
While PTFE's thermal range is its defining feature, the usable temperature in your specific application is governed by more than just the material. Factors like system pressure, chemical exposure, and whether the seal is static or dynamic will ultimately determine its real-world performance limits.
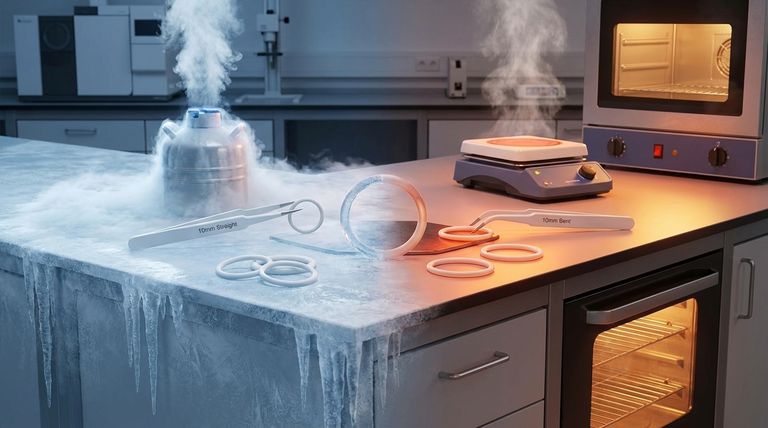

Why PTFE Excels in Extreme Temperatures
The remarkable thermal stability of Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is not an accident; it's a direct result of its molecular structure. Understanding this helps clarify why it's so often the material of choice for demanding environments.
The Strength of Fluorocarbon Bonds
At its core, PTFE consists of a carbon chain completely surrounded by fluorine atoms. The bond between carbon and fluorine is one of the strongest in organic chemistry, requiring immense energy to break. This inherent stability is what gives PTFE its well-known chemical inertness and high-temperature resistance.
Performance at Cryogenic Lows
Unlike rubber and other elastomers that become rigid and brittle at very low temperatures, PTFE maintains a useful degree of flexibility. This property allows it to function effectively in cryogenic applications, such as in systems handling liquid nitrogen, where other materials would fail.
Stability at High Temperatures
PTFE does not have a true melting point. Instead of turning to liquid, it maintains its structural integrity up to approximately 260°C (500°F). This allows it to provide a reliable seal in environments like aerospace, automotive, and industrial processing where many other plastics and rubbers would degrade or melt.
Deconstructing the "Standard" Temperature Range
You will often see slightly different temperature ratings for PTFE. This variation isn't a contradiction; it reflects the nuances of different material grades and seal designs.
Virgin PTFE vs. Filled Grades
The widest temperature range typically applies to virgin (unfilled) PTFE. However, fillers like glass, carbon, or bronze are often added to improve other properties such as wear resistance or compressive strength. These fillers can sometimes slightly alter the effective temperature range.
The Impact of Encapsulation
Some O-rings are PTFE encapsulated, meaning they have a core of a different elastomer (like Silicone or Viton™) wrapped in a thin PTFE jacket. The temperature range of these seals—typically from -60°C to 205°C (-75°F to 400°F)—is limited by the inner core material, not the outer PTFE shell.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
No material is perfect. To use PTFE O-rings successfully, you must be aware of their distinct mechanical limitations, especially when temperature is a factor.
The Issue of Cold Flow (Creep)
This is the most critical factor to consider. Under sustained pressure, especially at elevated temperatures, PTFE has a tendency to slowly deform permanently. This phenomenon, known as creep or cold flow, can lead to a loss of sealing force over time and must be accounted for in the hardware design.
Lack of "Memory" or Elasticity
PTFE is a plastic, not a true elastomer. It does not have the "springiness" of rubber and will not readily return to its original shape after being compressed. This makes it less suitable for dynamic sealing applications unless it is energized with an internal spring.
Thermal Expansion
PTFE has a higher coefficient of thermal expansion than most metals. In applications with wide temperature swings, the gland (the groove the O-ring sits in) must be designed to accommodate this expansion and prevent the O-ring from extruding or being damaged.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct seal requires matching the material's properties to the system's operational demands.
- If your primary focus is extreme low-temperature (cryogenic) sealing: Virgin PTFE is an excellent choice, as it avoids the embrittlement that causes other materials to fail.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature chemical resistance in a static seal: Standard PTFE is an industry benchmark, operating reliably up to 250°C (482°F) against nearly all chemicals.
- If your primary focus is a dynamic seal requiring good elasticity: Pure PTFE is often unsuitable. You should consider a PTFE-encapsulated O-ring or a spring-energized PTFE seal.
- If your application involves high pressure combined with high temperature: You must account for PTFE's tendency to creep in your design to prevent long-term seal failure.
Ultimately, leveraging PTFE's remarkable thermal stability depends on a clear understanding of its distinct physical properties and limitations.
Summary Table:
| Temperature Range | Key Application Notes |
|---|---|
| -200°C to 260°C (-328°F to 500°F) | Standard range for virgin PTFE. Ideal for extreme thermal cycling. |
| -60°C to 205°C (-75°F to 400°F) | Typical range for PTFE-encapsulated O-rings (limited by inner elastomer core). |
| Performance Factors | System pressure, chemical exposure, and static vs. dynamic use are critical. |
Need a high-performance PTFE seal for extreme temperatures?
KINTEK specializes in manufacturing precision PTFE components, including O-rings, seals, and custom labware. We serve the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors, providing solutions from prototypes to high-volume orders.
Our expertise ensures your seals deliver reliable performance, whether you're facing cryogenic challenges or high-heat environments. Let's discuss your specific requirements and material needs.
Contact KINTEK today for a consultation on your custom PTFE solution.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What are the main advantages of using PTFE parts in industrial applications? Unlock Unmatched Chemical Resistance and Reliability
- What are the key considerations when machining Teflon? Master Precision Machining for Soft Polymers
- What tips can improve Teflon machining results? Master Sharp Tools, Heat Control, and Rigid Support
- Why is CNC machining preferred for Teflon parts over other methods? Unlock Precision & Complex Designs
- What industries use PTFE machined parts and for what applications? Critical Components for Demanding Environments



















