At its core, porous Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) offers a unique combination of capabilities. It merges the extreme chemical and thermal resistance of solid PTFE with the functional benefits of a microporous structure. This allows it to perform tasks like high-efficiency filtration and controlled fluid transfer in environments where most other materials would instantly fail.
The true benefit of porous PTFE isn't just one single property, but its ability to maintain exceptional chemical and temperature stability while allowing for controlled flow and particle capture. It solves problems that demand both inertness and permeability.

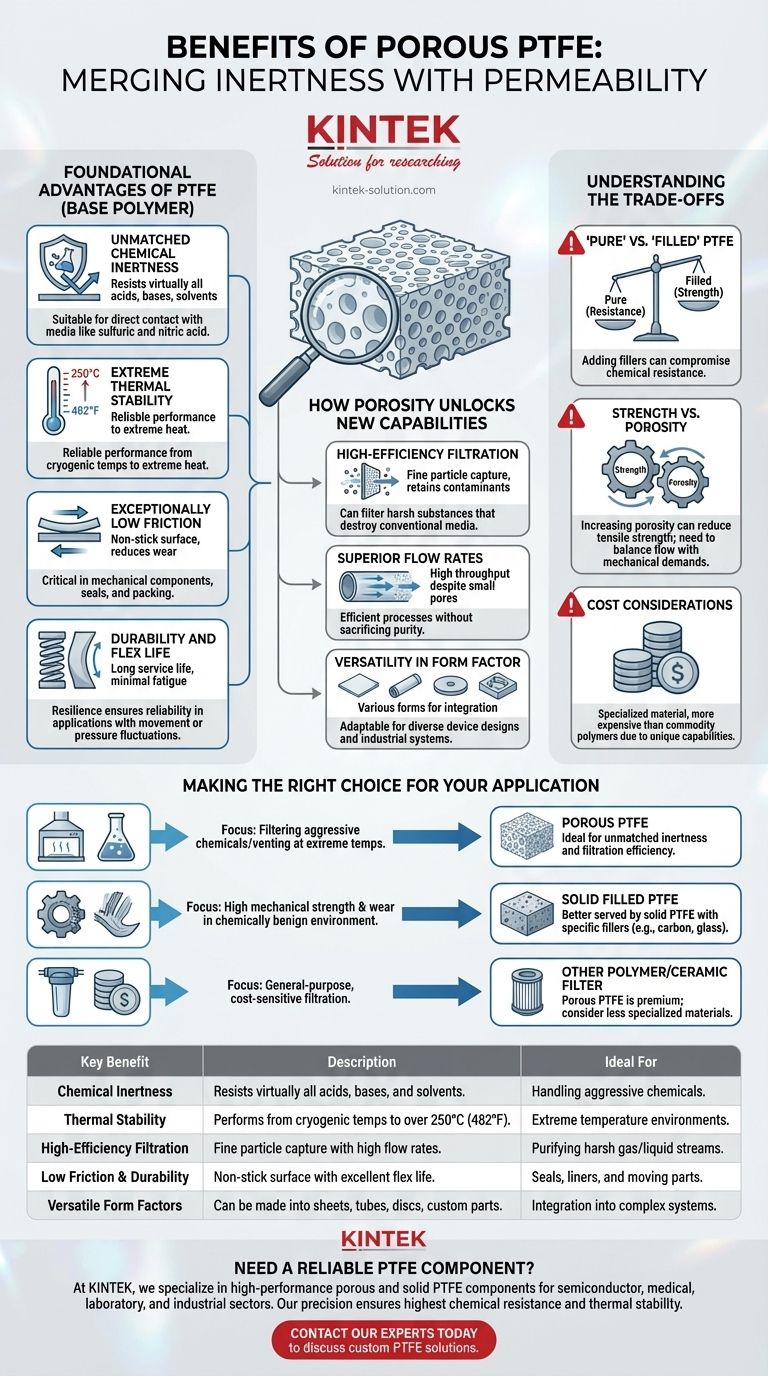
The Foundational Advantages of PTFE
Before understanding the role of porosity, it's essential to grasp the inherent properties of the base PTFE polymer. These characteristics are the foundation upon which the benefits of the porous version are built.
Unmatched Chemical Inertness
PTFE is one of the most chemically resistant materials known. It is nearly inert and does not react with the vast majority of industrial chemicals, including concentrated acids, bases, and aggressive solvents.
This makes it suitable for direct contact with media like sulfuric acid and nitric acid without degrading.
Extreme Thermal Stability
The material demonstrates remarkable performance across an exceptionally wide temperature range. It remains reliable and functional from cryogenic temperatures up to over 250°C (482°F).
This stability allows it to be used in processes involving extreme heat or cold where other polymers would become brittle or melt.
Exceptionally Low Friction
PTFE has one of the lowest coefficients of friction of any solid material, often compared to wet ice on wet ice. This "non-stick" quality is critical in mechanical applications.
In components like seals or packing, this property reduces wear on equipment and lowers the energy required for operation.
Durability and Flex Life
The material is known for its long service life and minimal fatigue from flexing. This resilience ensures reliability in applications that involve movement, vibration, or pressure fluctuations.
How Porosity Unlocks New Capabilities
Creating a microporous structure within PTFE transforms it from a simple inert barrier into a high-performance functional tool.
High-Efficiency Filtration
The primary application for porous PTFE is advanced filtration. The network of small, interconnected pores provides high particle retention, effectively capturing contaminants from a gas or liquid stream.
Its inherent chemical resistance means it can filter harsh substances that would destroy conventional filter media.
Superior Flow Rates
Despite having very small pore sizes, porous PTFE is engineered to provide exceptional flow rates. This combination of fine filtration and high throughput is a critical performance advantage.
It allows processes to run more efficiently without sacrificing the purity of the end product.
Versatility in Form Factor
Porous PTFE is not limited to a single shape. It can be manufactured into various forms, including sheets, rolls, tubing, and custom-molded discs.
This adaptability allows engineers to integrate it into a wide array of device designs and industrial systems.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No material is perfect for every situation. Acknowledging the limitations of porous PTFE is key to using it effectively.
"Pure" vs. "Filled" PTFE
While standard, solid PTFE can be modified with fillers like glass, carbon, or stainless steel to increase strength and abrasion resistance, this often comes at a price.
Adding these fillers can compromise the exceptional chemical resistance that is PTFE's defining characteristic.
Strength vs. Porosity
As a general principle, increasing a material's porosity can reduce its overall tensile strength compared to its solid counterpart. Engineers must balance the need for high flow rates (more porosity) with the mechanical demands of the application.
Cost Considerations
Porous PTFE is a high-performance, specialized material. Its manufacturing process and unique capabilities mean it is significantly more expensive than commodity polymers. Its use is typically justified by extreme environmental conditions or stringent performance requirements that other materials cannot meet.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct material requires aligning its properties with your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is filtering aggressive chemicals or venting at extreme temperatures: Porous PTFE is likely the ideal choice due to its unmatched combination of inertness and filtration efficiency.
- If your primary focus is high mechanical strength and wear resistance in a chemically benign environment: You may be better served by a solid PTFE variant that includes specific fillers like carbon or glass.
- If your primary focus is general-purpose, cost-sensitive filtration: A less specialized polymer or ceramic filter might be more appropriate, as porous PTFE is a premium material for the most demanding conditions.
Ultimately, understanding these core capabilities and trade-offs allows you to leverage porous PTFE precisely where its unique strengths deliver the most value.
Summary Table:
| Key Benefit | Description | Ideal For |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Inertness | Resists virtually all acids, bases, and solvents. | Handling aggressive chemicals. |
| Thermal Stability | Performs from cryogenic temps to over 250°C (482°F). | Extreme temperature environments. |
| High-Efficiency Filtration | Fine particle capture with high flow rates. | Purifying harsh gas/liquid streams. |
| Low Friction & Durability | Non-stick surface with excellent flex life. | Seals, liners, and moving parts. |
| Versatile Form Factors | Can be made into sheets, tubes, discs, and custom parts. | Integration into complex systems. |
Need a reliable PTFE component for a demanding application?
At KINTEK, we specialize in manufacturing high-performance porous and solid PTFE components—including seals, liners, labware, and custom parts—for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Our precision production ensures your components meet the highest standards of chemical resistance and thermal stability, whether you need a prototype or a high-volume order.
Contact our experts today to discuss how our custom PTFE solutions can solve your most challenging filtration, sealing, or fluid handling problems.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Customizable PTFE Seals Filter Holders for Versatile Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What are the primary applications of PTFE fasteners and custom parts? Critical Solutions for Extreme Environments
- Why is PTFE suitable for cryogenic or high-temperature applications? Unmatched Thermal Stability from -450°F to 500°F
- What are some common applications of machined PTFE? Leverage its Unique Properties for Demanding Applications
- What are the key benefits of PTFE in custom fabrication? Unlock Performance in Extreme Conditions
- What are the base characteristics of PTFE? Unlocking Extreme Performance in Friction, Temperature, and Chemical Resistance



















