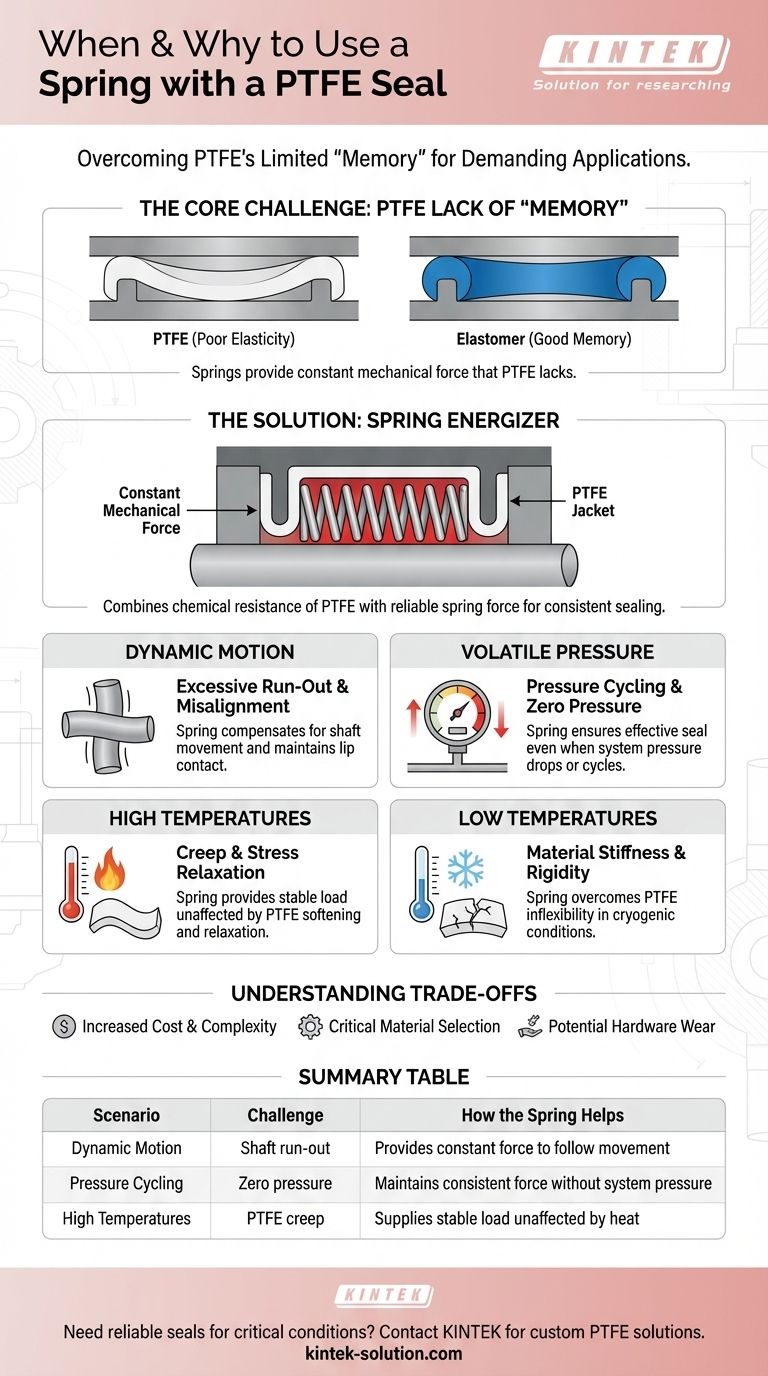
In short, a spring is required for a PTFE seal when the seal must perform under conditions that exceed the natural capabilities of the PTFE material itself. These situations fall into four key categories: significant dynamic motion, volatile pressure changes, and extreme high or low temperatures. The spring acts as an energizer, providing the constant mechanical force that PTFE, which lacks the "memory" of rubber, cannot provide on its own.
The fundamental reason for using a spring with a PTFE seal is to compensate for Polytetrafluoroethylene's (PTFE) poor elasticity. The spring provides a consistent, mechanical force that ensures the seal lips remain in contact with the sealing surface, especially under dynamic, thermal, or pressure-variant conditions where PTFE alone would fail.

The Core Challenge: PTFE's Lack of "Memory"
Understanding PTFE as a Sealing Material
PTFE is an exceptional polymer known for its extremely low friction, broad chemical inertness, and wide temperature tolerance. It is a workhorse in industries from aerospace to chemical processing.
However, PTFE is not an elastomer like nitrile rubber or FKM. It has very low resilience, or "memory." When compressed or deformed, it does not reliably spring back to its original shape.
The Role of the Spring Energizer
This is where the spring becomes critical. A spring-energized seal combines a durable PTFE jacket with a high-performance metal spring.
The PTFE jacket provides the chemical resistance and low-friction sealing surface. The internal spring provides the constant mechanical energy needed to activate the seal lips, ensuring a consistent and reliable sealing force over time.
When Mechanical Demands Require a Spring
Scenario 1: Excessive Shaft Run-Out or Misalignment
In dynamic applications, a rotating or reciprocating shaft may not be perfectly centered, leading to "run-out" or misalignment.
An unassisted PTFE seal lacks the rapid responsiveness to follow these movements, which can create intermittent leak paths. The spring provides the necessary elasticity, allowing the seal lips to constantly adjust and maintain contact with the moving shaft.
Scenario 2: Volatile Pressure Conditions
System pressure can help energize a seal, but it is often not constant. In applications with sudden pressure drops or cycles between high and low pressure, a problem arises.
When system pressure is removed, the PTFE's poor memory prevents it from maintaining a tight seal. The spring provides a constant baseline force, ensuring the seal remains effective even at very low or zero pressure.
When Temperature Extremes Compromise the Seal
Scenario 3: High Temperatures and Stress Relaxation
At elevated temperatures, PTFE can soften and become susceptible to creep and stress relaxation. The initial force applied during installation can diminish over time, compromising the seal.
A metal spring, chosen for its high-temperature resilience, provides a stable and continuous radial load that is unaffected by the PTFE's tendency to relax, ensuring a long-term, reliable seal.
Scenario 4: Low Temperatures and Material Stiffness
In cryogenic or very low-temperature environments, PTFE becomes extremely stiff and rigid, a state described as having a high flexural modulus.
This stiffness prevents the seal from conforming to the hardware's sealing surfaces. The spring provides the powerful mechanical force required to press the rigid PTFE lips against the shaft, overcoming the material's inflexibility.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Increased Cost and Complexity
Spring-energized seals are more complex to manufacture than a simple O-ring or a standard polymer lip seal. This results in a higher unit cost.
Careful Material Selection is Critical
The effectiveness of the seal depends on choosing the right materials for both the spring and the PTFE jacket. The spring material (e.g., stainless steel, Elgiloy) must be compatible with the system's temperature range and chemical environment to prevent corrosion or failure.
Potential for Hardware Wear
While PTFE has a low coefficient of friction, the high and constant force exerted by the spring can, in some aggressive applications, lead to faster wear on softer shaft materials compared to lower-force seals.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
To determine if a spring-energized PTFE seal is necessary, evaluate the demands of your system against the capabilities of the material.
- If your primary focus is dynamic sealing: A spring is essential to handle significant shaft run-out or misalignment.
- If your primary focus is reliability across pressure cycles: The spring ensures a consistent seal from high pressure down to zero.
- If your primary focus is performance in extreme temperatures: The spring provides a reliable force where unassisted PTFE would fail due to softening or stiffening.
- If your application is static with stable pressure and temperature: A less complex seal, such as a standard PTFE O-ring or gasket, may be a more cost-effective solution.
Ultimately, using a spring-energized seal is a strategic engineering decision to leverage PTFE's benefits while overcoming its inherent physical limitations.
Summary Table:
| Scenario | Challenge | How the Spring Helps |
|---|---|---|
| Dynamic Motion | Shaft run-out or misalignment | Provides constant force for lips to follow movement |
| Pressure Cycling | Volatile or zero-pressure conditions | Maintains consistent sealing force without system pressure |
| High Temperatures | PTFE softens and relaxes (creep) | Supplies stable radial load unaffected by heat |
| Low Temperatures | PTFE becomes stiff and rigid | Overcomes material inflexibility to maintain contact |
Need a reliable seal for demanding conditions?
At KINTEK, we specialize in manufacturing high-performance, custom PTFE components, including spring-energized seals for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Our precision production ensures your seals perform flawlessly under dynamic motion, pressure cycles, and extreme temperatures.
Let us provide the solution for your critical sealing challenges—from prototypes to high-volume orders. Contact our experts today to discuss your application!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Customizable PTFE Seals Filter Holders for Versatile Applications
People Also Ask
- What temperature range can PTFE encapsulated O-rings withstand? -60°C to 205°C, Depending on Core
- What are the properties of Teflon PFA encapsulated o-rings? Achieve Superior Sealing in Extreme Environments
- What materials are used in PTFE piston seals? A Guide to the Two-Part System for Superior Performance
- How should PTFE-lined bearings be maintained? The Essential Guide to Maintenance-Free Operation
- What are the benefits of porous PTFE? Unlock Superior Filtration and Chemical Resistance
- What are the different types of PTFE diaphragms and their applications? Optimize Your Chemical Processing System
- What are the two main methods for producing PTFE? Choose the Right Path for Your Application
- What are some application examples of PTFE O-ring seals in mechanical equipment? Solve Extreme Sealing Challenges



















